Abstract
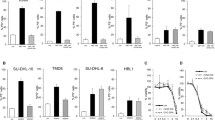
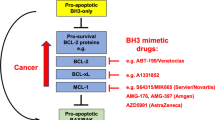
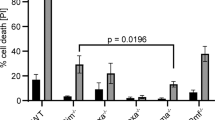
Enforced expression of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family protein Mcl-1 promotes lymphomagenesis in the mouse; however, the functional role of Mcl-1 in human B-cell lymphoma remains unclear. We demonstrate that Mcl-1 is widely expressed in malignant B-cells, and high-level expression of Mcl-1 is required for B-lymphoma cell survival, since transfection of Mcl-1-specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotides was sufficient to promote apoptosis in Akata6 lymphoma cells. Mcl-1 was efficiently cleaved by caspases at evolutionarily conserved aspartic acid residues in vitro, and during cisplatin-induced apoptosis in B-lymphoma cell lines and spontaneous apoptosis of primary malignant B-cells. Overexpression of the Mcl-1 cleavage product that accumulated during apoptosis was sufficient to kill cells. Therefore, Mcl-1 is an essential survival molecule for B-lymphoma cells and is cleaved by caspases to a death-promoting molecule during apoptosis. In contrast to Mcl-1, Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL were relatively resistant to caspase cleavage in vitro and in intact cells. Interfering with Mcl-1 function appears to be an effective means of inducing apoptosis in Mcl-1-positive B-cell lymphoma, and the unique sensitivity of Mcl-1 to caspase-mediated cleavage suggests an attractive strategy for converting it to a proapoptotic molecule.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM and Cory S . (2001). Trends Biochem. Sci., 26, 61–66.
Agarwal B and Naresh KN . (2002). Am. J. Hematol., 70, 278–282.
Akgul C, Moulding DA, White MR and Edwards SW . (2000). FEBS Lett., 478, 72–76.
Altmeyer A, Simmons RC, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Bornkamm GW and Chen-Kiang S . (1997). Immunity, 7, 667–677.
Bannerman DD, Tupper JC, Ricketts WA, Bennett CF, Winn RK and Harlan JM . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 14924–14932.
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Colomer D, Pons G, Montserrat E and Gil J . (1999). Blood, 94, 2836–2843.
Borner C . (2003). Mol. Immunol., 39, 615–647.
Byrd JC, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Aron JL, Pearson M, Lucas D and Reed JC . (2002). Blood, 99, 1038–1043.
Cazals-Hatem DL, Loie DC, Tanaka S and Reed JC . (1992). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1132, 109–113.
Chen M, Gong H-Y, Cheng C-Y, Wang J-P, Hong J-R and Wu J-L . (2001). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1519, 127–133.
Cheng EH, Kirsch DG, Clem RJ, Ravi R, Kastan MB, Bedi A, Ueno K and Hardwick JM . (1997). Science, 278, 1966–1968.
Clem RJ, Cheng EH, Karp CL, Kirsch DG, Ueno K, Takahashi A, Kastan MB, Griffin DE, Earnshaw WC, Veliuona MA and Hardwick JM . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 554–559.
Cohen GM . (1997). Biochem. J., 326, 1–16.
Craig RW . (2002). Leukemia, 16, 444–454.
Craig RW, Frankfurt OS, Sakagami H, Takeda K and Bloch A . (1984). Cancer Res., 44, 2421–2429.
Cuconati A, Mukherjee C, Perez D and White E . (2003). Genes Dev, 17, 2922–2932.
Dallman CL and Packham G . (2004). Purification of primary malignant B-cells and immunoblot analysis of Bcl-2 family proteins. Molecular Methods in Cancer, Illidge T and Johnson PWM (eds) (in press).
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM, Taylor JK, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL, Bataille R and Amiot M . (2002). Blood, 100, 194–199.
Drexler HG . 2001. The Leukemia–Lymphoma Cell Line Facts Book. Academic Press: London.
Ghia P, Boussiotis VA, Schultze JL, Cardoso AA, Dorfman DM, Gribben JG, Freedman AS and Nadler LM . (1998). Blood, 91, 244–251.
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1899–1911.
Herrant M, Luciano F, Loubat A and Auberger P . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 4957–4968.
Iglesias-Serret D, Pique M, Gil J, Pons G and Lopez JM . (2003). Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 417, 141–152.
Inman GJ, Binne UK, Parker GA, Farrell PJ and Allday MJ . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 2400–2410.
Johnson DE . (2000). Leukemia, 14, 1695–1703.
