Abstract
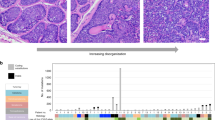
The p53-regulated 14-3-3σ gene encodes an inhibitor of cell cycle progression essential for senescence and clonal evolution of keratinocytes in vitro. Here we analysed the in vivo expression of 14-3-3σ protein in several skin diseases, which are characterized by hyperproliferative keratinocytes. Unexpectedly, the 14-3-3σ protein was expressed at high levels in psoriasis (11 of 11 patients), condylomata acuminata (11/11), actinic keratoses (11/11) and squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) (11/11). However, keratinocytes that had undergone transformation to basal cell carcinoma (BCC) showed partial (10 of 41; 24.4%) or complete (19 of 41; 46.3%) loss of 14-3-3σ protein expression. BCC (5/5), SCC (6/6) and actinic keratoses (7/7) concomitantly expressed the p53-homolog p63 and 14-3-3σ at high levels, ruling out potential inhibitory effects of p63 isoforms on 14-3-3σ transcription as the basis for loss of 14-3-3σ expression. Of 41 BCC samples isolated by laser-capture microdissection, 28 (68.3%) showed CpG-hypermethylation of the 14-3-3σ promoter combined with reduced or absent 14-3-3σ protein levels in 22 cases (78.6%). Since it has been reported that BCC retain wild-type p16INK4A and here BCC with CpG-methylation of 14-3-3σ did not show CpG-methylation of p16INK4A (0/17), silencing of 14-3-3σ may contribute to evasion of senescence in BCC. As experimental removal of 14-3-3σ sensitizes to DNA damage, silencing of 14-3-3σ may explain the high efficacy of radiation therapy in the treatment of BCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCC:
-
basal cell carcinoma
- bp:
-
base pair
- Cdk:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- HDF:
-
human diploid fibroblasts
- MSP:
-
methylation-specific PCR
- SCC:
-
squamous cell carcinoma
References
Chan TA, Hermeking H, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1999). Nature, 401, 616–620.
Dellambra E, Golisano O, Bondanza S, Siviero E, Lacal P, Molinari M, D'Atri S and De Luca M . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 149, 1117–1130.
Ferguson AT, Evron E, Umbricht CB, Pandita TK, Chan TA, Hermeking H, Marks JR, Lambers AR, Futreal PA, Stampfer MR and Sukumar S . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 6049–6054.
Gasco M, Sullivan A, Repellin C, Brooks L, Farrell PJ, Tidy JA, Dunne B, Gusterson B, Evans DJ and Crook T . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 1876–1881.
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD and Baylin SB . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 9821–9826.
Hermeking H, Lengauer C, Polyak K, He TC, Zhang L, Thiagalingam S, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1997). Mol. Cell, 1, 3–11.
Ivanova T, Petrenko A, Gritsko T, Vinokourova S, Eshilev E, Kobzeva V, Kisseljov F and Kisseljova N . (2002). BMC Cancer, 21, 4.
Iwata N, Yamamoto H, Sasaki S, Itoh F, Suzuki H, Kikuchi T, Kaneto H, Iku S, Ozeki I, Karino Y, Satoh T, Toyota J, Satoh M, Endo T and Imai K . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5298–5302.
Laronga C, Yang H Y, Neal C and Lee MH . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 23106–23112.
Li Z, Meng ZH, Chandrasekaran R, Kuo WL, Collins CC, Gray JW and Dairkee SH . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 1939–1943.
Miller SJ . (1991). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 24, 1–13.
Pellegrini G, Dellambra E, Golisano O, Martinelli E, Fantozzi I, Bondanza S, Ponzin D, McKeon F and De Luca M . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 3156–3161.
Samuel T, Weber HO, Rauch P, Verdoodt B, Eppel JT, McShea A, Hermeking H and Funk JO . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 45201–45206.
Saridaki Z, Koumantaki E, Liloglou T, Sourvinos G, Papadopoulos O, Zoras O and Spandidos DA . (2000). J. Invest. Dermatol., 115, 719–725.
Schubert J and Muller A . (1997). Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir., 1, 44–46.
Tokugawa T, Sugihara H, Tani T and Hattori T . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 4938–4944.
Umbricht CB, Evron E, Gabrielson E, Ferguson A, Marks J and Sukumar S . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 3348–3353.
Urano T, Saito T, Tsukui T, Fujita M, Hosoi T, Muramatsu M, Ouchi Y and Inoue S . (2002). Nature, 417, 871–875.
Westfall MD, Mays DJ, Sniczek JC and Pietenpol JA . (2003). Mol. Cell Biol., 23, 2264–2276.
Yaffe MB . (2002). FEBS Lett., 513, 53–57.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jens-Oliver Funk and the members of the Molecular Oncology lab for comments and discussions, and Bert Vogelstein and Axel Ullrich for providing cell lines. Heiko Hermeking's laboratory is supported by the Max-Planck-Society, the Rudolf-Bartling foundation and the Dr Mildred-Scheel foundation (Grant 10-1945).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lodygin, D., Yazdi, A., Sander, C. et al. Analysis of 14-3-3σ expression in hyperproliferative skin diseases reveals selective loss associated with CpG-methylation in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 22, 5519–5524 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206854
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206854
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
GLI2 induces genomic instability in human keratinocytes by inhibiting apoptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
Epigenetic alterations in sporadic basal cell carcinomas
Archives of Dermatological Research (2014)
-
Impaired Keratinocyte Proliferative and Clonogenic Potential in Transgenic Mice Overexpressing 14-3-3σ in the Epidermis
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2011)
-
The clinicopathological and prognostic impact of 14-3-3 sigma expression on vulvar squamous cell carcinomas
BMC Cancer (2008)
-
Differential proteomic analysis of HeLa cells treated with Honokiol using a quantitative proteomic strategy
Amino Acids (2008)