Abstract
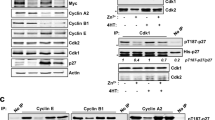
Myc is overexpressed in many cancers as a result of gene rearrangement or amplification, but coding sequence changes which cluster in the N-terminal transactivation domain also appear to play a role in tumour progression. The prototypic v-Myc gene of MC29 virus differs from avian c-Myc by a series of mutations, including a change at a regulatory phosphorylation site within the mutational hotspot (thr-61) which is known to potentiate transformation in vitro. We now show that the mutation at thr-61 stabilizes the v-Myc protein (turnover difference) and that this single mutation is both necessary and sufficient for the phenotype. A major involvement of the proteasome in Myc degradation was confirmed, but surprisingly, a dilysine motif adjacent to thr-61 proved not to be the ubiquitin target. Two other v-Myc genes which carry a mutation at thr-61 (avian MH2) or a large deletion encompassing this domain (feline T17) were found to be stabilized to a similar extent as MC29, showing that stabilization is a common feature of independently derived Myc oncogenes. These results suggest a common selective process in the genesis of these three viral oncoproteins and a mechanistic link with Jun, Fos and Myb oncoproteins which are also stabilized relative to their cellular counterparts.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bies J and Wolff L. . 1997 Oncogene 14: 203–212.
Breitschopf K, Bengal E, Ziv T, Admon A and Ciechanover A. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 5964–5973.
Chen R-H, Juo PC-H, Curran T and Blenis J. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 1493–1502.
Ciechanover A. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 7151–7160.
Coll J, Righi M, de Taisne C, Dissou C, Gegonne A and Stehelin D. . 1983 EMBO J. 12: 2189–2194.
Colman MS and Ostrowski MC. . 1996 Nucleic Acids Res. 24: 1971–1978.
Crouch DH, Fisher F, Clark W, Jayaraman PS, Goding CR and Gillespie DAF. . 1993 Oncogene 8: 1849–1855.
Crouch DH, Lang C and Gillespie DAF. . 1990 Oncogene 5: 683–689.
Curran T, Miller AD, Zokas L and Verma IM. . 1984 Cell 36: 259–268.
Fenteany G, Standaert RF, Lane WS, Choi S, Corey EJ and Schreiber SL. . 1995 Science 268: 726–731.
Flinn EM, Busch CMC and Wright APH. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 5961–5969.
Fulton R, Gallagher R, Crouch D and Neil JC. . 1996 J. Virol. 170: 1154–1162.
Gillespie DAF. . 1991 Seminars Virol. 2: 329–339.
Gross-Mesilaty S, Reinstein E, Bercovich B, Tobias KE, Schwartz AL, Kahana C and Ciechanover A. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 8058–8063.
Hann SR, Abrams HD, Rohrschneider LR and Eisenman RN. . 1983 Cell 34: 789–798.
Henriksson M, Bakardjiev A, Klein G and Luscher B. . 1993 Oncogene 8: 3199–3209.
Henriksson M and Luscher B. . 1996 Adv. Cancer Res. 68: 109–182.
Hoang AT, Lutterbach B, Lewis BC, Yano T, Chou T-Y, Barrett JF, Raffeld M, Hann SR and Dang CV. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 4031–4042.
Isaksson A, Musti AM and Bohmann D. . 1996 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1288: F21–F29.
Kilbey A, Black EJ, Unlu M and Gillespie DAF. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 2409–2418.
Krappmann D, Wulczyn FG and Scheidereit C. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 6716–6726.
La Rocca SA, Crouch DH and Gillespie DAF. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 3499–3508.
Luscher B, Kuenzel EA, Krebs EG and Eisenman RN. . 1989 EMBO J. 8: 1111–1119.
Lutterbach B and Hann SR. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 5510–5522.
May GHW, Funk M, Black EJ, Clark W, Hussain S, Woodgett JR and Gillespie DAF. . 1998 Curr. Biol. 8: 117–120.
Musti AM, Treier M and Bohmann D. . 1997 Science 275: 400–402.
Nakajima T, Morita K, Tsunoda H, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Tanaka H, Yasuda H and Oda K. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 20036–20045.
Okazaki K and Sagata N. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 5048–5059.
Pulverer BJ, Fisher C, Vousden K, Littlewood T, Evan G and Woodgett JR. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 59–70.
Rodriguez MS, Wright J, Thompson J, Thomas D, Baleux F, Virelizier J-L, Hay RT and Arenzana-Seisdedos F. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 2425–2435.
Salghetti SE, Kim SY and Tansey WP. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 717–726.
Sears R, Leone G, DeGregori J and Nevins JR. . 1999 Molecular Cell 3: 169–179.
Smith-Sorensen B, Hijmans EM, Beijersbergen RL and Bernards R. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 5513–5518.
Song A, Wang Q, Goebl MG and Harrington MA. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 4994–4999.
Stone J, de Lange T, Ramsay G, Jakobovits E, Bishop JM, Varmus H and Lee W. . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1697–1709.
Treier M, Staszewski LM and Bohmann D. . 1994 Cell 78: 787–798.
Walter N, Jansen W, Trachmann C and Bister K. . 1986 Virology 154: 219–223.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Jen Blake for technical assistance, RN Eisenman and DAF Gillespie for providing the anti-v-myc 12C and anti-jun antibodies respectively, and CNA Palmer and DW Meek for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavine, P., Neil, J. & Crouch, D. Protein stabilization: a common consequence of mutations in independently derived v-Myc alleles. Oncogene 18, 7552–7558 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203102