Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Obesity in rodents and humans is mostly associated with elevated plasma leptin concentrations, suggesting a new pathological concept of ‘leptin resistance’. We have demonstrated that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) can improve obesity and diabetes of C57BL/KsJ db/db (db/db) mice. In this study, we investigated whether or not BDNF is effective in two different models of leptin resistance, an acquired model and a genetic model.
DESIGN: C57BL/6J mice rendered obese by consumption of a high-fat diet (diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice) were used as an acquired model and lethal yellow agouti mice (KKAy mice) as a genetic model of leptin resistance. Food intake and glucose metabolism were studied after acute or repetitive administration of BDNF.
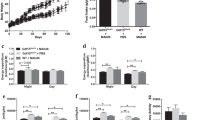
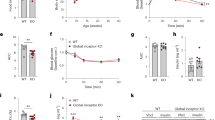
RESULTS:Intraperitoneal administration of BDNF (10 mg/kg, twice/day) significantly reduced cumulative food intake of DIO and KKAy mice, whereas they were unresponsive to leptin administration. Repetitive subcutaneous administration of BDNF (10 mg/kg daily for 6 days) reduced food intake and improved impaired glucose tolerance in DIO mice. Pair feeding of vehicle-treated DIO mice with the same amount of chow consumed by the BDNF-treated group did not improve the impaired glucose homeostasis, indicating that the antidiabetic effect is not due to decreased food intake. We also observed that BDNF is effective in improving obesity and diabetes of KKAy mice.
CONCLUSION:This study demonstrated antiobesity and antidiabetic effects of BDNF in two different models of leptin resistance, thereby suggesting the therapeutic potential of BDNF in the treatment of leptin-resistant obesity and diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiegelman BM, Flier JS . Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001; 104: 531–543.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994; 372: 425–432.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F . Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 1995; 269: 540–543.
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM . Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995; 269: 543–546.
Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Rau H, Wareham NJ, Sewter CP, Digby JE, Mohammed SN, Hurst JA, Cheetham CH, Earley AR, Barnett AH, Prins JB, O'Rahilly S . Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early onset obesity in humans. Nature 1997; 387: 903–908.
Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD . A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nat Genet 1998; 18: 213–215.
Farooqi IS, Jebb SA, Langmack G, Lawrence E, Cheetham CH, Prentice AM, Hughes IA, McCamish MA, O'Rahilly S . Effects of recombinant leptin therapy in a child with congenital leptin deficiency. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 879–884.
Considine RV, Considine EL, Williams CJ, Nyce MR, Magosin SA, Bauer TL, Rosato EL, Colberg J, Caro JF . Evidence against either a premature stop codon or the absence of obese gene mRNA in human obesity. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 2986–2988.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF . Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 292–295.
Heymsfield SB, Greenberg AS, Fujioka K, Dixon RM, Kushner R, Hunt T, Lubina JA, Patane J, Self B, Hunt P, McCamish M . Recombinant leptin for weight loss in obese and lean adults: a randomized, controlled, dose-escalation trial. JAMA 1999; 282: 1568–1575.
Hukshorn CJ, Saris WH, Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Farid AR, Smith FJ, Campfield LA . Weekly subcutaneous pegylated recombinant native human leptin (PEG-OB) administration in obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 4003–4009.
Lewin GR, Barde YA . Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu Rev Neurosci 1996; 19: 289–317.
Ono M, Ichihara J, Nonomura T, Itakura Y, Taiji M, Nakayama C, Noguchi H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces blood glucose level in obese diabetic mice but not in normal mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 238: 633–637.
Tonra JR, Ono M, Liu X, Garcia K, Jackson C, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ, Wong V . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor improves blood glucose control and alleviates fasting hyperglycemia in C57BLKS-leprdb/leprdb mice. Diabetes 1999; 48: 588–594.
Ono M, Itakura Y, Nonomura T, Nakagawa T, Nakayama C, Taiji M, Noguchi H . Intermittent administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor ameliorates glucose metabolism in obese diabetic mice. Metabolism 2000; 49: 129–133.
Nakagawa T, Tsuchida A, Itakura Y, Nonomura T, Ono M, Hirota F, Inoue T, Nakayama C, Taiji M, Noguchi H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates glucose metabolism by modulating energy balance in diabetic mice. Diabetes 2000; 49: 436–444.
Tsuchida A, Nonomura T, Ono-Kishino M, Nakagawa T, Taiji M, Noguchi H . Acute effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on energy expenditure in obese diabetic mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 1286–1293.
Barbacid M . The trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol 1994; 25: 1386–1403.
Lyons WE, Mamounas LA, Ricaurte GA, Coppola V, Reid SW, Bora SH, Cornelia W, Koliatsos VE, Tessarollo L . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-deficient mice develop aggressiveness and hyperphagia in conjunction with brain serotonergic abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 15239–15244.
Kernie SG, Liebl D, Parada L . BDNF regulates eating behavior and locomotor activity in mice. EMBO J 2000; 19: 1290–1300.
Chagnon YC, Bouchard C . Genetics of obesity: advances from rodent studies. Trends Genet 1996; 12: 441–444.
Surwit RS, Kuhn CM, Cochrane C, McCubbin JA, Feingros MN . Diet-induced type 2 diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 1998; 37: 1163–1167.
Van Heek M, Compton DS, France CF, Tedesco RP, Fawzi AB, Graziano MP, Sybertz EJ, Strader CD, Davis Jr HR . Diet-induced obese mice develop peripheral, but not central, resistance to leptin. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 385–390.
