Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Leptin, the product of the obesity (ob) gene, is a multi-functional polypeptide that is important in energy metabolism, which is strongly correlated with body fat mass and body mass index (BMI). In a recent prospective study, we found that leptin was positively associated with 4 y weight gain among overweight and obese men. This suggests that leptin resistance, marked by hyperleptinemia among obese subjects, may be an important marker for weight gain. The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether modifiable dietary and lifestyle factors are associated with plasma leptin concentrations among US men.
METHODS: We included 268 men aged 47–83 y (who were free of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus and cancer, except nonmelanoma skin cancer) from the ongoing Health Professionals Follow-up Study. These subjects completed a detailed dietary and lifestyle questionnaire (including cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking and physical activity) and provided a fasting venous blood sample in 1994. All blood samples were stored in a deep freeze (−70°C) for 4–5 y before being analyzed. Plasma leptin concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay.
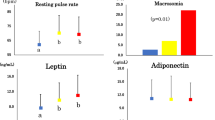
RESULTS: Men in the highest quintile of plasma leptin (mean=14.4 ng/ml) weighed more, were less physically active, and had higher total and saturated fat and cholesterol intake than men in the lowest quintile (mean=3.0 ng/ml). Physical activity and current smoking were inversely associated with plasma leptin concentrations (P<0.001). A 20 MET difference in physical activity per week (equivalent to approximately 3 h of jogging) was associated with 0.38–0.58 ng/ml lower plasma leptin concentrations for normal weight and overweight men after adjusting for total energy and fat intake, BMI and other confounding variables. Total fat and monounsaturated fat intakes were positively associated with plasma leptin concentrations even after adjusting for BMI and other confounding variables; however, this association was limited to men of normal weight (BMI<25 kg/m2).
CONCLUSION: These data suggest that physical activity may be a significant determinant of plasma leptin concentrations in men. Increasing physical activity is associated with lower plasma leptin concentrations even after adjusting for BMI. Physical activity may lower leptin concentrations not only due to decreased body fat mass, but potentially through an increase in leptin sensitivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue Nature 1994 372: 425–432.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB et al. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice Science 1995 269: 540–543.
Cusin I, Sainsbury A, Doyle P, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Jeanrenaud B . The ob gene and insulin. A relationship leading to clues to the understanding of obesity Diabetes 1995 44: 1467–1470.
Zimmet P, Hodge A, Nicolson M et al. Serum leptin concentration, obesity, and insulin resistance in Western Samoans: cross sectional study BMJ 1996 313: 965–969.
Caprio S, Tamborlane WV, Silver D et al. Hyperleptinemia: an early sign of juvenile obesity. Relations to body fat depots and insulin concentrations Am J Physiol 1996 271: E626–630.
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Burn P . The OB protein [leptin] pathway—a link between adipose tissue mass and central neural networks Horm Metab Res 1996 28: 619–632.
Bray GA, York DA . Clinical review 90: leptin and clinical medicine: a new piece in the puzzle of obesity J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 2771–2776.
Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Porte D Jr, Schwartz MW . Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis Science 1998 280: 1378–1383.
Auwerx J, Staels B . Leptin Lancet 1998 351: 737–742.
Hirschberg AL . Hormonal regulation of appetite and food intake Ann Med 1998 30: 7–20.
Flier JS . Clinical review 94: what's in a name? In search of leptin's physiologic role J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 1407–1413.
Friedman JM . Leptin, leptin receptors, and the control of body weight Nutr Rev 1998 56: s38–46.
Bray GA, York DA . The MONA LISA hypothesis in the time of leptin Recent Prog Horm Res 1998 53: 95–118.
Chu NF, Spiegelman D, Yu J, Rifai N, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB . Plasma leptin concentrations and 4-year weight gain among US men Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord (in press).
Racette SB, Kohrt WM, Landt M, Holloszy JO . Response of serum leptin concentrations to 7 d of energy restriction in centrally obese African Americans with impaired or diabetic glucose tolerance Am J Clin Nutr 1997 66: 33–37.
