Abstract
Objective:
To investigate whether adiponectin receptor genes (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) expression in human subcutaneous (SAT) and visceral (VAT) adipose tissue in severely obese patients with or without diabetes is related to adiponectin gene (APM1) expression and in vivo metabolic parameters.
Design:
Cross-sectional, clinical research study.
Subjects:
Total RNA was extracted from SAT and VAT tissue obtained during surgery from 13 lean controls, 30 obese diabetic patients, 19 obese glucose-intolerant patients and 54 obese subjects with normal glucose tolerance.
Measurements:
Tissue expression of APM1, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, tissue concentration of adiponectin (ApN), and metabolic variables.
Results:
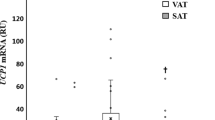
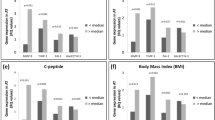
APM1 expression was higher in SAT than VAT (1.06±0.76 vs 0.69±0.52, P<0.0001) as was AdipoR1 (1.17±0.70 vs 0.66±0.38, P<0.0001) and AdipoR2 (7.02±6.19 vs 0.75±0.64, P<0.0001). In SAT, APM1 and AdipoR1 expression tended to be lower – by 0.38±0.22 and 0.35±0.22, respectively – and AdipoR2 expression was markedly depressed – by 4.82±1.93 – in association with obesity, whereas presence of diabetes had no additional effect. In VAT, APM1 and AdipoR1 expressions were also reduced – by 0.36±0.16 and 0.30±0.11, respectively – in association with obesity. Within both SAT and VAT, expression levels of APM1, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 were all positively interrelated. Tissue ApN concentrations in SAT were similar across groups, whereas ApN levels in VAT were substantially lower in association with obesity (by an average of 63±12 ng/mg total protein, P<0.0001). In multivariate models adjusting for sex, age and obesity, serum triglyceride concentrations were reciprocally related to APM1 (r=−0.27, P<0.02), AdipoR1 (r=−0.37, P<0.002 and AdipoR2 expression (r=−0.37, P<0.002) in VAT. Likewise, plasma insulin concentrations were inversely related only to APM1 in VAT (r=−0.25, P<0.03).
Conclusions:
Severe obesity is associated with suppressed expression of both ApN and its receptors in both SAT and VAT, the expression levels in VAT are specifically linked with hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kissebah AH . Intra-abdominal fat: is it a major factor in developing diabetes and coronary artery disease? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1996; 30 (Suppl): 25–30.
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G . Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001; 280: E745–E751.
Holst D, Grimaldi PA . New factors in the regulation of adipose differentiation and metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 2002; 13: 241–245.
Steppan CM, Lazar MA . Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002; 13: 18–23.
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Nakamura T . Molecular mechanism of metabolic syndrome X: contribution of adipocytokines adipocyte-derived bioactive substances. Ann N Y Acad Sci USA 1999; 18: 146–154.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19: 972–978.
Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM . AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 10697–10703.
Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K . cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript-1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 286–289.
Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF . A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 26746–26749.
Berg AH, Combs TP, Scherer PE . ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002; 13: 84–89.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 2001; 7: 941–946.
Combs TP, Berg AH, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L . Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1875–1881.
Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE . The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 2001; 7: 947–953.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000; 20: 1595–1599.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1930–1935.
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 257: 79–83.
Lindsay RS, Funahashi T, Hanson RL, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Tataranni PA et al. Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet 2002; 360: 57–58.
Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G . Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 2003; 52: 1779–1785.
Statnick MA, Beavers LS, Conner LJ, Corominola H, Johnson D, Hammond CD et al. Decreased expression of apM1 in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans with type 2 diabetes. Int J Exp Diabetes Res 2000; 1: 81–88.
Motoshima H, Wu X, Sinha MK, Hardy VE, Rosato EL, Barbot DJ et al. Differential regulation of adiponectin secretion from cultured human omental and subcutaneous adipocytes: effects of insulin and rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 5662–5667.
Lihn AS, Bruun JM, He G, Pedersen SB, Jensen PF, Richelsen B . Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2004; 219: 9–15.
Degawa-Yamauchi M, Moss KA, Bovenkerk JE, Shankar SS, Morrison CL, Lelliott CJ et al. Regulation of adiponectin expression in human adipocytes: effects of adiposity, glucocorticoids, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Obes Res 2005; 13: 662–669.
