Abstract
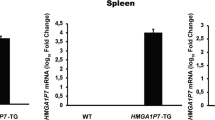
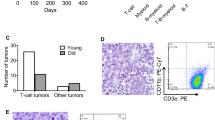
The proto-oncogene Frat1 was originally identified as a common site of proviral insertion in transplanted tumors of Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV)-infected Eμ-Pim1 transgenic mice. Contrary to most common insertion sites implicated in mouse T cell lymphomagenesis, retroviral insertional mutagenesis of Frat1 constitutes a relatively late event in M-MuLV-induced tumor development, suggesting that proviral activation of Frat1 contributes to progression of T cell lymphomas rather than their genesis. To substantiate this notion we have generated transgenic mice that overexpress Frat1 in various organs, including lymphoid tissues. Frat1 transgenic mice develop focal glomerulosclerosis and a nephrotic syndrome, but they do not exhibit an increased incidence of spontaneous lymphomas. Conversely, these mice are highly susceptible to M-MuLV-induced lymphomagenesis, and Frat1/Pim1 bitransgenic animals develop lymphomas with increased frequency compared to Pim1 transgenic littermates. These data support a role for Frat1 in tumor progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarden LA, de Groot ER and Feltkamp TEW. . 1979 NY Acad. Sci. USA 254: 505–515.
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD and Brinster RL. . 1985 Nature 318: 533–538.
Alkema MJ, Jacobs H, van Lohuizen M and Berns A. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 899–910.
Berns A, van der Lugt N, Alkema M, van Lohuizen M, Domen J, Acton D, Allen J, Laird PW and Jonkers J. . 1994 Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, Volume LIX. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY pp. 435–447.
Bishop JM. . 1991 Cell 64: 235–248.
Brady HJ, Salomons GS, Bobeldijk RC and Berns AJ. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 1221–1230.
Couser WG. . 1994 West. J. Med. 160: 440–446.
Cuypers HT, Selten G, Quint W, Zijlstra M, Robanus-Maandag E, Boelens W, van Wezenbeek P, Melief C and Berns A. . 1984 Cell 37: 141–150.
Harrison PTC. . 1984 Lab. Anim. 18: 325–331.
Haupt Y, Alexander WS, Barri G, Klinken SP and Adams JM. . 1991 Cell 65: 753–763.
Hunter T. . 1991 Cell 64: 249–270.
Izui S, Merino R, Fossati L and Iwamoto M. . 1994 Int. Rev. Immunol. 11: 211–230.
Jaenisch R, Fan H and Croker B. . 1975 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72: 4008–4012.
Jonkers J and Berns A. . 1996 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287: 29–57.
Jonkers J, Korswagen HC, Acton D, Breuer M and Berns A. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 441–450.
Kispert A, Vainio S and McMahon AP. . 1998 Development 125: 4225–4234.
Kispert A, Vainio S, Shen L, Rowitch DH and McMahon AP. . 1996 Development 122: 3627–3637.
Klein JB. . 1993 Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2: 225–230.
Kotzin BL. . 1996 Cell 85: 303–306.
Laird PW, Zijderveld A, Linders K, Rudnicki MA, Jaenisch R and Berns A. . 1991 Nucl. Acids Res. 19: 4293.
Mancini G, Carbonara AO and Heremans JF. . 1965 Immunochemistry 2: 235–254.
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC and Grigani F. . 1991 J. Immunol. Meth. 139: 271–279.
Nishimura M, Toki J, Sugiura K, Hashimoto F, Tomita T, Fujishima H, Hiramatsu Y, Nishioka N, Nagata N, Takahashi Y and Ikehara S. . 1994 J. Exp. Med. 179: 1053–1058.
Renauld J-C, van der Lugt N, Vink A, van Roon M, Godfraind C, Warnier G, Merz H, Feller A, Berns A and Van Snick J. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 1327–1332.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T. . 1989 Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sheehan DC and Hrapchak BB. . 1980 Theory and Practice of Histochemistry. Mosby: St. Louis, MO.
Shen-Ong GLC, Keath EJ, Piccoli SP and Cole MD. . 1982 Cell 31: 443–452.
Stark K, Vainio S, Vassileva G and McMahon AP. . 1994 Nature 372: 679–683.
Taketo M, Schroeder AC, Mobraaten LE, Gunning KB, Hanten G, Fox RR, Roderick TH, Stewart CL, Lilly F, Hansen CT and Overbeek PA. . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 2065–2069.
Taya Y, Mizusawa S and Nishimura S. . 1986 EMBO J. 5: 1215–1219.
van der Lugt NM, Domen J, Verhoeven E, Linders K, van der Gulden H, Allen J and Berns A. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 2536–2544.
van der Putten H, Terwindt E, Berns A and Jaenisch R. . 1979 Cell 18: 109–116.
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Krimpenfort P, Domen J, Saris C, Radaszkiewicz T and Berns A. . 1989 Cell 56: 673–682.
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Scheijen B, Wientjens E, van der Gulden H and Berns A. . 1991 Cell 65: 737–752.
Verbeek S, van Lohuizen M, van der Valk M, Domen J, Kraal G and Berns A. . 1991 Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 1176–1179.
Weening JJ, Beukers JJB, Grond J and Elema JD. . 1986 Kidney Int. 29: 789–798.
Yost C, Farr GH 3rd, Pierce SB, Ferkey DM, Chen MM and Kimelman D. . 1998 Cell 93: 1031–1041.
Zhang L, Eddy A, Teng YT, Fritzler M, Kluppel M, Melet F and Bernstein A. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 6961–6970.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Jan de Jong and Dr Ruud Smeenk (CLB, Amsterdam) for excellent analysis of the mouse sera. We wish to thank Dr KJM Assmann for quantitation of proteinuria, and Eric Noteboom for his help and advice on the FACS analysis. Thanks also to Hugh Brady and Gabriel Gil-Gomez for sharing both knowledge and reagents required for the apoptosis assays, and to Nikos Tripodis for statistical analysis. We also thank Dr Paul Krimpenfort for assistance in microinjection, Rein Regnerus for genotyping the mice, and the technical staff of the NKI animal facility for expert assistance in animal care, M-MuLV-infection of newborn mice, and collection of urine and blood samples: Fina van der Ahé, Nel Bosnie, Halfdan Raaso, Loes Rijswijk and Auke Zwerver. This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (J Jonkers).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonkers, J., Weening, J., van der Valk, M. et al. Overexpression of Frat1 in transgenic mice leads to glomerulosclerosis and nephrotic syndrome, and provides direct evidence for the involvement of Frat1 in lymphoma progression. Oncogene 18, 5982–5990 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202995
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202995
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The clinical significance of FRAT1 and ABCG2 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
FRAT1 expression and its correlation with pathologic grade, proliferation, and apoptosis in human astrocytomas
Medical Oncology (2011)
-
Overexpression of Frat1 correlates with malignant phenotype and advanced stage in human non-small cell lung cancer
Virchows Archiv (2011)
-
Frat oncoproteins act at the crossroad of canonical and noncanonical Wnt-signaling pathways
Oncogene (2010)
-
Tissue microarray analysis of human FRAT1 expression and its correlation with the subcellular localisation of β-catenin in ovarian tumours
British Journal of Cancer (2006)