Abstract
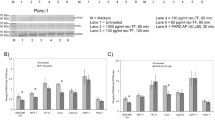
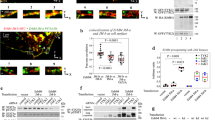
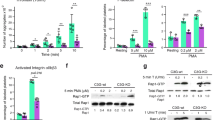
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade is a well documented mechanism for the G-protein-coupled receptors. Here, we have analysed the requirements for ERKs and p38 MAPK activation by thrombin in Jurkat T cells. We show that thrombin-mediated ERKs activation requires both PTK and PKC activities, whereas p38 MAPK activation is dependent only on PTKs. Thrombin-induced ERK and p38 MAPK activation was more pronounced in p56Lck deficient cells indicating that this PTK exerts a negative control on MAPK activity. Accordingly, overexpression of p50 Csk a kinase that inactivates p56Lck induced constitutive activation of ERKs. Requirement for a Src kinase was evidenced by expression of a constitutively active form of p59Fyn in Jurkat cells. Besides its effect on tyrosine phosphorylation events, thrombin also triggered a rapid and robust redistribution of PKCε and δ from the cytosol to the membrane. Expression of constitutively active and dominant negative PKCε demonstrates the pivotal role of this PKC isoform in ERKs activation by thrombin. These data are consistent with a model where thrombin induces ERK activation via both PKC-dependent and independent pathways, whereas p38 MAPK activation requires only PTKs. The PKC-independent pathway requires Src kinases other than p56Lck more likely p59Fyn, while the PKC-dependent mechanism depends on PKCε
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NG, Maller JL, Tonks NK, Sturgill TW . 1990 Nature 343: 651–653
Autero M, Saharinen J, Pessa-Morikawa T, Soula-Rothhut M, Oetken C, Gassmann M, Baier BG, Uberall F, Bauer B, Fresser F, Wachter H, Grunicke H, Utermann G, Altman A, Baier G . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 1842–1850
Bjorkoy G, Perander M, Overvatn A, Johansen T . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 11557–11565
Branch DR, Mills GB . 1995 J. Immunol. 154: 3678–3685
Buday L, Downward J . 1993 Cell 73: 611–620
Burgering BM, Bos JL . 1995 Trends Biochem. Sci. 20: 18–22
Cai H, Smola U, Wixler V, Eisenmann TI, Diaz MM, Moscat J, Rapp U, Cooper GM . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 732–741
Chen Y.-H, Pouyssegur J, Courtneidge SA, Van Obbergen-Schilling E . 1994 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 27312–27377
Conway AM, Rakhit S, Pyne S, Pyne NJ . 1999 Biochem. J 171–177
Deckert M, Tartare-Deckert S, Hernandez J, Rottapel R, Altman A . 19998 Immunity 9: 595–605
Dery O, Corvera CU, Steinhoff M, Bunnett NW . 1998 Am. J. Physiol 1429–1452
Diaz MM, Lozano J, Municio MM, Berra E, Frutos S, Sanz L, Moscat J . 1994 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 31706–31710
Dikic I, Tokiwa G, Lev S, Courtneidge SA, Schlessinger J . 1996 Nature 383: 547–550
Dikic I, Schlessinger J . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 31706–31710
Genot EM, Parker PJ, Cantrell DA . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 9833–9839
Ghaffari TN, Bauer B, Villunger A, Baier BG, Altman A, Utermann G, Uberall F, Baier G . 1999 Eur. J. Immunol. 29: 132–142
Goldsmith MA, Weiss A . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 6879–6883
Gutkind JS . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 1839–1842
Hanke JH, Gardner JP, Dow RL, Changelian PS, Brissette WH, Weringer EJ, Pollok BA, Connelly PA . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 695–701
Joyce DE, Chen Y, Erger RA, Koretzky GA, Lentz SR . 1997 Blood 90: 1893–1901
Kampfer S, Hellbert K, Villunger A, Doppler W, Baier G, Grunicke HH, Uberall F . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 4046–4055
Kawakami Y, Yao L, Tashiro M, Gibson S, Mills GB, Kawakami T . 1995 J. Immunol. 155: 3556–3562
Luttrell LM, Daaka Y, Della RG, Lefkowitz RJ . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 31648–31656
Mari B, Guerin S, Maulon L, Belhacene N, Farahi Far D, Imbert V, Rossi B, Peyron JF, Auberger P . 1997 FASEB J. 11: 869–879
Mari B, Imbert V, Belhacene N, Farahi Far D, Peyron J-F, Pouyssegur J, Van Obberghen-Schilling E, Rossi B, Auberger P . 1994 J. Biol. Chem. 269: 8517–8523
Marshall CJ . 1995 Cell 80: 179–185
Maulon L, Guerin S, Ricci JE, Breittmayer JP, Auberger P . 1998 Blood 91: 4232–4241
Medema RH, de V Smits AM, van der Zon GC, Maassen JA, Bos JL . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 155–162
Morrison DK, Heidecker G, Rapp UR, Copeland TD . 1993 J. Biol. Chem. 268: 17309–17316
Nada S, Yagi T, Takeda H, Tokunaga T, Nakagawa H, Ikawa Y, Okada M, Aizawa S . 1993 Cell 73: 1125–1135
Ron D, Napolitano EW, Voronova A, Vasquez NJ, Roberts DN, Calio BL, Caothien RH, Pettiford SM, Wellik S, Mandac JB, Kauvar LM . 1999 J. Biol. Chem. 274: 19003–19010
Rossomando AJ, Payne DM, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW . 1989 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 6940–6943
Sadoshim J, Izumo S . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 775–787
Satoh K, Ozaki Y, Asazuma N, Yatomi Y, Ruomei Q, Kuroda K, Yang L, Kume S . 1996 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 225: 1084–1089
Song JS, Swann PG, Szallasi Z, Blank U, Blumberg PM, Rivera J . 1998 Oncogene 16: 3357–3368
Stokoe D, Macdonald SG, Cadwallader K, Symons M, Hancock JF . 1994 Science 264: 1463–1467
Ueda Y, Hirai Si, Osada Si, Suzuki A, Mizuno K, Ohno S . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 23512–23519
Vu T-KH, Hung DT, Wheaton VI, Coughlin SR . 1991 Cell 64: 1057–1068
Wan Y, Kursaki T, Huang X-Y . 1996 Nature 380: 541–544
Wang XS, Diener K, Tan TH, Yao Z . 1998 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253: 33–37
Weiss A, Littman DR . 1994 Cell 76: 263–274
Werlen G, Jacinto E, Xia Y, Karin M . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 3101–3111
Yao L, Kawakami Y, Kawakami T . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 9175–9179
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by INSERM, the University of Nice Sophia Antipolis (BQR), the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC grants 6684 and 9502) and the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipe labellisée LNC). We thank Georges Bismuth for helpful suggestions. L Maulon is a fellowship from the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maulon, L., Mari, B., Bertolotto, C. et al. Differential requirements for ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK activation by thrombin in T cells. Role of P59Fyn and PKCε. Oncogene 20, 1964–1972 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of the antigen‐induced activation of rodent mast cells by putative Janus kinase 3 inhibitors WHI‐P131 and WHI‐P154 in a Janus kinase 3‐independent manner
British Journal of Pharmacology (2005)
-
Gene expression profiling of normal human pulmonary fibroblasts following coculture with non-small-cell lung cancer cells reveals alterations related to matrix degradation, angiogenesis, cell growth and survival
Oncogene (2003)