Abstract
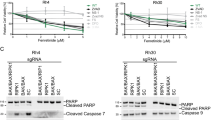
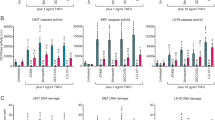
Aplidin™ is an antitumor drug that induces apoptosis and activates EGFR, Src, JNK and p38MAPK. Here, we show that Aplidin™ induces c-JUN, JUN B, JUN D, c-FOS, FRA-1 and FOS B genes of the activator-protein (AP)-1 family, and also p65/RELA, a major component of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB). Concordantly, Aplidin™ increases AP-1 and NF-κB activity. c-FOS induction depends on EGFR, Src and JNK/p38MAPK. In contrast, induction of c-JUN does not require EGFR activity and p65/RELA induction is only partially dependent on these kinases. We used several genetically deficient cells to identify the critical target of Aplidin™. Mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) deficient for src, yes and fyn, and those lacking all p38MAPK isoforms displayed normal Aplidin™ sensitivity (IC50=12 nM). In contrast, MEFs lacking jnk1 and jnk2, which do not express any JNK isoform, were much less sensitive (IC50>500 nM). Furthermore, cells lacking c-jun or expressing a c-Jun protein in which JNK targets Ser63/73 were mutated (c-JunAA) showed intermediate sensitivity (IC50=60 nM). Additionally, Aplidin™ has higher cytotoxic activity against proliferating than quiescent cells, which is reflected in higher JNK activation. We conclude that phosphorylation by JNK of c-Jun and additional substrate(s) is crucial for Aplidin™ activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswas G, Anandatheerhavarada HK, Zaidi M and Avandhani NG . (2003). J. Cell. Biol., 161, 507–519.
Bowie A and O'Neill LAJ . (2000). Biochem. Pharmacol., 59, 13–23.
Broggini M, Marchini SV, Galliera E, Borsotti P, Taraboletti G, Erba E, Sironi M, Jimeno J, Faircloth GT, Giavazzi R and D'Incalci M . (2003). Leukemia, 17, 52–59.
Canty Jr TG, Boyle Jr EM, Farr A, Morgan EN, Verrier ED and Pohlman TH . (1999). Circulation, 100 (suppl II), 361–364.
Cuadrado A, García-Fernández LF, González L, Suárez Y, Losada A, Alcaide V, Martínez T, Fernández-Sousa JM, Sánchez-Puelles JM and Muñoz A . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 241–250.
Davis RJ . (2000). Cell, 103, 239–252.
Depenbrock H, Peter R, Faircloth G, Manzanares I, Jimeno J and Hanauske A . (1998). Br. J. Cancer, 78, 739–744.
Erba E, Bassano L, Di Liberti G, Muradore I, Chiorino G, Ubezio P, Vignati S, Codegoni A, Desiderio MA, Faircloth G, Jimeno J and D'Incalci M . (2002). Br. J. Cancer, 86, 1510–1517.
Erba E, Ronzoni S, Bergamaschi D, Bassano L, Desiderio AM, Faircloth GT, Jimeno J and D'Incalci M . (1999). Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res., 40, 3.
Faircloth G, Hanauske A, Depenbrock H, Peter R, Crews C, Manzanares I, Meely K, Grant W and Jimeno J . (1997). Proc. Ann. Meet. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res., 38, 103.
Gajate C, An F and Mollinedo F . (2003). Clin Cancer Res., 9, 1535–1545.
García-Fernández LF, Losada A, Alcaide V, Álvarez AM, Cuadrado A, González L, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Fernández-Sousa JM, Sánchez-Puelles JM and Muñoz A . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 7533–7544.
Garg A and Aggarwal BB . (2002). Leukemia, 16, 1053–1068.
Gómez-Fabre PM, De Pedro E, Medina MA, Núñez de Castro I and Márquez J . (1997). Cancer Lett., 113, 141–144.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell, 100, 57–70.
