Abstract
Objective:
Human resistin has been stated to influence preadipocyte cell numbers and to stimulate adipocyte triglyceride lipolysis in vivo and in vitro. However, its role in human obesity remains unclear.
Design:
Cross-sectional study for comparisons of lean and obese subjects, and subsequent longitudinal 4-month weight loss intervention study in obese subjects.
Subjects:
Healthy subjects, lean (n=20, BMI<25) and overweight (n=43, BMI⩾25).
Measurements:
Serum resistin, body weight, body fat, waist-to-hip ratio, as well as markers of insulin resistance and lipid metabolism at baseline and after 4 months of intervention.
Results:
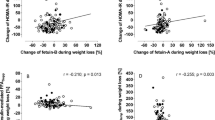
Serum resistin was positively correlated to HOMA-IR (partial r=0.288; P=0.055), serum fructosamines (partial r=0.280; P=0.062), serum NEFA (partial r=0.276; P=0.066) and negatively to age (partial r=−0.349; P=0.019) and serum apolipoprotein A-1 (partial r=−0.363; P=0.014). During the intervention, serum resistin increased significantly (P<0.001). The increase was inversely related to changes in waist-to-hip ratio (P=0.025) and positively to serum apolipoprotein B (P=0.011). In males only, the increase in resistin during weight loss was predicted by total serum cholesterol at baseline (r=0.703, P=0.007). No relation was observed between changes in resistin and changes in HOMA-IR.
Conclusion:
The present study indicates an association between serum resistin and markers of abdominal fat distribution as well as the regulation of lipid metabolism. However, human resistin is unlikely to play an independent role in the regulation of glucose metabolism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel L, Buckels AC, Kinghorn IJ, Murdock PR, Holbrook JD, Plumpton C et al. Resistin is expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPAR gamma activators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 300: 472–476.
Ort T, Arjona AA, Macdougall JR, Nelson PJ, Rothenberg ME, Wu F et al. Recombinant human FIZZ3/resistin stimulates lipolysis in cultured human adipocytes, mouse adipose explants and in normal mice. Endocrinology 2005; 146: 2200–2209.
Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Juliar BE, Watson W, Kerr K, Jones R et al. Serum resistin (FIZZ3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 5452–5455.
Silha JV, Krsek M, Skrha JV, Sucharda P, Nyomba BL, Murphy LJ . Plasma resistin, adiponectin and leptin levels in lean and obese subjects: correlations with insulin resistance. Eur J Endocrinol 2003; 149: 331–335.
Valsamakis G, McTernan PG, Chetty R, Al Daghri N, Field A, Hanif W et al. Modest weight loss and reduction in waist circumference after medical treatment are associated with favorable changes in serum adipocytokines. Metabolism 2004; 53: 430–434.
Heilbronn LK, Rood J, Janderova L, Albu JB, Kelley DE, Ravussin E et al. Relationship between serum resistin concentrations and insulin resistance in nonobese, obese, and obese diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1844–1848.
Lee JH, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Estrada E, Seip R et al. Circulating resistin levels are not associated with obesity or insulin resistance in humans and are not regulated by fasting or leptin administration: cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal, insulin-resistant, and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4848–4856.
Gerber M, Boettner A, Seidel B, Lammert A, Bar J, Schuster E et al. Serum resistin levels of obese and lean children and adolescents: biochemical analysis and clinical relevance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 4503–4509.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 409: 307–312.
Azuma K, Katsukawa F, Oguchi S, Murata M, Yamazaki H, Shimada A et al. Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obes Res 2003; 11: 997–1001.
Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Tong J, Wallace TM, Hull RL, Zraika S et al. Resistin is not associated with insulin sensitivity or the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 2330–2333.
Arner P . Resistin: yet another adipokine tells us that men are not mice. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 2203–2205.
Steppan CM, Lazar MA . Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2002; 13: 18–23.
Kusminski CM, McTernan PG, Kumar S . Role of resistin in obesity, insulin resistance and Type II diabetes. Clin Sci (London) 2005; 109: 243–256.
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U, Tarkowski A . Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol 2005; 174: 5789–5795.
Silswal N, Singh AK, Aruna B, Mukhopadhyay S, Ghosh S, Ehtesham NZ . Human resistin stimulates the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-12 in macrophages by NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 334: 1092–1101.
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A, Lazar MA, Rader DJ . Resistin is an inflammatory marker of atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation 2005; 111: 932–939.
Skilton MR, Nakhla S, Sieveking DP, Caterson ID, Celermajer DS . Pathophysiological levels of the obesity related peptides resistin and ghrelin increase adhesion molecule expression on human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2005; 32: 839–844.
Burnett MS, Lee CW, Kinnaird TD, Stabile E, Durrani S, Dullum MK et al. The potential role of resistin in atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2005; 182: 241–248.
Guldstrand M, Ahren B, Adamson U . Improved beta-cell function after standardized weight reduction in severely obese subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: E557–E565.
Steinberger J, Daniels SR . Obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in children: an American Heart Association scientific statement from the Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee (Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young) and the Diabetes Committee (Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism). Circulation 2003; 107: 1448–1453.
Rizkalla SW, Taghrid L, Laromiguiere M, Huet D, Boillot J, Rigoir A et al. Improved plasma glucose control, whole-body glucose utilization, and lipid profile on a low-glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetic men: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1866–1872.
