Abstract
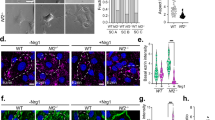
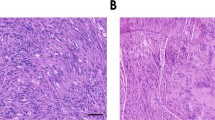
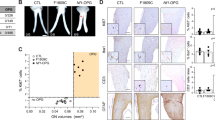
The neu/erbB2 protooncogene is overexpressed in numerous human cancers and is mutationally activated in N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-induced rodent tumors of the Schwann cell lineage. We investigated whether expression of activated neu in Schwann cells is sufficient to initiate their immortalization and transformation. Clones of embryonic dorsal root ganglia cells infected with a retrovirus bearing activated neu (NID cells) were selected based on their expression of Schwann cell-specific markers. Compared to embryonic Schwann cells infected with a virus encoding empty vector, we found that NID cells have altered shapes and disorganized cytoskeletons, grow in the absence of growth factors required for normal Schwann cell survival and proliferation, and can be repeatedly passaged. Furthermore, NID cells are invasive in an in vitro matrix invasion assay and form metastatic tumors when injected into syngeneic animals. The neu-induced growth and invasive phenotypes could be reversed by drugs that inhibit Ras and Src activity. Interestingly, later stage Schwann cells infected with activated neu failed to become immortalized. These findings indicate that constitutive activation of erbB2 is sufficient to initiate the immortalization and transformation of immature Schwann cells, and support the notion that Schwann cells have particular developmental stages during which they are susceptible to immortalizing and transforming events.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargmann CI and Weinberg RA. . 1988 EMBO J. 7: 2043–2052.
Bishop JM. . 1987 Science 235: 305–311.
Bradbury JM, Arno J and Edwards PA. . 1993 Oncogene 8: 1551–1558.
Carroll SL, Miller ML, Frohnert PW, Kim SS and Corbett JA. . 1997 J. Neurosci. 17: 1642–1659.
Cohen JA, Yachnis AT, Arai M, Davis JG and Scherer SS. . 1992 J. Neurosci. Res. 31: 622–634.
Di Fiore PP, Pierce JH, Kraus MH, Segatto O, King CR and Aaronson SA. . 1987 Science 237: 178–182.
Di Marco E, Pierce JH, Knicley CL and Di Fiore PP. . 1990 Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 3247–3252.
Dong Z, Brennan A, Liu N, Yarden Y, Lefkowitz G, Mirsky R and Jessen KR. . 1995 Neuron 15: 585–596.
Dougall WC, Qian X, Peterson NC, Miller MJ, Samanta A and Greene MI. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 2109–2123.
Druckrey H, Ivankovic S and Gimmy J. . 1973 Z. Krebsforsch. Klin. Onkol. 79: 282–297.
Fukazawa H, Li PM, Yamamoto C, Murakami Y, Mizuno S and Uehara Y. . 1991 Biochem. Pharmacol. 42: 1661–1671.
Goldman R, Levy RB, Peles E and Yarden Y. . 1990 Biochemistry 29: 11024–11028.
Graus-Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM and Hynes NE. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 1647–1655.
Grinspan JB, Marchionni MA, Reeves M, Coulaloglou M and Scherer SS. . 1996 J. Neurosci. 16: 6107–6118.
Hennigan RF, Hawker KL and Ozanne BW. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 3591–3600.
Hudziak RM, Schlessinger J and Ullrich A. . 1987 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 7159–7163.
Hynes NE and Stern DF. . 1994 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1198: 165–184.
James GL, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Rawson TE, Somers TC, McDowell RS, Crowley CW, Lucas BK, Levinson AD and Marsters Jr JC. . 1993 Science 260: 1937–1942.
Janes PW, Daly RJ, deFazio A and Sutherland RL. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 3601–3608.
Jenuwein T, Muller D, Curran T and Muller R. . 1985 Cell 41: 629–637.
Jin JJ, Nikitin AY and Rajewsky MF. . 1993 Cell Growth Differ. 4: 227–237.
Kim HA, DeClue JE and Ratner N. . 1997a J. Neurosci. Res. 49: 236–247.
Kim HA, Ling B and Ratner N. . 1997b Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 862–872.
Kleitman N, Wood P and Bunge RP. . 1991 In: Culturing Nerve Cells. G Banker and K Goslin. (eds). The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA pp. 251–278.
Lamb RF, Hennigan RF, Turnbull K, Katsanakis KD, MacKenzie ED, Birnie GD and Ozanne BW. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 963–976.
Levi AD, Bunge RP, Lofgren JA, Meima L, Hefti F, Nikolics K and Sliwkowski MX. . 1995 J. Neurosci. 15: 1329–1340.
Luttrell DK, Lee A, Lansing TJ, Crosby RM, Jung KD, Willard D, Luther M, Rodriguez M, Berman J and Gilmer TM. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 83–87.
Marchionni MA, Goodearl AD, Chen MS, Bermingham-McDonogh O, Kirk C, Hendricks M, Danehy F, Misumi D, Sudhalter J, Kobayashi K, et al. 1993 Nature 362: 312–318.
