Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Blood flow regulation is thought to mediate the metabolic functions of adipose tissue. Different depots, and even different layers within the subcutaneous adipose tissue, may vary in metabolic activity and blood flow. Therefore, we investigated if any differences in subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow (ATBF) exist at different locations of the anterior abdominal wall.
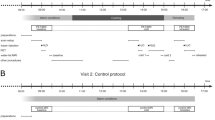
METHODS: ATBF was measured 8–10 cm above or below the umbilicus, at 8–10 cm (both sides) from the midline, in 18 healthy subjects (BMI range 18–33 kg/m2). Measurements of ATBF were performed using 133xenon washout, during a stable baseline period and after ingestion of 75 g of glucose.
RESULTS: At baseline, ATBF was greater at the upper level compared to the lower level (4.4±0.3 vs 3.8±0.2 ml min−1 100 g tissue−1, P=0.005), but was not different between the right and the left sides at either level. ATBF increased in response to oral glucose at all sites. The mean increase at the superior level was also greater than the inferior level (3.5±0.7 vs 2.2±0.6 ml min−1 100 g tissue−1, P=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS: Even at a constant depth and with only 16–20 cm difference between sites, there are significant differences in function of the same adipose depot. These findings have physiological and methodological implications for in vivo metabolic studies of human adipose tissue.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frayn KN, Karpe F, Fielding B, Macdonald I, Coppack S . The integrative physiology of human adipose tissue. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 875–888.
Jansson PA, Larsson A, Lönnroth PN . Relationship between blood pressure, metabolic variables and blood flow in obese subjects with or without non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest 1998; 28: 813–818.
Karpe F, Fielding BA, Ilic V, Macdonald IA, Summers LK, Frayn KN . Impaired postprandial adipose tissue blood flow response is related to aspects of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2467–2473.
Summers LK, Samra JS, Frayn KN . Impaired postprandial tissue regulation of blood flow in insulin resistance: a determinant of cardiovascular risk? Atherosclerosis 1999; 147: 11–15.
Virtanen KA, Peltoniemi P, Marjamäki P, Asola M, Strindberg L, Parkkola R, Huupponen R, Knuuti J, Lönnroth P, Nuutila P . Human adipose tissue glucose uptake determined using [(18)F]-fluoro-deoxy-glucose ([(18)F]FDG) and PET in combination with microdialysis. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 2171–2179.
Deschenes D, Couture P, Dupont P, Tchernof A . Subdivision of the subcutaneous adipose tissue compartment and lipid–lipoprotein levels in women. Obes Res 2003; 11: 469–476.
Enevoldsen LH, Simonsen L, Stallknecht B, Galbo H, Bulow J . In vivo human lipolytic activity in preperitoneal and subdivisions of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001; 281: E1110–E1114.
Kelley DE, Thaete FL, Troost F, Huwe T, Goodpaster BH . Subdivisions of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 278: E941–E948.
Virtanen KA, Lönnroth P, Parkkola R, Peltoniemi P, Asola M, Viljanen T, Tolvanen T, Knuuti J, Rönnemaa T, Huupponen R, Nuutila P . Glucose uptake and perfusion in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue during insulin stimulation in nonobese and obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 3902–3910.
Jensen MD . Adipose tissue and fatty acid metabolism in humans. J R Soc Med 2002; 95 (Suppl 42): 3–7.
Karpe F, Fielding BA, Ardilouze JL, Ilic V, Macdonald IA, Frayn KN . Effects of insulin on adipose tissue blood flow in man. J Physiol 2002; 540: 1087–1093.
Frid A, Linde B . Intraregional differences in the absorption of unmodified insulin from the abdominal wall. Diabet Med 1992; 9: 236–239.
Clauson PG, Linde B . Absorption of rapid-acting insulin in obese and nonobese NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1995; 18: 986–991.
Berger M, Cuppers HJ, Hegner H, Jorgens V, Berchtold P . Absorption kinetics and biologic effects of subcutaneously injected insulin preparations. Diabetes Care 1982; 5: 77–91.
Koivisto VA, Felig P . Alterations in insulin absorption and in blood glucose control associated with varying insulin injection sites in diabetic patients. Ann Intern Med 1980; 92: 59–61.
Vora JP, Burch A, Peters JR, Owens DR . Relationship between absorption of radiolabeled soluble insulin, subcutaneous blood flow, and anthropometry. Diabetes Care 1992; 15: 1484–1493.
Vora JP, Burch A, Peters JR, Owens DR . Absorption of radiolabelled soluble insulin in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: influence of subcutaneous blood flow and anthropometry. Diabet Med 1993; 10: 736–743.
Hildebrant P, Mehlsen J, Birch K, Kuhl C . Relationship between subcutaneous blood flow and absorption of lente type insulin. Diabetes Res 1987; 4: 179–181.
