Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effects of moderate-intensity regular exercise on serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and glucose and lipid metabolism parameters.
DESIGN: Longitudinal intervention study of a 5 month exercise training program (30–45 min/day, 4–5 days/week).
SUBJECTS: Forty-one healthy Japanese women aged 41–69 y at baseline; 27 participants in the exercise program.
MEASUREMENTS: Body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), percentage body fat, and fasting levels for serum TNF-α, serum soluble TNF receptor p55 (TNF-RI) and TNF receptor p75 (TNF-RII), serum lipids, HbA1c, and serum insulin before and after exercise.
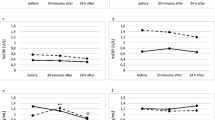
RESULTS: In overweight to obese subjects, serum levels of TNF-α, TNF-RI and TNF-RII were significantly higher than those in lean subjects. There were significant correlations between log serum TNF-α and BMI, percentage body fat, WHR, HbA1c and log insulin. TNF-RI was significantly correlated with BMI, percentage body fat, WHR and HbA1c. TNF-RII was also associated with BMI, percentage body fat and WHR. However, the correlation between TNF-RII and HbA1c did not reach statistical significance. Neither TNF-RI nor TNF-RII was correlated with log insulin. In contrast, TNF-α, TNF-RI and TNF-RII were negatively correlated with HDL cholesterol. Regular exercise decreased BMI, percentage body fat, HbA1c, serum TNF-α, TNF-RI and TNF-RII and increased HDL cholesterol levels. In addition, exercise-induced change in serum TNF-α was independently correlated with changes in HbA1c and serum insulin, after being adjusted for the change in fat-free mass.
CONCLUSION: Changes in serum TNF-α that occur with exercise may play an important role in improving glucose metabolism parameters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM . Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: direct roll in obesity-linked insulin resistance Science 1993 259: 87–91.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM . Tumor necrosis factor-α: a key component of the obesity–diabetes link Diabetes 1994 43: 1271–1278.
Kern PA, Saghizadeh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ, Deem R, Simsolo RB . The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue, regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2111–2119.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in human obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2409–2415.
Saghizadeh M, Ong JM, Garvey WT, Henry RR, Kern PA . The expression of TNFα by human muscle: relationship to insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1996 97: 1111–1116.
Katsuki A, Sumida Y, Murashima S, Murata K, Takarada Y, Ito K, Fujii M, Tsuchihashi K, Goto H, Nakatani K, Yano Y . Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α are increased in obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 859–862.
Schneider SH, Amorosa LF, Khachadurian AK, Ruderman NB . Studies on the mechanism of improved glucose control during regular exercise in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes Diabetologia 1984 26: 355–360.
Koivisto VA, Yki-Järvinen H, DeFronzo R . Physical training and insulin sensitivity Diabetes Metab Rev 1986 1: 445–481.
Oshida Y, Yamanouchi K, Hayamizu S, Sato Y . Long-term mild jogging increases insulin action despite no influence on body mass index or VO2max J Appl Physiol 1989 66: 2206–2210.
Huttunen JK, Länsimies E, Voutilainen E, Ehnholm C, Hietanen E, Penttilä I, Siitonen O, Rauramaa E . Effect of moderate physical exercise on serum lipoproteins: a controlled trial with special reference to serum high-density lipoproteins Circulation 1979 60: 1220–1229.
Winkler G, Lakatos P, Nagy Z, Speer G, Salamon F, Szekeres O, Kovács M, Cseh K . Elevated serum tumor necrosis factor-α and endothelin 1 levels correlate with increased c-peptide concentration in android type obesity Diabetes Care 1998 21: 1778–1779.
Zinman B, Hanley AJG, Harris SB, Kwan J, Fantus IG . Circulating turmor necrosis factor-α concentrations in a Native Canadian population with high rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999 84: 272–278.
Hollenbeck C, Reaven GM . Variations in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in healthy individuals with normal glucose tolerance J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1987 64: 1169–1173.
Fernández-Real J-M, Broch M, Ricart W, Casamitjana R, Gutierrez C, Vendrell J, Richart C . Plasma levels of the soluble fraction of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 and insulin resistance Diabetes 1998 47: 1757–1762.
James DE, Kraegen EW, Chisholm DJ . Effects of exercise training on in vivo insulin action in individual tissues of the rats J Clin Invest 1985 76: 657–666.
Mondon CE, Dolkas B, Reaven GM . Site of enhanced insulin sensitivity in exercise-trained rats at rest Am J Physiol 1987 239: E169–E177.
Bemelmans HMA, van Tis LJH, Buurman WA . Tumor necrosis factor: function, release and clearance Crit Rev Immunol 1996 16: 1–11.
Shroder J, Stuber F, Galatti H, Schade FU, Kremer B . Pattern of soluble TNF receptors I and II in sepsis Infection 1995 23: 143–148.
Gattorno M, Picco P, Buoncompagni A, Stalla F, Facchetti P, Sormani MP, Pistoia V . Serum p55 and p75 tumor necrosis factor receptors as markers of disease activity in juvenile chronic arthritis Ann Rheumat Dis 1996 55: 243–247.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Atkinson RIL, Spiegelman BM . Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance Diabetes 1997 46: 451–455.
Corica F, Allegra A, Corsonello A, Buemi M, Calapai G, Ruello A, Mauro AR, Ceruso D . Relationship between plasma leptin levels and the tumor necrosis factor- α system in obese subjects Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 355–360.
Fried SK, Zechner R . Cachectin and tumor necrosis factor decreases human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase mRNA levels, synthesis, and activity J Lipid Res 1989 30: 1917–1923.
Grunfeld C, Gulli R, Moser AH, Gavin LA, Feingold KR . Effects of tumor necrosis factor administration in vivo on lipoprotein lipase activity in various tissues of the rat J Lipid Res 1989 30: 579–585.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mr Y Fukumura for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukui, S., Kanda, T., Nara, M. et al. Moderate-intensity regular exercise decreases serum tumor necrosis factor-α and HbA1c levels in healthy women. Int J Obes 24, 1207–1211 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801373
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801373
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of exercise and hypoxia on glucose transport and regulation
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2023)
-
The Effect of Physical Activity Interventions on Glycosylated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) in Non-diabetic Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sports Medicine (2018)
-
Leisure-time, occupational, and commuting physical activity and risk of type 2 diabetes in Japanese workers: a cohort study
BMC Public Health (2015)
-
Inflammatory markers and bariatric surgery: a meta-analysis
Inflammation Research (2012)
-
Risk Factors for Barrett's Esophagus Among Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Community Clinic-Based Case–Control Study
The American Journal of Gastroenterology (2009)