Widdowson PS, Upton R, Buckingham R, Arch J, Williams G . Inhibition of food response to intracerebroventricular injection of leptin is attenuated in rats with diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 1997; 46: 1782–1785.
Lin S, Thomas TC, Storlien LH, Huang XF . Development of high fat diet-induced obesity and leptin resistance in C57Bl/6J mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000; 24: 639–646.
Ogawa Y, Masuzaki H, Hosoda K, Aizawa-Abe M, Suga J, Suda M, Ebihara K, Iwais H, Matsuoka N, Satoh N, Odaka H, Kasuga H, Fujisawa Y, Inoue G, Nishimura H, Yoshimasa Y, Nakao K . Increased glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in transgenic skinny mice overexpressing leptin. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1822–1829.
Lu D, Willard D, Patel IR, Kadwell S, Overton L, Kost T, Luther M, Chen W, Woychik RP, Wilkison WO . Agouti protein is an antagonist of the melanocyte-stimulating-hormone receptor. Nature 1994; 371: 799–802.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Aizawa-Abe M, Hosoda K, Suga J, Ebihara K, Satoh N, Iwai H, Inoue G, Nishimura H, Yoshimasa Y, Nakao K . Glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in transgenic mice overexpressing leptin with lethal yellow agouti mutation: usefulness of leptin for the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1615–1622.
Satoh N, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, Numata Y, Masuzaki H, Yoshimasa Y, Nakao K . Satiety effect and sympathetic activation of leptin are mediated by hypothalamic melanocortin system. Neurosci Lett 1998; 249: 107–110.
El-Haschimi K, Pierroz DD, Hileman SM, Bjørbæk C, Flier JS . Two defects contribute to hypothalamic leptin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 1827–1832.
Baumann H, Morella KK, White DW, Dembski M, Bailon PS, Kim H, Lai CF, Tartaglia LA . The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 8374–8378.
Bjørbæk C, Uotani S, da Silva B, Flier JS . Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 32686–32695.
Kim YB, Uotani S, Pierroz DD, Flier JS, Kahn BB . In vivo administration of leptin activates signal transduction directly in insulin-sensitive tissues: overlapping but distinct pathways from insulin. Endocrinology 2000; 141: 2328–2339.
Marsh HN, Scholz WK, Lamballe F, Klein R, Nanduri V, Barbacid M, Palfrey HC . Signal transduction events mediated by the BDNF receptor gp145 TrkB in primary hippocampal pyramidal cell culture. J Neurosci 1993; 13: 4281–4292.
Nakamura T, Sanokawa R, Sasaki Y, Ayusawa D, Oishi M, Mori N . N-Shc: a neural-specific adapter molecule that mediates signaling from neurotrophin/Trk to Ras/MAPK pathway. Oncogene 1996; 13: 1111–1121.
Yamada M, Ohnishi H, Sano S, Nakatani A, Ikeuchi T, Hatanaka H . Insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 are tyrosine-phosphorylated and associated with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 30334–30339.
Seeley RJ, Yagaloff KA, Fisher SL, Burn P, Thiele TE, van Dijk G, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW . Melanocortin receptors in leptin effects. Nature 1997; 390: 349.
Gloaguen I, Costa P, Demartis A, Lazzaro D, Marco AD, Graziani R, Paonessa G, Chen F, Rosenblum CI, Van der Ploeg LHT, Cortese R, Ciliberto G, Laufer R . Ciliary neurotrophic factor corrects obesity and diabetes associated with leptin deficiency and resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 6456–6461.
Lambert PD, Anderson KD, Sleeman MW, Wong V, Tan J, Hijarunguru A, Corcoran TL, Murray JD, Thabet KE, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ . Ciliary neurotrophic factor activates leptin-like pathways and reduces body fat, without cachexia or rebound weight gain, even in leptin-resistant obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 4652–4657.
Henderson JT, Seniuk NA, Richardson PM, Gauldie J, Roder JC . Systemic administration of ciliary neurotrophic factor induces cachexia in rodents. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 2632–2638.
Kishimoto T, Akira S, Narazaki M, Taga T . Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood 1995; 86: 1243–1254.
Ip NY, Yancopoulos GD . The neurotrophins and CNTF: two families of collaborative neurotrophic factors. Annu Rev Neurosci 1996; 19: 491–515.
Gearing DP, Thut CJ, VandeBos T, Gimpel SD, Delaney PB, King J, Price V, Cosman D, Beckmann MP . Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J 1991; 10: 2839–2848.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Hidaka and M Shintani for valuable discussions. This work is supported in part by research grants from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, and the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, T., Ogawa, Y., Ebihara, K. et al. Antiobesity and antidiabetic effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent models of leptin resistance. Int J Obes 27, 557–565 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802265
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802265
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The PI3K/Akt Cascade Is Involved in the Antidiabetic Effect of Compound GSB-214, a Low-Molecular-Weight BDNF Mimetic
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2020)
-
Deficit of Neurotrophins in Experimental Diabetes – Correction with a Proline-Containing Dipeptide
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2019)
-
Ethylacetate extracts of the muscles of Anguilla japonica suppress glucose levels in db/db mice via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase
Food Science and Biotechnology (2014)
-
Molecular therapy of obesity and diabetes by a physiological autoregulatory approach
Nature Medicine (2009)
-
Evaluation of the effect of caloric restriction on serum BDNF in overweight and obese subjects: preliminary evidences
Endocrine (2008)