Khoury JD, Medeiros LJ, Rassidakis GZ, McDonnell TJ, Abruzzo LV and Lai R . (2003). J. Pathol., 199, 90–97.
Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S, Wang HG, Zhang X, Bullrich F, Croce CM, Rai K, Hines J and Reed JC . (1998). Blood, 91, 3379–3389.
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P and Craig RW . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 3516–3520.
Lenoir GM, Vuillaume M and Bonnardel C . (1985). IARC Sci. Publ., 60, 309–318.
Lomo J, Smeland EB, Krajewski S, Reed JC and Blomhoff HK . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 40–43.
Moulding DA, Giles RV, Spiller DG, White MR, Tidd DM and Edwards SW . (2000). Blood, 96, 1756–1763.
Nicholson DW . (1999). Cell Death Differ., 6, 1028–1042.
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E, Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F and Wang X . (2003). Genes Dev., 17, 1475–1486.
Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C, Sorcinelli MD, Ong CC and Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). Nature, 426, 671–676.
Oxford SME, Dallman CL, Johnson PWM, Ganesan A and Packham G . (2004). Current Med. Chem., (in press).
Packham G . (1998). Apoptosis, 326, 75–82.
Packham G, Brimmell M and Cleveland JL . (1997). Biochem. J., 328, 807–813.
Pagnano KB, Silva MD, Vassallo J, Aranha FJ and Saad ST . (2002). Acta Haematol., 107, 29–34.
Pedersen IM, Kitada S, Leoni LM, Zapata JM, Karras JG, Tsukada N, Kipps TJ, Choi YS, Bennett F and Reed JC . (2002). Blood, 100, 1795–1801.
Pepper C, Ali K, Thomas A, Hoy T, Fegan C, Chowdary P, Kell J and Bentley P . (2002). Eur. J. Haematol., 69, 227–235.
Samejima K, Svingen PA, Basi GS, Kottke T, Mesner Jr PW, Stewart L, Durrieu F, Poirier GG, Alnemri ES, Champoux JJ, Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 4335–4340.
Snowden RT, Sun XM, Dyer MJ and Cohen GM . (2003). Leukemia, 17, 1981–1989.
Soini Y, Raunio H and Paakko P . (1998). Tumour Biol., 19, 176–185.
Spender LC, Cannell EJ, Hollyoake M, Wensing B, Gawn JM, Brimmell M, Packham G and Farrell PJ . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 4678–4688.
Spets H, Stromberg T, Georgii-Hemming P, Siljason J, Nilsson K and Jernberg-Wiklund H . (2002). Eur. J. Haematol., 69, 76–89.
Takada K, Horinouchi K, Ono Y, Aya T, Osato T, Takahashi M and Hayasaka S . (1991). Virus Genes, 5, 47–156.
Thornberry NA, Rano TA, Peterson EP, Rasper DM, Timkey T, Garcia-Calvo M, Houtzager VM, Nordstrom PA, Roy S, Vaillancourt JP, Chapman KT and Nicholson DW . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 17907–17911.
Vrana JA, Bieszczad CK, Cleaveland ES, Ma Y, Park JP, Mohandas TK and Craig RW . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 892–900.
Yang T, Kozopas KM and Craig RW . (1995). J. Cell. Biol., 128, 1173–1184.
Zhang B, Gojo I and Fenton RG . (2002). Blood, 99, 1885–1893.
Zhou P, Levy NB, Xie H, Qian L, Lee CY, Gascoyne RD and Craig RW . (2001). Blood, 97, 3902–3909.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs X Lu, K Vousden, DM Hockenbery and SJ Korsmeyer for the kind gift of reagents, and the FHCRC Proteomic Resources Center for N-terminal sequencing. This work was supported by NIH Grant RO1-CA57359 (RWC), American Cancer Society Grant RPG-97-173-01-LBC (KYJZ) and grants from Cancer Research UK and the Leukemia Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michels, J., O'Neill, J., Dallman, C. et al. Mcl-1 is required for Akata6 B-lymphoma cell survival and is converted to a cell death molecule by efficient caspase-mediated cleavage. Oncogene 23, 4818–4827 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207648
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207648
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2023)
-
Loss of FBXW7-mediated degradation of BRAF elicits resistance to BET inhibitors in adult T cell leukemia cells
Molecular Cancer (2020)
-
Separase-triggered apoptosis enforces minimal length of mitosis
Nature (2020)
-
BFL1 modulates apoptosis at the membrane level through a bifunctional and multimodal mechanism showing key differences with BCLXL
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)
-
FBXW7: a critical tumor suppressor of human cancers
Molecular Cancer (2018)