Abstract
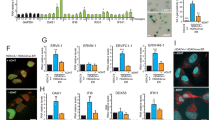
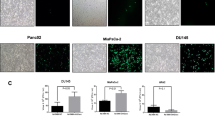
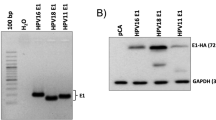
Polyomavirus (Py) large and small tumorantigens together are competent to induce S phase in growth-arrested mouse fibroblasts. The capacity of the large tumorantigen to bind the pocket proteins, pRB, p130 and p107, is important for the transactivation of DNA synthesis enzymes and the cyclins E and A, while the interference of small tumorantigen with protein phosphatase PP2A causes a destabilization of the cdk2 inhibitor p27, and thus leads to strong cyclin E- and cyclin A-dependent cdk2 activity. Py small tumorantigen, in addition, is able to transactivate cyclin A. Hence, this protein might have a much wider effect on gene expression in arrested mouse fibroblasts than hitherto suspected. This may have a profound part in the known capacity of Py to form tumors in mice. Therefore, it was interesting to gain an insight into the spectrum of transcriptional deregulation by Py tumorantigens. Accordingly, we performed microarray analysis of quiescent mouse fibroblasts in the absence and presence of small or large tumorantigen. We found that the viral proteins can induce or repress a great variety of genes beyond those involved in the S phase induction and DNA synthesis. The results of the microarray analysis were confirmed for selected genes by several methods, including real-time PCR. Interestingly, a mutation of the binding site for pocket proteins in case of LT and for PP2A in case of ST has a variable effect on the deregulation of genes by the viral proteins depending on the gene in question. In fact, some genes are transactivated by LT as well as ST completely independent of an interaction with their major cellular targets, pocket proteins and PP2A, respectively.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczewiski JP, Gannon JV and Hunt T . (1993). J. Virol., 67, 6551–6557.
Bell SP and Dutta A . (2002). Ann. Rev. Biochem., 71, 333–374.
Benjamin T . (2001). Virology, 289, 167–173.
Bikel I and Loeken MR . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 1489–1494.
Campbell KS, Auger KR, Hemmings BA, Roberts TM and Pallas DC . (1995). J. Virol., 69, 3721–3728.
Coller HA, Grandori C, Tamayo P, Colbert T, Lander ES, Eisenman RN and Golub TR . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 3260–3265.
Damania B, Lieberman P and Alwine JC . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 3926–3935.
Eckner R, Ludlow JW, Lill NL, Oldread E, Arany Z, Modjtahedi N, De Caprio JA, Livingston DM and Morgan JA . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 3454–3464.
Felton-Edkins ZA and White RJ . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 48182–48191.
Fernandez PC, Frank SR, Wang L, Schroeder M, Liu S, Green J, Cocito A and Amati B . (2003). Genes Dev., 17, 1115–1129.
Frost JA, Alberts AS, Sonntag E, Guan K, Mumby MC and Feramisco JR . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 6244–6252.
Gottlieb KA and Villarreal LP . (2001). Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 65, 288–318.
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS, Beijersberger RL, Brooks MW and Weinberg RA . (1999). Nature, 400, 464–468.
Hahn WC, Dessain SK, Brooks MW, King JE, Elenbaas B, Sabatini DM, DeCaprio JA and Weinberg RA . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 2111–2123.
Kino T, Takeshima H, Nakao M, Nishi T and Yamamoto K . (2001). Genes Cells, 6, 441–454.
Kresse H. and Schönherr E . (2001). J Cell. Physiol., 189, 266–274.
Lecanda F, Cheng S-L, Shin CS, Davidson MK, Warlow P, Avioli LV and Civitelli R . (2000). J Cell. Biochem., 77, 499–506.
Loeken M, Bikel I, Livingston DM and Brady J . (1988). Cell, 55, 1171–1177.
Loeken MR . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 2551–2555.
Lukas J, Müller H, Bartkova J, Spitkovsky D, Kjerulff AA, Jansen-Dürr P, Strauss M and Bartek J . (1994). J. Cell Biol., 125, 625–638.
Lutchman M and Rouleau GA . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 2270–2274.
Menssen A and Hermeking H . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 6274–6279.
Moran E . (1993). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 3, 63–70.
Mudrak I, Ogris E, Rotheneder H and Wintersberger E . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 1886–1892.
Nemethova M and Wintersberger E . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 1734–1739.
Ogris E, Mudrak I and Wintersberger E . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 53–61.
Ogris E, Mudrak I and Wintersberger E . (1993a). Oncogene, 8, 1277–1283.
Ogris E, Rotheneder H, Mudrak I, Pichler A and Wintersberger E . (1993b). J. Virol., 67, 1765–1771.
Ohtani K, Iwanaga R, Nakamura M, Ikeda M-a, Yabuta N, Tsuruga H and Nojima H . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 2299–2309.
Pipas JM . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 3979–3985.
Porras A., Bennet J, Howe A, Tokos K, Bouk N, Henglein B, Sathayamangalam S, Thimmapaya B and Rundell K . (1996). J. Virol., 70, 6902–6909.
Porras A, Gaillard S and Rundell K . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 3102–3107.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Schüchner S, Nemethova M, Belisova A, Klucky B, Holnthoner W and Wintersberger E. . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 6498–6507.
Schüchner S and Wintersberger E . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 9266–9273.
Shin CS, Lecanda F, Sheikh S, Weitzmann L, Cheng S-L and Civitelly R . (2000). J. Cell Biochem., 78, 566–577.
Ständer M, Naumann U, Wick W and Weller M . (1999). Cell Tissue Res., 296, 221–227.
Sonntag E, Fedorov S, Kambayashi C, Robbins D, Cobb M and Mumby MC . (1993). Cell, 75, 887–897.
Tsuruga H, Yabuta N, Hosoya S, Tamura K, Endo Y and Nojima H . (1997). Genes Cells, 2, 381–399.
Watanabe G, Howe A, Lee RJ, Albanese C, Shu I-W, Karnezis AN, Zon L, Kyriakis J, Rundell K and Pestell RG . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 12861–12866.
Yu J, Boyapati A and Rundell K . (2001). Virology, 290, 192–198.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klucky, B., Koch, B., Radolf, M. et al. Polyomavirus tumorantigens have a profound effect on gene expression in mouse fibroblasts. Oncogene 23, 4707–4721 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207640
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207640
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Backbone assignment of the N-terminal polyomavirus large T antigen
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2009)
-
Polyomavirus small T antigen transactivates genes by its ability to provoke the synthesis and the stabilization of MYC
Oncogene (2007)
-
Role of the interaction between large T antigen and Rb family members in the oncogenicity of JC virus
Oncogene (2006)