Imbert V, Rupec RA, Livolsi A, Pahl HL, Traenckner EB, Mueller-Dieckmann C, Farahifar D, Rossi B, Auberger P, Bauerle PA and Peyron JF . (1996). Cell, 86, 787–798.
Janssen-Heininger YMW, Macara I and Mossman BT . (1999). Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 20, 942–952.
Janssen-Heininger YMW, Poynter ME and Baeuerle PA . (2000). Free Rad. Biol. Med., 28, 1317–1327.
Juin P, Hueber A-O, Littlewood T and Evan G . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1367–1381.
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Hofmann TG, Hehner SP, Dröge W and Schmitz ML . (2000). Eur. J. Biochem., 267, 3828–3835.
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y and Gélinas C . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 8961–8982.
Li N and Karin M . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 13012–13017.
Liedtke C, Plumpe J, Kubicka S, Bradham CA, Manns MP, Brenner DA and Trautwein C . (2002). Hepatology, 36, 315–325.
Lobo C, García-Pozo SG, Núñez de Castro I and Alonso FJ . (1997). Anticancer Res., 17, 333–336.
López Ongil S, Hernández-Perera O, Navarro Antolín J, Pérez de Lema G, Rodríguez Puyol M, Lamas S and Rodríguez Puyol D . (1998). Br. J. Pharmacol., 124, 447–454.
Morton S, Davis RJ, McLaren A and Cohen P . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 3876–3886.
Newton TR, Patel NM, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Stauss CR, Goulet Jr RJ and Nakshatri H . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 18827–18835.
Noguchi K, Kitanaka C, Yamana H, Kokubu A, Mochizuki T and Kuchino Y . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 32580–32587.
Raymond E, Paz-Ares L, Izquierdo M, Belanger K, Maroun J, Bowman A, Anthoney A, Jodrell D, Armand JP, Cortés-Funes H, Germa-Lluch J, Twelves C, Celli N, Guzman C and Jimeno J . (2001). Eur. J. Cancer, 37 (Suppl 6), S32.
Sakai R, Rinehart KL, Kishore V, Kundu B, Faircloth G, Gloer JB, Carney JR, Namikoshi M, Sun F, Hughes Jr RG, García Grávalos D, García de Quesada T, Wilson GR and Heid RM . (1996). J. Med. Chem., 39, 2819–2834.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Shaulian E and Karin M . (2002). Nat. Cell Biol., 4, E131–E136.
Singh S, Darnay BG and Aggarwal VBB . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 31049–31054.
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA and Davis RJ . (2000). Science, 288, 870–874.
Urdiales JL, Morata P, Núñez de Castro I and Sánchez-Jiménez F . (1996). Cancer Lett., 102, 31–37.
Wang X, Rao J and Studzinski GP . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 258, 425–437.
Weiss C, Schneider S, Wagner E, Zhang X, Seto E and Bohmann D . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 3686–3695.
Yao L . (2003). IDrugs, 6, 246–250.
Acknowledgements
We thank those who appear in the section on Materials and methods for providing us with cells or antibodies and Robin Rycroft for his valuable assistance in the preparation of the English manuscript. This work was partly supported by Grant SAF01-2291 from Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología of Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuadrado, A., González, L., Suárez, Y. et al. JNK activation is critical for Aplidin™-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23, 4673–4680 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207636
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207636
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Randomized phase III study (ADMYRE) of plitidepsin in combination with dexamethasone vs. dexamethasone alone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
Annals of Hematology (2019)
-
Novel β-phenylacrylic acid derivatives exert anti-cancer activity by inducing Src-mediated apoptosis in wild-type KRAS colon cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Natural Products Diversity of Marine Ascidians (Tunicates; Ascidiacea) and Successful Drugs in Clinical Development
Natural Products and Bioprospecting (2017)
-
Translation Elongation Factor eEF1A2 is a Novel Anticancer Target for the Marine Natural Product Plitidepsin
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Role of C-Jun N-terminal Kinase in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development
Targeted Oncology (2016)