Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To determine whether altered central and/or peripheral gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic mechanisms acting in GABAA receptors contribute to the abnormal ventilatory response to acute and sustained hypoxia in obese Zucker rats.
METHODS:
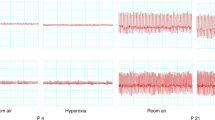
In all, 10 lean and 10 obese Zucker rats were studied at 12 weeks of age. Ventilation (V̇E), tidal volume (VT), and breathing frequency (f) during room air breathing and in response to sustained (30 min) hypoxic (10% O2) challenges were measured on three separate occasions by the barometric method following the randomized blinded administration of equal volumes of DMSO (vehicle), bicuculline methiodide (BM, 1 mg/kg, peripheral GABAA receptor antagonist), or bicuculline hydrochloride (BHCl, 1 mg/kg, peripheral and central GABAA receptor antagonist).
RESULTS:
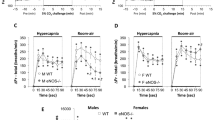
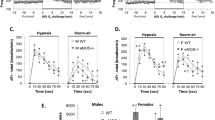
Administration of BM and BHCl in lean animals had no effect on ventilation either during room air breathing or 30 min of sustained exposure to hypoxia. Similarly, BM failed to alter ventilation in obese rats. In contrast, BHCl significantly (P<0.05) increased V̇E and VT during room air breathing and 10–30 min of hypoxic exposure in obese rats. During 5 min of acute hypoxic exposure, VT remained elevated with BHCl in obese rats, but the V̇E appeared not to be increased with BHCl due to a decrease in f.
CONCLUSION:
Thus, endogenous GABA modulates both ventilation during room air breathing and ventilatory response to sustained hypoxia in obese, not in lean, Zucker rats by acting specifically on GABAA receptors located within the central, not peripheral, nervous system. However, endogenous GABA does not modulate ventilation but the pattern of breathing during acute hypoxia in obesity in a different manner from that during sustained hypoxia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morgan EJ, Zwillich CW . The obesity–hypoventilation syndrome. West J Med 1978; 129: 387–393.
Zwillich CW, Sutton FD, Pierson DJ, Greagh EM, Weil JV . Decreased hypoxic ventilatory drive in the obesity–hypoventilation syndrome. Am J Med 1975; 59: 343–348.
Dempsey JA, Reddan W, Rankin J, Balke B . Alveolar–arterial gas exchange during muscular work in obesity. J Appl Physiol 1966; 21: 1807–1814.
Farkas GA, Schlenker EH . Pulmonary ventilation and mechanics in morbidly obese Zucker rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 150: 356–362.
Lee SD, Nakano H, Farkas GA . GABAergic modulation of ventilation and peak oxygen consumption in obese Zucker rats. J Appl Physiol 2001; 90: 1707–1713.
Lee SD, Nakano H, Farkas GA . NMDA receptor mediated modulation of hypoxic ventilatory response in obese Zucker rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 997–1004.
Lee SD, Nakano H, Gosselin LE, Krasney JA, Schlenker EH, Farkas GA . Endogenous opioids modulate ventilation and peak oxygen consumption in obese Zucker rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 1009–1015.
Lee SD, Magalang UJ, Krasney JA, Farkas GA . Opioidergic modulation of ventilatory response to sustained hypoxia in obese Zucker rats. Obes Res 2001; 9: 407–413.
Nakano K, Lee SD, Ray A, Krasney JA, Farkas GA . Role of nitric oxide in thermoregulation and hypoxic ventilatory response in obese Zucker rats. Am J Resp Crit Care 2001; 164: 437–442.
Nakano H, Lee SD, Farkas GA . Dopaminergic modulation of ventilation in obese Zucker rats. J Appl Physiol 2002; 92: 25–32.
Bloom FE, Iversen LL . Localizing 3H-GABA in nerve microscopic autoradiography. Nature (Lond) 1971; 229: 628–630.
Hedner J, Hedner T, Wessberg P, Jonason J . An analysis of the mechanisms by which ϒ-aminobutyric acid depresses ventilation in the rat. J Appl Physiol 1984; 56: 849–856.
Kazemi H, Hoop B . Glutamic acid and ϒ-aminobutyric acid neurotransmitters in central control of breathing. J Appl Physiol 1991; 70: 1–7.
Wood JD, Watson WJ, Ducker AJ . The effect of hypoxia on brain GABA levels. J Neurochem 1968; 15: 603–608.
Melton JE, Neubauer JA, Edelman NH . GABA antagonism reverses hypoxic respiratory depression in the cat. J Appl Physiol 1990; 69: 1296–1301.
Orosco M, Jacquot C, Wepierre J, Cohen Y . GABA levels and synthesis index in different brain areas of two obese rat models. Gen Pharmacol 1981; 12: 369–371.
Coscina DV, Castonguay TW, Stern JS . Effects of increasing brain GABA on the meal patterns of genetically obese vs lean Zucker rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1992; 16: 425–433.
Kaczynska K, Szereda-Przestaszewska M . Apnoeic response to stimulation of peripheral GABA receptors in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2002; 131: 189–197.
Gozal D, Gozal E, Simakajornboon N . Signaling pathways of the acute hypoxic ventilatory response in the nucleus tractus solitarius. Respir Physiol 2000; 121: 209–221.
Drorbaugh JE, Fenn WO . A barometric method for measuring ventilation in newborn infants. Pediatrics 1955; 16: 81–86.
Jacky JP . Barometric measurement of tidal volume: effects of pattern and nasal temperature. J Appl Physiol 1980; 49: 319–325.
Refinetti R . Computation of the body mass for metabolic studies of lean and obese rats. Metabolism 1989; 38: 763–766 (Erratum 1990;39:215).
Minano FJ, Serrano JS, Pascual J, Sancibrian M . Effects of GABA on gastric acid secretion and ulcer formation in rats. Life Sci 1987; 41: 1651–1658.
Chebib M, Johnston GA . The ‘ABC’ of GABA receptors: a brief review. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1999; 26: 937–940.
Hayashi F, Lipski J . The role of inhibitory amino acids in control of respiratory motor output in an arterially perfused rat. Respir Physiol 1992; 89: 47–63.
Holtman Jr JR, King KA . Regulation of respiratory motor outflow to the larynx and diaphragm by GABA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1988; 156: 181–187.
Kneussl MP, Pappagianopoulos P, Hoop B, Kazemi H . Reversible depression of ventilation and cardiovascular function by ventriculocisternal perfusion with gamma-aminobutyric acid in dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986; 133: 1024–1028.
Kneussl MP, Pappagianopoulos P, Hoop B, Kazemi H . Effect of centrally administered gamma-aminobutyric acid on metabolic function. J Appl Physiol 1986; 61: 472–476.
Rochester DF, Enson Y . Current concepts in the pathogenesis of the obesity-hypoventilation syndrome. Am J Physiol 1974; 57: 402–420.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Gaspar A Farkas for his help in construction of the ideas. The paper is supported by grant NSC 91-2314-B-040-025 from the National Science Council, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TB., Lo, MJ., Huang, CY. et al. GABAergic modulation of ventilatory response to acute and sustained hypoxia in obese Zucker rats. Int J Obes 29, 188–195 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802828
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802828