Wadden TA, Considine RV, Foster GD, Anderson DA, Sarwer DB, Caro JS . Short-and long-term changes in serum leptin dieting obese women: effects of calorie restriction and weight loss J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 214–218.
Kolaczynski JW, Considine RV, Ohannesian J et al. Responses of leptin to short-term fasting and refeeding in humans: a link with ketogenesis but not ketones themselves Diabetes 1996 45: 1511–1515.
Kolaczynski JW, Ohannesian JP, Considine RV, Marco CC, Caro JF . Response of leptin to short-term and prolonged overfeeding in humans J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 4162–4165.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Kawada T, Fushiki T, Nakao K . Augmented expression of the obese gene in the adipose tissue from rats fed high-fat diet Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995 216: 355–358.
Surwit RS, Petro AE, Parekh P, Collins S . Low plasma leptin in response to dietary fat in diabetes and obesity-prone mice Diabetes 1997 46: 1516–1520.
Ahren B, Mansson S, Gingerich RL, Havel PJ . Regulation of plasma leptin in mice: influence of age, high-fat diet, and fasting Am J Physiol 1997 273: R113–R120.
Dreon DM, Frey-Hewitt B, Ellsworth N, Williams PT, Terry RB, Wood PD . Dietary fat:carbohydrate ratio and obesity in middle-aged men Am J Clin Nutr 1988 47: 995–1000.
George V, Tremblay A, Despres JP, Leblanc C, Bouchard C . Effect of dietary fat content on total and regional adiposity in men and women Int J Obes 1990 14: 1085–1094.
Miller WC, Niederpruem MG, Wallace JP, Lindeman AK . Dietary fat, sugar, and fiber predict body fat content J Am Diet Assoc 1994 94: 612–615.
Willett WC . is dietary fat a major determinant of body fat? Am J Clin Nutr 1998 67: 556S–562S.
MacDougald OA, Hwang CS, Fan H, Lane MD . Regulated expression of the obese gene product (leptin) in white adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 9034–9037.
Saladin R, De Vos P, Guerre-Millo M et al. Transient increase in obese gene expression after food intake or insulin administration Nature 1995 377: 527–529.
Jenkins AB, Markovic TP, Fleury A, Campbell LV . Carbohydrate intake and short-term regulation of leptin in humans Diabetologia 1997 40: 348–351.
Havel PJ, Kasim-Karakas S, Mueller W, Johnson PR, Gingerich RL, Stern JS . Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma insulin and adiposity in normal weight and overweight women: effects of dietary fat content and sustained weight loss J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 4406–4413.
Schrauwen P, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Westerterp KR, Saris WH . Effect of diet composition on leptin concentration in lean subjects Metabolism 1997 46: 420–424.
Kohrt WM . Landt M, Birge SJ Jr. Serum leptin levels are reduced in response to exercise training, but not hormone replacement therapy, in older women J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 3980–3985.
Perusse L, Collier G, Gagnon J et al. Acute and chronic effects of exercise on leptin levels in humans J Appl Physiol 1997 83: 5–10.
van Aggel-Leijssen DPC, van Baak MA, Tenenbaum R, Campfield LA, Saris WHM . Regulation of average 24h human plasma leptin level; the influence of exercise and physiological changes in energy balance Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 151–159.
Pasman WJ, Westerterp-Plantenga MS . Saris WH. The effect of exercise training on leptin levels in obese males Am J Physiol 1998 274: E280–286.
Wei M, Stern MP, Haffner SM . Serum leptin levels in Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic whites: association with body mass index and cigarette smoking Ann Epidemiol 1997 7: 81–86.
Mantzoros CS, Liolios AD, Tritos NA et al. Circulating insulin concentrations, smoking, and alcohol intake are important independent predictors of leptin in young healthy men Obes Res 1998 6: 179–186.
Department of Agriculture . Composition of foods: raw, processed and prepared, 1966–1991, Agricultural Handbook no. 8-128-21 series Washington DC US Government Printing Office 1992.