Yang WS, Chen MH, Lee WJ, Lee KC, Chao CL, Huang KC et al. Adiponectin mRNA levels in the abdominal adipose depots of nondiabetic women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 896–900.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003; 423: 762–769.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1288–1295.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Imai Y, Shimozawa N, Hioki K et al. Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 2461–2468.
Tomas E, Tsao TS, Saha AK, Murrey HE, Zhang Cc C, Itani SI et al. Enhanced muscle fat oxidation and glucose transport by ACRP30 globular domain: acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition and AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 16309–16313.
Fasshauer M, Klein J, Kralisch S, Klier M, Lossner U, Bluher M et al. Growth hormone is a positive regulator of adiponectin receptor 2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS 2004; 558: 27–32.
Rasmussen MS, Lihn AS, Pedersen SB, Bruun JM, Rasmussen M, Richelsen B . Adiponectin receptors in human adipose tissue: effects of obesity, weight loss, and fat depots. Obesity 2006; 14: 28–35.
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: S5–S20.
Nannipieri M, Manganiello M, Pezzatini A, De Bellis A, Seghieri G, Ferrannini E . Polymorphisms in the hANP (human atrial natriuretic peptide) gene, albuminuria, and hypertension. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1416–1422.
Grohmann M, Sabin M, Holly J, Shield J, Crowne E, Stewart C . Characterization of differentiated subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue from children: the influences of TNF-alpha and IGF-1. J Lipid Res 2005; 46: 93–103.
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ et al. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 459–469.
Lihn AS, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB, Haugaard SB, Rathje GS, Madsbad S et al. Increased expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 in HALS: implications for reduced adiponectin expression and plasma levels. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 285: E1072–E1080.
Chandran M, Phillips SA, Ciaraldi T, Henry RR . Adiponectin: more than just another fat cell hormone? Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 2442–2450.
Tan GD, Debard C, Funahashi T, Humphreys SM, Matsuzawa Y, Frayn KN et al. Changes in adiponectin receptor expression in muscle and adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic patients during rosiglitazone therapy. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 1585–1589.
Hoffstedt J, Arvidsson E, Sjolin E, Wahlén K, Arner P . Adipose tissue adiponectin production and adiponectin concentration in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1391–1396.
Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K et al. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 2001; 50: 2094–2099.
Fisher FM, McTernan PG, Valsamakis G, Chetty R, Harte AL, Anwar AJ et al. Differences in adiponectin protein expression: effect of fat depots and type 2 diabetic status. Horm Metab Res 2002; 34: 650–654.
Koistinen HA, Forsgren M, Wallberg-Henriksson H, Zierath JR . Insulin action on expression of novel adipose genes in healthy and type 2 diabetic subjects. Obes Res 2004; 12: 25–31.
Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Ito Y, Hada Y, Maki T, Takekawa S et al. Insulin/Foxo1 pathway regulates expression levels of adiponectin receptors and adiponectin sensitivity. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 30817–30822.
Civitarese AE, Jenkinson CP, Richardson D, Bajaj M, Cusi K, Kashyap S et al. Adiponectin receptors gene expression and insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic Mexican Americans with or without a family history of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 816–820.
Staiger H, Kaltenbach S, Staiger K, Stefan N, Fritsche A, Guirguis A et al. Expression of adiponectin receptor mRNA in human skeletal muscle cells is related to in vivo parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2004; 53: 2195–2201.
Debard C, Laville M, Berbe V, Loizon E, Guillet C, Morio-Liondore B et al. Expression of key genes of fatty acid oxidation, including adiponectin receptors, in skeletal muscle of Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 917–925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nannipieri, M., Bonotti, A., Anselmino, M. et al. Pattern of expression of adiponectin receptors in human adipose tissue depots and its relation to the metabolic state. Int J Obes 31, 1843–1848 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803676
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803676
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Diet, exercise or diet with exercise: comparing the effectiveness of treatment options for weight-loss and changes in fitness for adults (18–65 years old) who are overfat, or obese; systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2015)
-
Designer Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Stabilizes Metabolic Function and Prevents Brain Injury Caused by HIV Protease Inhibitors
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2014)
-
An overview of the contribution of fatness and fitness factors, and the role of exercise, in the formation of health status for individuals who are overweight
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2012)
-
Adiponectin levels and expression of adiponectin receptors in isolated monocytes from overweight patients with coronary artery disease
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2011)
-
Association of ADIPOR2 gene variants with cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes risk in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance: the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2011)