McCormick JJ and Maher VM. . 1988 Mutat. Res. 199: 273–291.
Morrissey TK, Levi AD, Nuijens A, Sliwkowski MX and Bunge RP. . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 1431–1435.
Muthuswamy SK and Muller WJ. . 1995 Oncogene 11: 271–279.
Muthswamy SK, Siegel PM, Dankort DL, Webster MA and Muller WJ. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 735–743.
Namba M, Mihara K and Fushimi K. . 1996 Crit. Rev. Oncog. 7: 19–31.
Newbold RF, Cuthbert AP, Themis M, Trott DA, Blair AL and Li W. . 1993 Tox. Lett. 67: 211–230.
Nikitin AY, Ballering LA, Lyons J and Rajewsky MF. . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 9939–9943.
Nikitin AY, Jin JJ, Papewalis J, Prokopenko SN, Pozharisski KM, Winterhager E, Flesken-Nikitin A and Rajewsky MF. . 1996 Oncogene 12: 1309–1317.
Pelton PD, Sherman LS, Rizvi TA, Marchionni MA, Wood P, Friedman RA and Ratner N. . 1998 Oncogene 17: 2195–2209.
Peng WW, Bressler JP, Tiffany-Castiglioni E and de Vellis J. . 1982 Science 215: 1102–1104.
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Soussan L, Waterman H, Levkowitz G, Alroy I, Klapper L, Lavi S, Seger R, Ratzkin B, Sela M and Yarden Y. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 2452–2467.
Perantoni AO, Rice JM, Reed CD, Watatani M and Wenk ML. . 1987 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 6317–6321.
Prendergast GC, Davide JP, deSolms SJ, Giuliani EA, Graham SL, Gibbs JB, Oliff A and Kohl NE. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 4193–4202.
Rajewsky MF. . 1983 Rec. Results Cancer Res. 84: 63–76.
Rhim JS, Yoo JH, Park JH, Thraves P, Salehi Z and Dritschilo A. . 1990 Cancer Res. 50: 5653S–5657S.
Salzer JL and Bunge RP. . 1980 J. Cell. Biol. 84: 739–752.
Schubert D, Heinemann S, Carlisle W, Tarikas H, Kimes B, Patrick J, Steinbach JH, Culp W and Brandt BL. . 1974 Nature 249: 224–227.
Sherman L, Xu HM, Geist RT, Saporito-Irwin S, Howells N, Ponta H, Herrlich P and Gutmann DH. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 2505–2509.
Sobko A, Peretz A and Attali B. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 4723–4734.
Stancovski I, Sela M and Yarden Y. . 1994 Cancer Treat. Res. 71: 161–191.
Tomozawa Y and Sueoka N. (1978). . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75: 6305–6309.
Tzahar E, Waterman H, Chen X, Levkowitz G, Karunagaran D, Lavi S, Ratzkin BJ and Yarden Y. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 5276–5287.
Tzahar E and Yarden Y. . 1998 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1377: M25–M37.
Uehara Y, Fukazawa H, Murakami Y and Mizuno S. . 1989 Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163: 803–809.
Vartanian T, Goodearl A, Viehover A and Fischbach G. . 1997 J. Cell Biol. 137: 211–220.
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW. . 1993 Trends Genet. 9: 138–141.
Wada T, Qian XL and Greene MI. . 1990 Cell 61: 1339–1347.
Weinberg RA. . 1989 Cancer Res. 49: 3713–3721.
Weiner DB, Liu J, Cohen JA, Williams WV and Greene MI. . 1989 Nature 339: 230–231.
Acknowledgements
We thank Tanja Schüler and Saikumar Karyala for technical assistance, Norma Howells for assistance with animal breeding, and Helmut Ponta for helpful discussions and ideas. We are also grateful to Paul Edwards from the Department of Pathology at the University of Cambridge for the ψ-2 pINA-neu and ψ-2 pINA cell lines, to Mark Marchionni from Cambridge Neuroscience for the rh-GGF2, to Jackson Gibbs and Nancy Krohl from Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories for the L-739,749. This work was supported by NIH NS28840 to N Ratner, NRSA NS10297 to L Sherman and He551/8-2 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to P Herrlich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherman, L., Sleeman, J., Hennigan, R. et al. Overexpression of activated neu/erbB2 initiates immortalization and malignant transformation of immature Schwann cells in vitro. Oncogene 18, 6692–6699 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203055
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203055
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Merlin regulates transmembrane receptor accumulation and signaling at the plasma membrane in primary mouse Schwann cells and in human schwannomas
Oncogene (2009)
-
Activation of the neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling pathway promotes the proliferation of neoplastic Schwann cells in human malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Oncogene (2005)
-
Synergy of Nf2 and p53 mutations in development of malignant tumours of neural crest origin
Oncogene (2004)
-
Expression of ErbB2 enhances radiation-induced NF-κB activation
Oncogene (2004)