Abstract
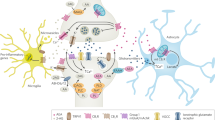
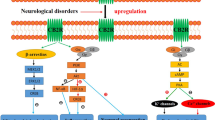
The CB1 cannabinoid receptor has attracted much recent interest because of the observation that CB1 receptor antagonists have efficacy in treating metabolic syndrome and obesity. CB1 receptors also mediate most of the psychotropic effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC), the principal psychoactive component of cannabis. In addition, they are one component of an interesting and widespread paracrine signaling system, the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system is comprised of cannabinoid receptors, endogenous cannabinoids, and the metabolic pathways responsible for their synthesis and degradation. The details of the endocannabinoid system have been most thoroughly studied in the brain. Here it has been shown to be intimately involved in several forms of neuronal plasticity. That is, activation of CB1 receptors by endocannabinoids produces either short- or long-term changes in the efficacy of synaptic transmission. The behavioral consequences of these changes are many, but some of the most striking and relevant to the current symposium are those associated with endogenous reward and consumptive behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2002; 54: 161–202.
Jarai Z, Wagner JA, Varga K, Lake KD, Compton DR, Martin BR et al. Cannabinoid-induced mesenteric vasodilation through an endothelial site distinct from CB1 or CB2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 14136–14141.
Breivogel CS, Griffin G, Di Marzo V, Martin BR . Evidence for a new G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor in mouse brain. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 60: 155–163.
Hajos N, Freund TF . Distinct cannabinoid sensitive receptors regulate hippocampal excitation and inhibition. Chem Phys Lipids 2002; 121: 73–82.
Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI . Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990; 346: 561–564.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC . Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci 1991; 11: 563–583.
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Sik A, Kafalvi A, Vizi ES, Mackie K et al. Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4544–4558.
Marsicano G, Lutz B . Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 1999; 11: 4213–4225.
Marsicano G, Goodenough S, Monory K, Hermann H, Eder M, Cannich A et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 2003; 302: 84–88.
Hoffman AF, Lupica CR . Mechanisms of cannabinoid inhibition of GABA(A) synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 2470–2479.
Hajos N, Katona I, Naiem SS, MacKie K, Ledent C, Mody I et al. Cannabinoids inhibit hippocampal GABAergic transmission and network oscillations. Eur J Neurosci 2000; 12: 3239–3249.
Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D . Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev 2003; 83: 1017–1066.
Walker JM, Krey JF, Chu CJ, Huang SM . Endocannabinoids and related fatty acid derivatives in pain modulation. Chem Phys Lipids 2002; 121: 159–172.
Gulyas AI, Cravatt BF, Bracey MH, Dinh TP, Piomelli D, Boscia F et al. Segregation of two endocannabinoid-hydrolyzing enzymes into pre- and postsynaptic compartments in the rat hippocampus, cerebellum and amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 2004; 20: 441–458.
Walker JM, Huang SM, Strangman NM, Tsou K, Sanudo-Pena MC . Pain modulation by release of the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 12198–12203.
Giuffrida A, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Navarro M, Piomelli D . Dopamine activation of endogenous cannabinoid signaling in dorsal striatum. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 358–363.
Luk T, Jin W, Zvonok A, Lu D, Lin XZ, Chavkin C et al. Identification of a potent and highly efficacious, yet slowly desensitizing CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 142: 495–500.
Huestis MA, Gorelick DA, Heishman SJ, Preston KL, Nelson RA, Moolchan ET et al. Blockade of effects of smoked marijuana by the CB1-selective cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 322–328.
Wilson RI, Kunos G, Nicoll RA . Presynaptic specificity of endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus. Neuron 2001; 31: 453–462.
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA . Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signalling at hippocampal synapses. Nature 2001; 410: 588–592.
Alger BE . Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol 2002; 68: 247–286.
Jo YH, Chen YJ, Chua Jr SC, Talmage DA, Role LW . Integration of endocannabinoid and leptin signalling in an appetite-related neural circuit. Neuron 2005; 48: 1055–1066.
Stella N . Cannabinoid signaling in glial cells. Glia 2004; 48: 267–277.
Bacci A, Huguenard JR, Prince DA . Long-lasting self-inhibition of neocortical interneurons mediated by endocannabinoids. Nature 2004; 431: 312–316.
Kreitzer AC, Carter AG, Regehr WG . Inhibition of interneuron firing extends the spread of endocannabinoid signaling in the cerebellum. Neuron 2002; 34: 787–796.
Gerdeman GL, Lovinger DM . Emerging roles for endocannabinoids in long-term synaptic plasticity. Br J Pharmacol 2003; 140: 781–789.
Lupica CR, Riegel AC, Hoffman AF . Marijuana and cannabinoid regulation of brain reward circuits. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 143: 227–234.
Sjostrom PJ, Turrigiano GG, Nelson SB . Neocortical LTD via coincident activation of presynaptic NMDA and cannabinoid receptors. Neuron 2003; 39: 641–654.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackie, K. Mechanisms of CB1 receptor signaling: endocannabinoid modulation of synaptic strength. Int J Obes 30 (Suppl 1), S19–S23 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803273
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803273
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A randomized, controlled trial of ZYN002 cannabidiol transdermal gel in children and adolescents with fragile X syndrome (CONNECT-FX)
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2022)
-
Cannabinoid receptors distribution in mouse cortical plasma membrane compartments
Molecular Brain (2021)
-
Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Compounds as Potential Strategies for Treating Parkinson’s Disease and l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia
Neurotoxicity Research (2020)
-
Cannabinoids for the treatment of rheumatic diseases — where do we stand?
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2018)
-
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System and Genetic Variation in Adolescent Brain Development
Neuropsychopharmacology (2018)