Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access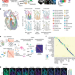 Spatially organized cellular communities form the developing human heart
Spatially organized cellular communities form the developing human heart
Combining single-cell RNA-sequencing with high-resolution multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization reveals in detail the cellular interactions and specialization of cardiac cell types that form and remodel the human heart.
- Elie N. Farah
- , Robert K. Hu
- & Neil C. Chi
-
Article
| Open Access A single-cell time-lapse of mouse prenatal development from gastrula to birth
A single-cell time-lapse of mouse prenatal development from gastrula to birth
Single-cell transcriptome profiling of mouse embryos and newborn pups is combined with previously published data to construct a tree of cell-type relationships tracing development from zygote to birth.
- Chengxiang Qiu
- , Beth K. Martin
- & Jay Shendure
-
Article
| Open Access A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
A human embryonic limb cell atlas resolved in space and time
Using single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, human embryonic limb development across space and time and the diversification and cross-species conservation of cells are demonstrated.
- Bao Zhang
- , Peng He
- & Sarah A. Teichmann
-
Article |
 A pan-grass transcriptome reveals patterns of cellular divergence in crops
A pan-grass transcriptome reveals patterns of cellular divergence in crops
Complementary single-cell and single-nucleus transcriptomic analyses of Zea mays, Sorghum bicolor and Setaria viridis root cells provide insights into the evolution of cell types and gene modules that control key traits in these important crop species.
- Bruno Guillotin
- , Ramin Rahni
- & Kenneth D. Birnbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Primate gastrulation and early organogenesis at single-cell resolution
Primate gastrulation and early organogenesis at single-cell resolution
In-depth transcriptomic analyses of 56,636 single cells from monkey embryos revealed transcriptional features of major perigastrulation cell types, and comparative analyses with mouse embryos and human embryoids uncovered conserved and divergent features of perigastrulation development across species.
- Jinglei Zhai
- , Jing Guo
- & Hongmei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Embryo model completes gastrulation to neurulation and organogenesis
Embryo model completes gastrulation to neurulation and organogenesis
Synthetic mouse embryos assembled from embryonic stem cells, trophoblast stem cells and induced extraembryonic endoderm stem cells closely recapitulate the development of wild-type and mutant natural mouse embryos up to embryonic day 8.5.
- Gianluca Amadei
- , Charlotte E. Handford
- & Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz
-
Article |
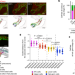 Tracing the origin of hair follicle stem cells
Tracing the origin of hair follicle stem cells
Live imaging and single-cell transcriptomics of mouse hair follicles reveal their development from 2D concentric zones in the placode to 3D longitudinal compartments, one of which is a stem cell compartment.
- Ritsuko Morita
- , Noriko Sanzen
- & Hironobu Fujiwara
-
Article |
 Lymphoangiocrine signals promote cardiac growth and repair
Lymphoangiocrine signals promote cardiac growth and repair
Lymphatic endothelium secretes factors needed for heart growth and repair such as RELN, which helps with heart regeneration and cardioprotection after myocardial infarction.
- Xiaolei Liu
- , Ester De la Cruz
- & Guillermo Oliver
-
Article |
 Capillary cell-type specialization in the alveolus
Capillary cell-type specialization in the alveolus
Single-cell analysis of blood vessels in the alveolus, the site of chronic disease and virus-induced lung injury, reveals two intermingled endothelial cell types with specialized gas exchange and stem cell functions.
- Astrid Gillich
- , Fan Zhang
- & Ross J. Metzger
-
Matters Arising |
 Zebrafish prrx1a mutants have normal hearts
Zebrafish prrx1a mutants have normal hearts
- Federico Tessadori
- , Dennis E. M. de Bakker
- & Jeroen Bakkers
-
Article |
 Homeostatic mini-intestines through scaffold-guided organoid morphogenesis
Homeostatic mini-intestines through scaffold-guided organoid morphogenesis
Miniature gut tubes grown in vitro from mouse intestinal stem cells are perfusable, can be colonized with microorganisms and exhibit a similar arrangement and diversity of specialized cell types to intestines in vivo.
- Mikhail Nikolaev
- , Olga Mitrofanova
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Article |
 Adaptable haemodynamic endothelial cells for organogenesis and tumorigenesis
Adaptable haemodynamic endothelial cells for organogenesis and tumorigenesis
The transient reactivation of ETV2 in adult human endothelial cells reprograms these cells to become adaptable vasculogenic endothelia that in three-dimensional matrices self-assemble into vascular networks that can transport blood and physiologically arborize organoids and decellularized tissues.
- Brisa Palikuqi
- , Duc-Huy T. Nguyen
- & Shahin Rafii
-
Article |
 Hair-bearing human skin generated entirely from pluripotent stem cells
Hair-bearing human skin generated entirely from pluripotent stem cells
Skin organoids generated in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells form complex, multilayered skin tissue with hair follicles, sebaceous glands and neural circuitry, and integrate with endogenous skin when grafted onto immunocompromised mice.
- Jiyoon Lee
- , Cyrus C. Rabbani
- & Karl R. Koehler
-
Article |
 Recapitulating the human segmentation clock with pluripotent stem cells
Recapitulating the human segmentation clock with pluripotent stem cells
A system involving in vitro induction of presomitic mesoderm recapitulates oscillatory expression of core segmentation clock genes and travelling-wave-like gene expression, suggesting that this system can be used to study the human segmentation clock and provide insights into diseases associated with human axial skeletogenesis.
