Abstract
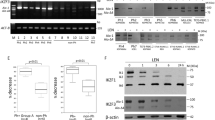
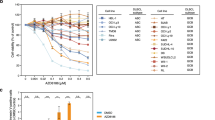
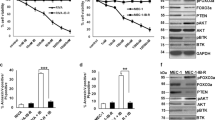
We have recently reported that Rituximab (anti-CD20) sensitizes drug-resistant 2F7 and 10C9 B Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) cell lines to the apoptotic effects of various chemotherapeutic drugs by downregulation of IL-10 and Bcl-2 expression. The mechanism by which Rituximab induces downregulation of IL-10 was examined. We hypothesized that Rituximab may inhibit p38 MAPK activity that regulates IL-10 expression via Sp1. Treatment of 2F7 cells with Rituximab or the p38 inhibitor SB203580 inhibited the constitutive p38 MAPK activity and resulted in the inhibition of Sp1, IL-10, STAT3, and Bcl-2. Inhibition of the Src-family PTKs, Lyn, and Src-family PTKs upstream signaling molecules of the p38MAPK pathway, by PP2, a specific Src-family kinase inhibitor, resulted in the inhibition of p38MAPK and IL-10 expression. In addition to p38 MAPK, Rituximab also inhibited NF-κB activity. Inhibition of the Src PTKs, MAPK, and NF-κB activities by Rituximab or by specific chemical inhibitors sensitized the cells to CDDP-mediated apoptosis. The above signaling-mediated effects by Rituximab were observed with similar kinetics beginning at 1 h following treatment. Thus, altogether, these results demonstrate that signaling by Rituximab results in the inhibition of the p38MAPK pathway, which in turn inhibits the transcription of IL-10 via Sp1. Inhibition of the IL-10 autocrine/paracrine loop results in the inhibition of STAT3 activity and, consequently, inhibition of Bcl-2 expression and sensitization to drugs-apoptosis. Further, Rituximab-mediated signaling identifies several new intracellular targets in NHL that may be of potential therapeutic interest for the development of new drugs in the treatment of drug-refractory NHL tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alas S and Bonavida B . (2001). Cancer Res., 6, 1–8.
Alas S, Emmanouilides C and Bonavida B . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 709–723.
Battle TE and Frank DA . (2002). Curr. Mol. Med., 2, 381–392.
Berghe WV, Plaisance S, Boone E, De Bosscher K, Schmitz ML, Fiers W and Haegeman G . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 3285–3290.
Brightbill HD, Plevy SE, Modlin RL and Smale ST . (2000). J. Immunol., 164, 1940–1951.
Carter AB, Knudtson KL, Monick MM and Hunninghake GW . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 30858–30863.
Chang L and Karin M . (2001). Nature, 140, 37–40.
Coiffier B . (2003). Blood Rev., 17, 25–31.
Demiden A, Lam T, Alas S, Hariharan K, Hanna N and Bonavida B . (1997). Cancer Biother. Radiopharm., 12, 177–186.
Dong C, Davis RJ and Flavell RA . (2002). Annu. Rev. Immunol., 20, 55–72.
Eliopoulos AG, Gallagher NJ, Blake SMS, Dawson CW and Young LS . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 16086–16096.
Eskdale J, Kube D, Tesch H and Gallegher G . (1997). Immunogenetics, 46, 120–128.
Foey AD, Parry SL, Williams LM, Feldmann M, Foxwell BM and Brennan FM . (1998). J. Immunol., 160, 920–928.
Foran JM . (2002). Best Prac. Res. Clin. Haematol., 15, 449–465.
Freedman AS and Nadler LM . (1991). Hematol Oncol Clin. N. Am., 5, 871–889.
Gan X-H and Bonavida B . (1999). Cell Immunol., 193, 125–133.
Garban H and Bonavida B . (2001). J. Immunol., 167, 75–81.
Han I and Kudlow JE . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 2550–2558.
Han Q, Leng J, Bian D, Mahanivong C, Carpenter KA, Pan ZK, Han J and Huang S . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 48379–48385.
Hanke JH, Gardener JP, Dow RL, Changelin PS, Brissette WH, Weringer EJ, Pollok BA and Connelly PA . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 695.
Harada H, Takahashi E, Itoh S, Harada K, Hori TA and Taniguchi T . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 4, 1500–1509.
Hu X, Janssen WE, Moscinski LC, Bryington M, Dangsupa A, Rezai-Zedeh N, Babbin BA and Zuckerman S . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6290–6296.
