Abstract
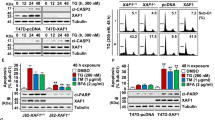
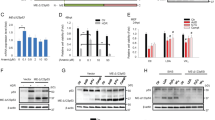
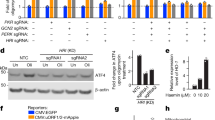
p73, like its family member p53, can induce programmed cell death following DNA damage. Here, we report that this mechanism also involves endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the transactivation of scotin, a protein identified recently as a p53 target able to induce ER stress. By using Tet-On inducible cell lines (Saos 2 osteosarcoma cells that lack p53), we observed that TAp73α elicits significant alterations in the morphology of the ER system, namely in the fine subcellular localization of calnexin. We found that both TAp73α and p53 are strong inducers of scotin. On the other hand, the transcriptionally deficient short isoforms ΔNp73α did not upregulate the steady-state mRNA level of scotin, as evaluated by real-time RT–PCR. Following the induction of scotin, ER staining with calnexin showed evidence of morphological alteration, with variations in the intracellular concentration of free calcium, visualized by fluo-3 staining. The induction of ER stress by p73 was further supported by the transcriptional induction of Gadd 153, a transcription factor induced under ER stress conditions. In conclusion, the data reported indicate the ability of TAp73α and p53 (not ΔNp73α) to elicit scotin transactivation and ER stress. This molecular mechanism might contribute to the effector events inducing apoptosis downstream of p73.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M and Shaul Y . (1999). Nature, 399, 809–813.
Bourdon JC, Renzing J, Robertson PL, Fernandes KN and Lane DP . (2002). J Cell Biol., 158, 235–246.
Costanzo A, Merlo P, Pediconi N, Fulco M, Sartorelli V, Cole PA, Fontemaggi G, Fanciulli M, Schiltz L, Blandino G, Balsano C and Levrero M . (2002). Mol Cell, 9, 175–186.
De Laurenzi V, Catani MV, Terrinoni A, Corazzari M, Melino G, Costanzo A, Levrero M and Knight RA . (1999). Cell Death Differ., 6, 389–390.
De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Barcaroli D, Terrinoni A, Falco M, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Levrero M and Melino G . (1998). J. Exp. Med., 188, 1763–1768.
De Laurenzi V, Raschella G, Barcaroli D, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Ranalli M, Catani MV, Tanno B, Costanzo A, Levrero M and Melino G . (2000a). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 15226–15231.
De Laurenzi V, Rossi A, Terrinoni A, Barcaroli D, Levrero M, Costanzo A, Knight RA, Guerrieri P and Melino G . (2000b). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 273, 342–346.
Ferri KF and Kroemer G . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, E255–E263.
Fillippovich I, Sorokina N, Gatei M, Haupt Y, Hobson K, Moallem E, Spring K, Mould M, McGuckin MA, Lavin MF and Khanna KK . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 514–522.
Gong JC, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin Jr WG, Levrero M and Wang JY . (1999). Nature, 399, 806–809.
Grob TJ, Novak U, Maisse C, Barcaroli D, Lüthi AU, Pirnia F, Hügli B, Graber HU, De Laurenzi V, Fey MF, Melino G and Tobler A . (2001). Cell Death Differ., 8, 1213–1223.
Irwin M, Marin MC, Phillips AC, Seelan RS, Smith DI, Liu W, Flores ER, Tsai KY, Jacks T, Vousden KH and Kaelin WG . (2000). Nature, 407, 645–648.
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, Ferrara P, McKeon F and Caput D . (1997). Cell, 90, 809–819.
Kaufman RJ . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1211–1233.
Marin MC, Jost CA, Brooks LA, Irwin MS, O'Nions J, Tidy JA, James N, McGregor JM, Harwood CA, Yulug IG, Vousden KH, Allday MJ, Gusterson B, Ikawa S, Hinds PW, Crook T and Kaelin W . (2000). Nat. Genet., 25, 47–54.
Matsumoto M, Minami M, Takeda K, Sakao Y and Akira S . (1996). FEBS Lett., 395, 143–147.
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY and Holbrook NJ . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 1249–1259.
Melino G, De Laurenzi V and Vousden KH . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 605–615.
Melino G, Lu X, Gasco M, Crook T and Knight RA . (2003). Functional regulation of p73 and p63: development and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci., 28 (12), 663–670.
Nakano K, Bàlint E, Ashcroft M and Vousden KH . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 4283–4289.
Steengenga WT, Shvarts A, Riteco N, Bos JL and Jochemsen AG . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 3885–3894.
Tschan MP, Grob TJ, Peters UR, De Laurenzi V, Huegli B, Kreuzner KA, Schmidt CA, Melino G, Fey MF, Tobler A and Cajot JF . (2000). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 277, 62–65.
Wang XZ, Lawson B, Brewer JW, Zinszner H, Sanjay A, Mi LJ, Boorstein R, Kreibich G, Hendershot LM and Ron D . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 4273–4280.
Yang A, Kaghad M, Caput D and McKeon F . (2002). Trends Genet., 18, 90–95.
Yang A, Walker N, Bronson R, Kaghad M, Oosterwegel M, Bonnin J, Vagner C, Bonnet H, Dikkes P, Sharpe A, McKeon F and Caput D . (2000). Nature, 404, 99–103.
Yuan ZM, Shioya H, Ishiko T, Sun X, Gu J, Huang YY, Lu H, Kharbanda S, Weichselbaum R and Kufe D . (1999). Nature, 399, 814–817.
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W and Chen X . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5061–5065.
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang XZ, Batchvarova N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL and Ron D . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 982–995.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Telethon (E1224), AIRC, EU (QLG1-1999-00739 and QLK-CT-2002-01956), MIUR, MinSan. MR is a recipient of an FIRC fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terrinoni, A., Ranalli, M., Cadot, B. et al. p73-alpha is capable of inducing scotin and ER stress. Oncogene 23, 3721–3725 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207342
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207342
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
WWOX sensitises ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel via modulation of the ER stress response
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
A balancing act: orchestrating amino-truncated and full-length p73 variants as decisive factors in cancer progression
Oncogene (2015)
-
α-TEA cooperates with chemotherapeutic agents to induce apoptosis of p53 mutant, triple-negative human breast cancer cells via activating p73
Breast Cancer Research (2011)
-
Analysis of the intracellular localization of p73 N-terminal protein isoforms TAp73 and ∆Np73 in medulloblastoma cell lines
Journal of Molecular Histology (2010)
-
Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2008)