Abstract
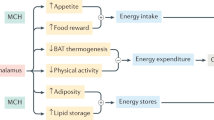
AIM: Although melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) is believed to be an important regulator of feeding behavior, both its acute and chronic effects on food intake as well as its interaction with other brain peptides involved in the control of appetite remain unclear. Therefore, the acute effects of MCH on food intake and the chronic effect of MCH on food intake and the gene expression of various hypothalamic peptides involved in the control of appetite were studied in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS: Either the acute or the continuous intraventricular infusion of MCH for 12 days stimulated feeding in both Wistar or Sprague–Dawley rats. Removal of the hypothalamus at the end of the chronic infusion studies allowed measurement of the expression of mRNAs encoding for MCH, neuropeptide Y (NPY), orexin, agouti gene-related peptide, cocaine and amphetamine-related transcript and neurotensin–neuropeptides involved in the control of appetite. Chronic intraventricular infusion of MCH activated only NPY mRNA synthesis in Sprague–Dawley rats. The increase in food intake in response to MCH in Sprague–Dawley rats did not appear to be due to the release of NPY since combination studies demonstrated consistently additive effects of the two peptides on food intake at maximum or near maximum doses.
CONCLUSIONS: These results strongly suggest that MCH is an orexigenic peptide involved in the control of both short- and long term food intake in satiated rats and further indicate that the MCH pathway is a possible target for the control of food intake and obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaughan JM, Fischer WH, Hoeger C, Rivier J, Vale W . Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone from rat hypothalamus Endocrinology 1989 125: 1660–1665.
Bittencourt JC, Presse F, Arias C, Peto C, Vaughan J, Nahon JL, Vale W, Sawchenko PE . The melanin-concentrating hormone system of the rat brain: an immuno- and hybridization histochemical characterization J Comp Neurol 1992 319: 218–245.
Tritos NA, Maratos-Flier E . Two important systems in energy homeostasis: melanocortins and melanin-concentrating hormone Neuropeptides 1999 33: 339–349.
Shimada M, Tritos NA, Lowell BB, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E . Mice lacking melanin concentrating hormone are hypophagic and lean Nature 1998 396: 670–674.
Elias CF, Saper CB, Maratos-Flier E, Tritos NA, Lee C, Kelly J, Tatro JB, Hoffman GE, Ollmann MM, Barsh GS, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Elmquist JK . Chemically defined projections linking the mediobasal hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area Comp Neurol 1998 402: 442–459.
Rossi M, Choi SJ, O'Shea D, Miyoshi T, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR . Melanin-concentrating hormone acutely stimulates feeding, but chronic administration has no effect on body weight Endocrinology 1997 138: 351–356.
Qu D, Ludwig DS, Gammeltoft S, Piper M, Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Mathes WF, Przypek R, Kanarek R, Maratos-Flier E . A role for melanin-concentrating hormone in the central regulation of feeding behaviour Nature 1996 380: 243–247.
Sahu A . Leptin decreases food intake induced by melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), galanin (GAL) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the rat Endocrinology 1998 139: 4739–4742.
Rossi M, Beak SA, Choi SJ, Small CJ, Morgan DG, Ghatei MA, Smith DM, Bloom SR . Investigation of the feeding effects of melanin concentrating hormone on food intake—action independent of galanin and the melanocortin receptors Brain Res 1999 846: 164–170.
Presse F, Sorokovsky I, Max JP, Nicolaidis S, Nahon JL . Melanin-concentrating hormone is a potent anorectic peptide regulated by food-deprivation and glucopenia in the rat Neuroscience 1996 71: 735–745.
Ludwig DS, Tritos NA, Mastaitis JW, Kulkarni R, Kokkotou E, Elmquist J, Lowell B, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E . Melanin-concentrating hormone overexpression in transgenic mice leads to obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 2001 107: 379–386.
Brunner L, Levens N . The regulatory role of leptin in food intake Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 1998 1: 565–571.
Broberger C . Hypothalamic cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) neurons: histochemical relationship to thyrotropin-releasing hormone, melanin-concentrating hormone, orexin/hypocretin and neuropeptide Y Brain Res 1999 848: 101–113.
Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB . From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food-intake and body weight Neuron 1999 22: 221–232.
Sergeyev V, Broberger C, Gorbatyuk O, Hokfelt T . Effect of 2-mercaptoacetate and 2-deoxy-D-glucose administration on the expression of NPY, AGRP, POMC, MCH and hypocretin/orexin in the rat hypothalamus Neuroreport 2000 11: 117–121.
Tritos NA, Vicent D, Gillette J, Ludwig DS, Flier ES, Maratos-Flier E . Functional interactions between melanin-concentrating hormone, neuropeptide Y, and anorectic neuropeptides in the rat hypothalamus Diabetes 1998 47: 1687–1692.
Yamada M, Miyakawa T, Duttaroy A, Yamanaka A, Moriguchi T, Makita R, Ogawa M, Chou CJ, Xia B, Crawley JN, Felder CC, Deng C-X, Wess J . Mice lacking the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor are hypophagic and lean Nature 2000 410: 207–212.
Glowinski J, Iversen LL . Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H] norepinephrine, [3H] dopamine and [3H] dopa in various regions of the brain J. Neurochem 1966 13: 655–669.
Presse F, Hervieu G, Imaki T, Sawchenko PE, Vale W, Nahon JL . Rat melanin-concentrating hormone messenger ribonucleic acid expression: marked changes during development and after stress and glucocorticoid stimuli Endocrinology 1992 131: 1241–1250.
Saito Y, Cheng M, Leslie FM, Civelli O . Expression of the melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) receptor mRNA in the rat brain J Comp Neurol 2001 435: 1–5.
Kuhn ER, Bellon K, Huybrechts L, Heyns W . Endocrine differences between the Wistar and Sprague–Dawley laboratory rat: influence of cold adaptation Horm Metab Res 1983 15: 491–498.
Chamorro S, Della-Zuana O, Fauchère J-L, Félétou M, Galizzi J-P, Levens N . Appetite suppression based on selective inhibition of NPY receptors Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002 26: 281–298.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank E Douillet, J Staczeck and O Tondu of the Division of Metabolic Diseases at the Servier Research Institute for their expertise in contributing to the food intake studies. This work was supported in part by grants from the Servier Research Institute, the Danone Institute and CNRS to F Presse, C Ortola and JL Nahon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Della-Zuana, O., Presse, F., Ortola, C. et al. Acute and chronic administration of melanin-concentrating hormone enhances food intake and body weight in Wistar and Sprague–Dawley rats. Int J Obes 26, 1289–1295 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802079
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Acts of appetite: neural circuits governing the appetitive, consummatory, and terminating phases of feeding
Nature Metabolism (2022)
-
Regulation of Brain Primary Cilia Length by MCH Signaling: Evidence from Pharmacological, Genetic, Optogenetic, and Chemogenic Manipulations
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Acupuncture Alleviates Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia via Melanin-Concentrating Hormone in Pitx3-Deficient aphakia and 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Mice
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
Molecular characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) in Schizothorax prenanti: cloning, tissue distribution and role in food intake regulation
Fish Physiology and Biochemistry (2016)
-
Influence of density and background color to stress response, appetite, growth, and blind-side hypermelanosis of flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus
Fish Physiology and Biochemistry (2013)