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Masella M, Marfella R et al. Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003; 289: 1799–1804.
Fernandez ML, Metghalchi S, Vega-Lopez S, Conde-Knape K, Lohman TG, Cordero-MacIntyre ZR . Beneficial effects of weight loss on plasma apolipoproteins in postmenopausal women. J Nutr Biochem 2004; 15: 717–721.
Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumers and Veterinary Medicine. The German Food Code and Nutrient Data Base (BLS II.3): conception, structure and documentation of the data base blsdat. Berlin, Germany: BgVV Publications, 1999.
Koebnick C, Wagner K, Thielecke F, Dieter G, Höhne A, Franke A et al. An easy-to-use semiquantitative food record validated for energy intake by using doubly labelled water technique. Eur J Clin Nutr 2005; 59: 989–995.
Asensio C, Muzzin P, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F . Role of glucocorticoids in the physiopathology of excessive fat deposition and insulin resistance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: S45–S52.
Nogueiras R, Gualillo O, Caminos JE, Casanueva FF, Dieguez C . Regualtion of resistin by gonadal, thyroid hormone, and nutritional status. Obes Res 2003; 11: 408–414.
Gui Y, Silha JV, Murphy LJ . Sexual dimorphism and regulation of resistin, adiponectin, and leptin expression in the mouse. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1481–1491.
Yannakoulia M, Yiannakouris N, Bluher S, Matalas AL, Klimis-Zacas D, Mantzoros CS . Body fat mass and macronutrient intake in relation to circulating soluble leptin receptor, free leptin index, adiponectin, and resistin concentrations in healthy humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1730–1736.
Reinehr T, Roth CL, Menke T, Andler W . Resistin concentrations before and after weight loss in obese children. Int J Obes (London) 2006; in press [epub sept 2005].
Volarova de Courten B, Degawa-Yamauchi M, Considine RV, Tataranni PA . High serum resistin is associated with an increase in adiposity but not a worsening of insulin resistance in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1279–1284.
Vendrell J, Broch M, Vilarrasa N, Molina A, Gomez JM, Gutierrez C et al. Resistin, adiponectin, ghrelin, leptin, and proinflammatory cytokines: relationships in obesity. Obes Res 2004; 12: 962–971.
Wolfe BE, Jimerson DC, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS . Effect of dieting on plasma leptin, soluble leptin receptor, adiponectin and resistin levels in healthy volunteers. Clin Endocrinol (Oxford) 2004; 61: 332–338.
Nagaev I, Smith U . Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are not related to resistin expression in human fat cells or skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 285: 561–564.
Harsch IA, Koebnick C, Wallaschofski H, Schahin SP, Hahn EG, Ficker JH et al. Resistin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome – the link to subclinical inflammation? Med Sci Monit 2004; 10: CR510–CR515.
Juan CC, Au LC, Fang VS, Kang SF, Ko YH, Kuo SF et al. Suppressed gene expression of adipocyte resistin in an insulin-resistant rat model probably by elevated free fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 289: 1328–1333.
Walldius G, Jungner I, Holme I, Aastveit AH, Kolar W, Steiner E . High apolipoprotein B, low apolipoprotein A-I, and improvement in the prediction of fatal myocardial infarction (AMORIS study): a prospective study. Lancet 2001; 358: 2026–2033.
Shetty GK, Economides PA, Horton ES, Mantzoros CS, Veves A . Circulating adiponectin and resistin levels in relation to metabolic factors, inflammatory markers, and vascular reactivity in diabetic patients and subjects at risk for diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 2450–2457.
Sniderman AD, Furberg CD, Keech A, Roeters van Lennep JE, Frohlich J, Jungner I et al. Apolipoproteins versus lipids as indices of coronary risk and as targets for statin treatment. Lancet 2003; 361: 777–780.
Walldius G, Jungner I . Apolipoprotein B and apolipoprotein A-I: risk indicators of coronary heart disease and targets for lipid-modifying therapy. J Intern Med 2004; 255: 188–205.
Julius U . Influence of plasma free fatty acids on lipoprotein synthesis and diabetic dyslipidemia. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabet 2003; 111: 246–250.
Huang SW, Seow KM, Ho LT, Chien Y, Chung DY, Chang CL et al. Resistin mRNA levels are downregulated by estrogen in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 449–454.
Palanivel R, Sweeney G . Regulation of fatty acid uptake and metabolism in L6 skeletal muscle cells by resistin. FEBS Lett 2005; 579: 5049–5054.
Jung HS, Park KH, Cho YM, Chung SS, Cho HJ, Cho SY et al. Resistin is secreted from macrophages in atheromas and promotes atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 2006; in press [epub Nov 2005].
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with financial support from the Commission of the European Communities, BodyLife IST-2000-25410, specific RTD programme ‘User-friendly Information Society’. It does not necessarily reflect its views and in no way anticipates the Commission's future policy in this area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koebnick, C., Wagner, K., Garcia, A. et al. Increase in serum resistin during weight loss in overweight subjects is related to lipid metabolism. Int J Obes 30, 1097–1103 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803242
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803242
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The transtheoretical model is an effective weight management intervention: a randomized controlled trial
BMC Public Health (2020)
-
Acute and short-term effects of caloric restriction on metabolic profile and brain activation in obese, postmenopausal women
International Journal of Obesity (2016)
-
Serum resistin increases in a postprandial state during liquid meal challenge test in healthy human subjects
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2006)