Kolendorf K, Bojsen J, Deckert T . Clinical factors influencing the absorption of 125I-NPH insulin in diabetic patients. Horm Metab Res 1983; 15: 274–278.
Linde B . Dissociation of insulin absorption and blood flow during massage of a subcutaneous injection site. Diabetes Care 1986; 9: 570–574.
Fernqvist E, Gunnarsson R, Linde B . Influence of circulating epinephrine on absorption of subcutaneously injected insulin. Diabetes 1988; 37: 694–701.
Fernqvist-Forbes E, Linde B . Insulin absorption, glucose homeostasis, and lipolysis in IDDM during mental stress. Diabetes Care 1991; 14: 1006–1012.
Frid A, Linde B . Clinically important differences in insulin absorption from abdomen in IDDM. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1993; 21: 137–141.
Samra JS, Frayn KN, Giddings JA, Clark ML, Macdonald IA . Modification and validation of a commercially available portable detector for measurement of adipose tissue blood flow. Clin Physiol 1995; 15: 241–248.
Karpe F, Fielding B, Ilic V, Humphreys S, Frayn K . Monitoring adipose tissue blood flow in man: a comparison between the 133xenon washout method and microdialysis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 1–5.
Clark ML, Humphreys SM, Frayn KN . Stability of plasma glucose during storage. Ann Clin Biochem 1990; 27 (Part 4): 373–377.
Bulow J . Measurement of adipose tissue blood flow. In: Ailhaud G (ed). Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ; 2000. pp 281–293.
Ardilouze JL, Fielding BA, Currie JM, Frayn KN, Karpe F . Nitric oxide and beta-adrenergic stimulation are major regulators of pre- and postprandial subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow in humans. Circulation, (in press).
Belfiore F, Iannello S, Volpicelli G . Insulin sensitivity indices calculated from basal and OGTT-induced insulin, glucose, and FFA levels. Mol Genet Metab 1998; 63: 134–141.
Summers LK, Samra JS, Humphreys SM, Morris RJ, Frayn KN . Subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue blood flow: variation within and between subjects and relationship to obesity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1996; 91: 679–683.
Kissebah AH, Krakower GR . Regional adiposity and morbidity. Physiol Rev 1994; 74: 761–811.
Pouliot MC, Despres JP, Nadeau A, Moorjani S, Prud' Homme D, Lupien PJ, Tremblay A, Bouchard C . Visceral obesity in men. Associations with glucose tolerance, plasma insulin, and lipoprotein levels. Diabetes 1992; 41: 826–834.
Ross R, Aru J, Freeman J, Hudson R, Janssen I . Abdominal adiposity and insulin resistance in obese men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2002; 282: E657–63.
Goossens G, Tan GD, Humphreys SM, Vidal H, Karpe F . Upper and lower body adipose tissue function: a direct comparison of fat mobilization (Abstract). Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27 (Suppl 1): 549.
Bulow J, Jelnes R, Astrup A, Madsen J, Vilmann P . Tissue/blood partition coefficients for xenon in various adipose tissue depots in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1987; 47: 1–3.
Jansson PA, Lönnroth P . Comparison of two methods to assess the tissue/blood partition coefficient for xenon in subcutaneous adipose tissue in man. Clin Physiol 1995; 15: 47–55.
Romanski SA, Nelson RM, Jensen MD . Meal fatty acid uptake in human adipose tissue: technical and experimental design issues. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 279: E447–54.
Samra JS, Simpson EJ, Clark ML, Forster CD, Humphreys SM, Macdonald IA, Frayn KN . Effects of epinephrine infusion on adipose tissue: interactions between blood flow and lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: E834–9.
Summers LK, Fielding BA, Ilic V, Quinlan PT, Frayn KN . The effect of triacylglycerol–fatty acid positional distribution on postprandial metabolism in subcutaneous adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 1998; 79: 141–147.
Markman B, Barton Jr FE . Anatomy of the subcutaneous tissue of the trunk and lower extremity. Plast Reconstr Surg 1987; 80: 248–254.
Johnson D, Cormack GC, Abrahams PH, Dixon AK . Computed tomographic observations on subcutaneous fat: implications for liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1996; 97: 387–396.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Wellcome Trust for financial support
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ardilouze, JL., Karpe, F., Currie, J. et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow varies between superior and inferior levels of the anterior abdominal wall. Int J Obes 28, 228–233 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802541
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802541
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Subcutaneous injection sites impact brain uptake of blood-brain barrier impermeable paclitaxel
Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation (2023)
-
Pharmacodynamics of Insulin Preparations Administered in Different Subcutaneous Injection Sites: Are There Differences Between Healthy Subjects Versus Diabetic Patients?
Clinical Drug Investigation (2017)
-
Patients on subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy are at risk of intramuscular injections
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2014)