Huhn D, von Schilling C, Wilhelm M, Ho A, Hallek M, Kuse R, Knauf W, Riedel U, Hinke A, Srock S, Serke S, Peschel C and Emmerich B . (2001). Blood, 98, 1326–1331.
Jazirehi A, Gan XH, De Vos S, Emmanouilides C and Bonavida B . (2003). Mol. Cancer Ther., 2, 1183–1193.
Kube D, Platzer C, von Knethen A, Straub H, Bohlen H, Hafner M and Tesch H . (1995). Cytokin, 7, 1–7.
Levine AM . (1992). Blood, 80, 8–20.
Lida M, Towatari M, Nakao A, Lida H, Kiyoi J, Nakano Y, Tanimoto M, Saito H and Naoe T . (1999). Leukemia, 13, 585–589.
Lin YZ, Yao S, Veach RA, Torgerson TR and Hawiger J . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 14255.
Ma W, Lim W, Gee K, Aucoin S, Nandan D, Kozlowski M, Diaz-Mitoma F and Kumar A . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 13664–13674.
Martin-Blanco E . (2000). BioEssays, 22, 637–645.
Miki H, Yamada H and Mitamura K . (1999). Anticancer Res., 19, 5283–5291.
Mori N and Prager D . (1997). Eur. J. Hematol., 59 (3), 162–170.
Pedersen IM, Buhl AM, Klausen P, Geisler CH and Jurlander J . (2002). Blood, 99, 1314–1319.
Polak MJ, Taylor SH and Deans JP . (1998). J. Immunol., 161, 3242–3248.
Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, Chinn PC, Leonard JE, Raab R, Newman RA, Hanna N and Anderson D.R . (1994). Blood, 83, 435–445.
Riley JK and Sliwkowski MX . (2000). Sem. Oncol., 27, 17–24.
Saccani S, Pantano S and Natoli G . (2002). Nat. Immunol., 3, 69–75.
Sato N, Sadar MD, Bruchovsky M, Saatcioglu F, Rennie PS, Sato S, Lange PH and Gleave ME . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 17485–17494.
Semac I, Palomba C, Kulangara K, Klages N, van Echten-Deckert G, Borisch B and Hoessli DC . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 534–540.
Shan D, Ledbetter JA and Press OW . (1998). Blood, 91, 1644–1652.
Stashenko P, Nadler LM, Ardi R and Schlossman SF . (1980). J. Immunol., 125, 1678–1685.
Steinman RA et al. (2003). Oncogene, 22, 3608–3615.
Tedder TF and Engel P . (1994). Immunol. Today, 15, 450–454.
Thieblemont C and Coiffier B . (2002). Int. J. Hematol., 76, 394–400.
Vockerodt M, Haier B, Buttgereit P, Tesch H and Kube D . (2001). Virology, 280, 183–198.
Voorzanger N, Touitou R, Garcia E, Delecluse HJ, Rousset F, Joab I, Favrot MC and Blay JY . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 5499–5505.
Wang D and Richmond A . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 3650–3659.
Acknowledgements
We extend our gratitude to Dr Otoniel Martinez-Maza for valuable input and support. We also thank Kate Dinh for the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported in part by grants from Genentech, Fogarty International Center Fellowship (S.H., H.G. D43 TW00013-14), and the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at UCLA (M.V., A.J.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vega, M., Huerta-Yepaz, S., Garban, H. et al. Rituximab inhibits p38 MAPK activity in 2F7 B NHL and decreases IL-10 transcription: Pivotal role of p38 MAPK in drug resistance. Oncogene 23, 3530–3540 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207336
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207336
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An exploratory study examining how nano-liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and phosphoproteomics can differentiate patients with advanced fibrosis and higher percentage collagen in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
BMC Medicine (2018)
-
Regulation of glucose uptake in lymphoma cell lines by c-MYC- and PI3K-dependent signaling pathways and impact of glycolytic pathways on cell viability
Journal of Translational Medicine (2017)
-
P38 MAPK expression and activation predicts failure of response to CHOP in patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Increased drug resistance in breast cancer by tumor-associated macrophages through IL-10/STAT3/bcl-2 signaling pathway
Medical Oncology (2015)
-
Modulation of deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) and glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3β) by anti-CD20 (rituximab) and 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (2-CdA) in human lymphoid malignancies
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2014)