Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To compare the effects of weight control on simple obese women between electroacupuncture and sit-up exercise.
DESIGN:
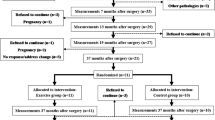
Randomized and crossover trial conducted from 1 January 2002 to 31 December 2002. The subjects were randomly divided into groups A and B. Group A received electroacupuncture treatment first while group B received sit-up exercise treatment first. After 6 weeks of treatment and 7 days of washout, group A switched to sit-up exercise treatment and group B received electroacupuncture treatment for another 6 weeks.
PATIENTS:
In total, 54 simple obese women, with waist circumference (WC)>90 cm and body mass index (BMI)>30 kg/m2, and who had not received any other weight control maneuver within the last 3 months.
MEASUREMENT:
The measurements of body weight (BW), BMI and WC were performed at the beginning, 6, 8 and 13 weeks. The data at different time periods were compared and expressed as % reductions.
RESULTS:
Electroacupuncture (n=46) showed significant differences in the % reductions in BW (P=0.001), BMI (P=0.003) and WC (P=0.005) compared with sit-up exercise. At the end of 13 weeks, there were no significant difference between groups A (n=24) and B (n=22) in all the measurements. At the end of the study, groups A and B showed significant differences in the % reductions in BW (P=0.004; 0.001), BMI (P=0.003; 0.021) and WC (P≤0.001; 0.001) compared with the initial values.
CONCLUSIONS:
Electroacupuncture treatment is more effective than sit-up exercise in reducing weight and WC, making it an alternative treatment option for weight and WC control on obese women.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Expert panel on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight in adults. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and obesity in adults: executive summary. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 899–917.
Sturm R . Increases in clinically severe obesity in the United States, 1986–2000. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163: 2146–2148.
Prescott-Clark P, Primatesta P . Health survey for England 1995. Department of Health HMSO: London; 1997.
Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Campbell SM, Johnson CL . Increasing prevalence of obesity of overweight among US adults: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1960 to 1961. JAMA 1994; 272: 205–211.
Lissau I, Overpeck MD, June Ruan W, Due P, Holstein BE, Mediger ML . Body mass index and overweight in adolescents in 13 European countries, Israel, and the United States. Arch Pediatr Med 2004; 158: 27–33.
Colditz GA, Willett WC, Rotnitzky A, Manson JE . Weight gain as a risk factor for clinical diabetes mellitus in women. Ann Intern Med 1995; 122: 481–486.
Must A, Spadano J, Cokley EH, Field AE, Colditz AE, Dietz WH . The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 1999; 282: 1523–1529.
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, Van Itallie TB . Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA 1999; 282: 1530–1538.
SIGN. Obesity Scotland: integrating prevention with weight management. A National Clinical Guideline recommended for use in Scotland by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Pilot edition, November, 1996.
Goldstein DJ . Beneficial health effects of modest weight loss. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1992; 6: 397–415.
Lacey JM, Tershakovec AM, Foster GD . Acupuncture for the treatment of obesity; a review of evidence. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 419–427.
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Heshka S, Mentore J, Heymsfield SB . Alternative treatments for weight loss: critical reviews in food science and nutrition. Boca Raton 2001; 41: 1–28.
Mulhisen L, Roger JZ . Complementary and alternative modes of therapy for the treatment of the obese patient. J Am Osteopath Assoc 1991; 99 (Part 2): S8–S12.
Huang MH, Yang RC, Hu SH . Preliminary results of triple therapy for obesity. Int J Obese Rel Metab Disord 1996; 20: 830–836.
Shiraishi T, Onoe M, Kageyama T, Sameshima Y, Kojima T, Konishi S, Yoshimatsu H, Sakata T . Effect of auricular acupuncture stimulation on nonobese, healthy volunteer subjects. Obes Res 1995; 3: 667–673.
Richards D, Marley J . Stimulation of auricular acupuncture points in weight loss. Aust Fam Phys 1998; 27: S73–S77.
Sun QXY . Simple obesity and obesity hyperlipidemia treated with otoacupoint pellet pressure and body acupuncture. J Tradit Chin Med 1993; 13: 22–26.
Zhan J . Observation on the treatment of 393 cases of obesity by seed pressure on auricular point. J Tradit Chin Med 1993; 13: 27–30.
Feinstein AR . Current problems and future challenges in randomized trial. Circulation 1984; 70: 767–774.
Streitberger K, Kleinhenz J . Introducing a placebo needle into acupuncture research. Lancet 1998; 352: 364–365.
Shiraishe T, Ono M, Kageyama T, Sawatsugawa S, Sakurai K, Yoshimatsu H, Sakata T . Effects of auricular stimulation on non-obese, healthy volunteers subjects. Obesity Res 1995; 3: 667–673.
Wozniak P, Stachowiak G, Pieta-Dolinska A, Oszukowski P . Laser acupuncture and low-calorie diet during visceral obesity therapy after menopause. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scandi 2003; 82: 69–73.
Shiraishi T, One M, Kojima T, Sameshima Y, Kageyama T . Effect of auricular stimulation on feeding related hypothalamic neuronal activity in normal and obese rats. Brain Res Bull 1995; 36: 141–148.
Chen XH, Han JS . Analgesia induced by electroacupuncture of different frequencies is mediated by different types of opioid receptors: another cross-tolerance study. Behav Brain Res 1992; 47: 143–149.
Cheng RS, Pomeranz B . Monaminergic mechanism of electroacupuncture analgesia. Brain Res 1981; 215: 77–92.
Christensen PA, Rotne M, Vedelsdal R, Jensen RH, Jacobsen K, Husted C . Electroacupuncture in anaesthesia for hysterectomy. Br J Anaesth 1993; 71: 835–838.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shier-Chieg Huang, Chien-Chung Chen, Yen-Yi Ho, Shu-Ling Hsie, Chi-Jung Wang and Ying-Li Liao for conducting this trial. We also thank all colleagues in Taipei Hospital, Taiwan for helping with this study. This study was supported by grants from the Taipei Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, CH., Hwang, KC., Chao, CL. et al. Effects of electroacupuncture in reducing weight and waist circumference in obese women: a randomized crossover trial. Int J Obes 29, 1379–1384 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802997
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802997
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The clinical evaluation of electroacupuncture combined with mindfulness meditation for overweight and obesity: study protocol for a randomized sham-controlled clinical trial
Trials (2022)
-
Effects of green tea extract on overweight and obese women with high levels of low density-lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C): a randomised, double-blind, and cross-over placebo-controlled clinical trial
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2018)
-
Acupuncture for obesity: a systematic review
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science (2016)
-
Effect of laser acupuncture on obesity: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2015)
-
Comparative effectiveness of electro-acupuncture plus lifestyle modification treatment for patients with simple obesity and overweight: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2015)