Abstract
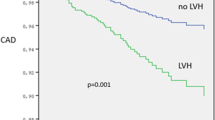
Plasma levels of von Willebrand factor (vWF), a marker of endothelial dysfunction/damage, are elevated in high-risk hypertensive patients and in patients with severe aortic regurgitation (AR). Patients with mild-to-moderate AR, frequently detected in hypertensive elderly, have additional left ventricular morphological and functional dysfunctions. We hypothesized that hypertensive patients with mild-to-moderate AR may have enhanced endothelial and/or left ventricular dysfunctions that may lead to a deteriorated prognosis. We measured vWF, prothrombin F1+2 (F1+2) as a marker of thrombin generation, brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in 104 hypertensive patients with mild-to-moderate AR and 66 hypertensive patients without AR. The left ventricular diameter at systole (LVDs) and left ventricular posterior wall thickness (LVWT) were determined by echocardiography and indexed by body surface area (LVDs/BSA and LVWT/BSA). VWF (median, interquartile range (IQR) 154, 120–196%) and BNP (34.7 pg ml−1, 15–65%) levels were greater in patients with AR than in those without AR (135, 98–175% and 20, 10.3–49 pg ml−1). All patients were prospectively followed up for cardiac events during the period of median 43 months (IQR 31–81). Patients with AR had an increased risk of cardiac events (regression ratio (RR) 1.87, 95% confidence interval 1.28–2.87) when compared to those without AR. A multivariate Cox hazard analysis indicated that log vWF (RR 4.93) and log BNP (RR 1.9) were independent predictors in patients with AR. VWF was an independent predictor of clinical outcome in hypertensive patients with mild-to-moderate AR.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lip GY, Foster W, Blann AD . Plasma von Willebrand factor levels and surrogates of atherosclerosis. J Thromb Haemost 2005; 3: 659–661.
Blann AD . Plasma von Willebrand factor, thrombosis, and the endothelium: the first 30 years. Thromb Haemost 2006; 95: 49–55.
Stam F, van Guldener C, Becker A, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Bouter LM et al. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to renal function-associated cardiovascular mortality in a population with mild renal insufficiency: the Hoorn study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 537–545.
Goldsmith IR, Blann AD, Patel RL, Lip GY . Effect of aortic valve replacement on plasma soluble P-selectin, von Willebrand factor, and fibrinogen. Am J Cardiol 2001; 87: 107–110, A9.
Chong AY, Freestone B, Patel J, Lim HS, Hughes E, Blann AD et al. Endothelial activation, dysfunction, and damage in congestive heart failure and the relation to brain natriuretic peptide and outcomes. Am J Cardiol 2006; 97: 671–675.
Chong AY, Blann AD, Patel J, Freestone B, Hughes E, Lip GY . Endothelial dysfunction and damage in congestive heart failure: relation of flow-mediated dilation to circulating endothelial cells, plasma indexes of endothelial damage, and brain natriuretic peptide. Circulation 2004; 110: 1794–1798.
Lebowitz NE, Bella JN, Roman MJ, Liu JE, Fishman DP, Paranicas M et al. Prevalence and correlates of aortic regurgitation in American Indians: the Strong Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000; 36: 461–467.
Lindroos M, Kupari M, Heikkila J, Tilvis R . Prevalence of aortic valve abnormalities in the elderly: an echocardiographic study of a random population sample. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 21: 1220–1225.
Kontos J, Papademetriou V, Wachtell K, Palmieri V, Liu JE, Gerdts E et al. Impact of valvular regurgitation on left ventricular geometry and function in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the LIFE study. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18: 431–436.
Sechi LA, Zingaro L, Catena C, Casaccio D, De Marchi S . Relationship of fibrinogen levels and hemostatic abnormalities with organ damage in hypertension. Hypertension 2000; 36: 978–985.
Sechi LA, Zingaro L, Catena C, De Marchi S . Increased fibrinogen levels and hemostatic abnormalities in patients with arteriolar nephrosclerosis: association with cardiovascular events. Thromb Haemost 2000; 84: 565–570.
Jafri SM, Mammen EF, Masura J, Goldstein S . Effects of warfarin on markers of hypercoagulability in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J 1997; 134: 27–36.
Otto CM . Aortic regurgitation.In: Otto CM (ed). Valvular Heart Disease, 2nd edn. Saunders: Philadelphia, 2004, pp 303–335.
Hillege HL, Girbes AR, de Kam PJ, Boomsma F, de Zeeuw D, Charlesworth A et al. Renal function, neurohormonal activation, and survival in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2000; 102: 203–210.
Zile MR, Brutsaert DL . New concepts in diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure: part II: causal mechanisms and treatment. Circulation 2002; 105: 1503–1508.
Lip GY, Pearce LA, Chin BS, Conway DS, Hart RG . Effects of congestive heart failure on plasma von Willebrand factor and soluble P-selectin concentrations in patients with non-valvar atrial fibrillation. Heart 2005; 91: 759–763.
Varughese GI, Patel JV, Tomson J, Lip GY . Effects of blood pressure on the prothrombotic risk in 1235 patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Heart 2007; 93: 495–499.
Stewart BF, Siscovick D, Lind BK, Gardin JM, Gottdiener JS, Smith VE et al. Clinical factors associated with calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 29: 630–634.
Agmon Y, Khandheria BK, Meissner I, Sicks JR, O'Fallon WM, Wiebers DO et al. Aortic valve sclerosis and aortic atherosclerosis: different manifestations of the same disease? Insights from a population-based study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38: 827–834.
Gerber IL, Stewart RA, French JK, Legget ME, Greaves SC, West TM et al. Associations between plasma natriuretic peptide levels, symptoms, and left ventricular function in patients with chronic aortic regurgitation. Am J Cardiol 2003; 92: 755–758.
Varughese GI, Patel JV, Tomson J, Blann AD, Hughes EA, Lip GY . Prognostic value of plasma soluble P-selectin and von Willebrand factor as indices of platelet activation and endothelial damage/dysfunction in high-risk patients with hypertension: a sub-study of the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial. J Intern Med 2007; 261: 384–391.
Biasucci LM, Liuzzo G, Caligiuri G, Quaranta G, Andreotti F, Sperti G et al. Temporal relation between ischemic episodes and activation of the coagulation system in unstable angina. Circulation 1996; 93: 2121–2127.
Agewall S, Wikstrand J . Prothrombin fragment 1+2 is a risk factor for myocardial infarction in treated hypertensive men. J Hypertens 1998; 16: 1557–1559.
Lowe GD, Rumley A, Sweetnam PM, Yarnell JW, Rumley J . Fibrin D-dimer, markers of coagulation activation and the risk of major ischaemic heart disease in the Caerphilly Study. Thromb Haemost 2001; 86: 822–827.
Palmieri V, Bella JN, Arnett DK, Roman MJ, Oberman A, Kitzman DW et al. Aortic root dilatation at sinuses of valsalva and aortic regurgitation in hypertensive and normotensive subjects: the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network Study. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1229–1235.
Bekeredjian R, Grayburn PA . Valvular heart disease: aortic regurgitation. Circulation 2005; 112: 125–134.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr Christopher Wood for checking our writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iida, M., Nihei, M., Yamazaki, M. et al. Predictive value of von Willebrand factor for adverse clinical outcome in hypertensive patients with mild-to-moderate aortic regurgitation. J Hum Hypertens 22, 275–281 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002321
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002321
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Endothelium, Arterial Stiffness, and von Willebrand Factor Levels in Hypertensive Women: Effects of Ethnicity
American Journal of Hypertension (2008)