Willett WC, Stampfer MJ . Total energy intake: Implications for epidemiological analysis Am J Epidemiol 1986 124: 17–27.
Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC . Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals Am J Epidemiol 1992 135: 1114–1126.
Chasan-Taber S, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ et al. Reproducibility and validity of a self-administered physical activity questionnaire for male health professionals Epidemiology 1996 7: 81–86.
Giovannucci E, Colditz G, Stampfer MJ et al. The assessment of alcohol consumption by a simple self-administered questionnaire Am J Epidemiol 1991 133: 810–817.
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Chute CG, Litin LB, Willett WC . Validity of self-reported waist and hip circumferences in men and women Epidemiology 1990 1: 466–473.
Ma Z, Gingerich RL, Santiago JV, Klein S, Smith CH, Landt M . Radioimmunoassay of leptin in human plasma Clin Chem 1996 42: 942–946.
Chu NF, Makowski L, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB . Stability of human plasma leptin concentrations with 36 hours following specimen collection Clin Biochem 1999 32: 87–89.
White H . A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity Econometrica 1980 48: 817–838.
Frederich RC, Hamann A, Anderson S, Lollmann B, Lowell BB, Flier JS . Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action Nature Med 1995 1: 1311–1314.
Christensen JO, Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Christiansen C . Leptin in overweight postmenopausal women: no relationship with metabolic syndrome X or effect of exercise in addition to diet Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 195–199.
Ostlund RE Jr, Yang JW, Klein S, Gingerich R . Relation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat, gender, diet, age, and metabolic covariates J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 3909–3913.
Weigle DS, Duell PB, Connor WE, Steiner RA, Soules MR, Kuijper JL . Effect of fasting, refeeding, and dietary fat restriction on plasma leptin levels J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 561–565.
Grace DM, Pederson L, Speechley KN, McAlpine D . A longitudinal study of smoking status and weight loss following gastroplasty in a group of morbidly obese patients Int J Obes 1990 14: 311–317.
Lissner L, Bengtsson C, Lapidus L, Bjorkelund C . Smoking initiation and cessation in relation to body fat distribution based on data from a study of Swedish women Am J Public Health 1992 82: 273–275.
Perkins KA . Metabolic effects of tobacco smoking J Appl Physiol 1992 72: 401–409.
Audrain JE, Klesges RC, DePue K, Klesges LM . The individual and combined effects of cigarette smoking and food on resting energy expenditure Int J Obes 1991 15: 813–821.
Tremblay A, Wouters E, Wenker M, St-Pierre S, Bouchard C, Despres JP . Alcohol and a high-fat diet: a combination favoring overfeeding Am J Clin Nutr 1995 62: 639–644.
Suter PM, Schutz Y, Jequier E . The effect of ethanol on fat storage in healthy subjects New Engl J Med 1992 326: 983–987.
Colditz GA, Giovannucci E, Rimm EB et al. Alcohol intake in relation to diet and obesity in women and men Am J Clin Nutr 1991 54: 47–48.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by research grants HL35464, CA55075 and AA11181. Dr Chu's work is supported by a Research Award from the National Defense Medical Center, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, N., Stampfer, M., Spiegelman, D. et al. Dietary and lifestyle factors in relation to plasma leptin concentrations among normal weight and overweight men. Int J Obes 25, 106–114 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801468
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801468
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A mixture of poly-γ-glutamic acid and levan ameliorates obesity in high fat diet-induced mice
Food Science and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Inter-relationship of serum leptin levels with selected anthropometric parameters among a non-diabetic population: a cross-sectional study
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2019)
-
Fatty acids derived from a food frequency questionnaire and measured in the erythrocyte membrane in relation to adiponectin and leptin concentrations
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2014)
-
BP regulation VI: elevated sympathetic outflow with human aging: hypertensive or homeostatic?
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2014)
-
Examining the relationship between diet-induced acidosis and cancer
Nutrition & Metabolism (2012)