- Mitsuhiro Matsuda
- , Yoshihiro Yamanaka
- & Cantas Alev
-
Article |
 RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signalling
RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signalling
RITF1, a newly identified plant transcription factor, links signalling through the peptide hormone RGF1 to the balance of reactive oxygen species and thereby enhances the stability of another transcription factor, PLETHORA2, a master regulator of root stem cells.
- Masashi Yamada
- , Xinwei Han
- & Philip N. Benfey
-
Letter |
 Modelling human hepato-biliary-pancreatic organogenesis from the foregut–midgut boundary
Modelling human hepato-biliary-pancreatic organogenesis from the foregut–midgut boundary
Juxtaposition of region-specific gut spheroids derived from human pluripotent stem cells in the absence of extrinsic factors results in development of segregated hepato-biliary-pancreatic anlages that recapitulate early morphogenetic events.
- Hiroyuki Koike
- , Kentaro Iwasawa
- & Takanori Takebe
-
Letter |
 Single-cell analysis of cardiogenesis reveals basis for organ-level developmental defects
Single-cell analysis of cardiogenesis reveals basis for organ-level developmental defects
Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis reveals functions of lineage-specifying transcription factors underlying congenital defects in heart development.
- T. Yvanka de Soysa
- , Sanjeev S. Ranade
- & Deepak Srivastava
-
Article |
 Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species
Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species
A transcriptome dataset from seven organs and seven mammalian species throughout development is used to analyse the expression of long noncoding RNAs in tissues within and between species, and at different stages of organ development.
- Ioannis Sarropoulos
- , Ray Marin
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
Article |
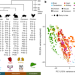 Gene expression across mammalian organ development
Gene expression across mammalian organ development
The transcriptomes of seven major organs across developmental stages from several mammalian species are used for comparative analyses of gene expression and evolution across organ development.
- Margarida Cardoso-Moreira
- , Jean Halbert
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
Letter |
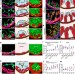 Control of cardiac jelly dynamics by NOTCH1 and NRG1 defines the building plan for trabeculation
Control of cardiac jelly dynamics by NOTCH1 and NRG1 defines the building plan for trabeculation
A new model of cardiac trabeculation in mice is presented in which NOTCH1 and NRG1 have opposing roles in extracellular matrix degradation and synthesis that are essential for defining trabecular architecture.
- Gonzalo del Monte-Nieto
- , Mirana Ramialison
- & Richard P. Harvey
-
Letter |
 Multilineage communication regulates human liver bud development from pluripotency
Multilineage communication regulates human liver bud development from pluripotency
Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of two- and three-dimensional hepatic differentiation reveals that both systems recapitulate certain transcriptomic features of human hepatogenesis.
- J. Gray Camp
- , Keisuke Sekine
- & Barbara Treutlein
-
Article |
 Wnt/β-catenin promotes gastric fundus specification in mice and humans
Wnt/β-catenin promotes gastric fundus specification in mice and humans
Wnt signalling is shown to be required for specification of the gastric fundus in mice, and was used to develop human gastric organoids with functional fundic cell types.
- Kyle W. McCracken
- , Eitaro Aihara
- & James M. Wells
-
Letter |
 Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture
Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture
The authors have designed modular synthetic hydrogel networks for mouse and human intestinal stem cell cultures that support intestinal organoid formation.
- Nikolce Gjorevski
- , Norman Sachs
- & Matthias P. Lutolf
-
Letter |
 FGF8 and SHH substitute for anterior–posterior tissue interactions to induce limb regeneration
FGF8 and SHH substitute for anterior–posterior tissue interactions to induce limb regeneration
The long-standing puzzle of why salamander limb regeneration requires anterior and posterior tissue interaction has been solved by the demonstration that fibroblast growth factor 8 and sonic hedgehog are key anterior and posterior cross-inductive signals that drive regeneration.
- Eugeniu Nacu
- , Elena Gromberg
- & Elly M. Tanaka
-
Letter |
 Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids
Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids
The in vitro generation, from pluripotent stem cells, of three-dimensional human gastric organoids (hGOs) that contain a physiological gastric epithelium comprising both progenitor and differentiated cell types, and have expected functional characteristics is described, as is modelling the pathophysiological response of the human stomach to Helicobacter pylori using these hGOs.
- Kyle W. McCracken
- , Emily M. Catá
- & James M. Wells
-
Letter |
 Luminal signalling links cell communication to tissue architecture during organogenesis
Luminal signalling links cell communication to tissue architecture during organogenesis
Groups of cells within a migrating collective assemble shared luminal cavities that trap and concentrate the signalling molecule fibroblast growth factor, providing a self-organising mechanism to focus and coordinate cell communication within tissues.
- Sevi Durdu
- , Murat Iskar
- & Darren Gilmour
-
Letter |
 DENR–MCT-1 promotes translation re-initiation downstream of uORFs to control tissue growth
DENR–MCT-1 promotes translation re-initiation downstream of uORFs to control tissue growth
This study identifies the DENR–MCT-1 complex as the first factors in animals specific for translation re-initiation downstream of upstream Open Reading Frames (uORFs).
- Sibylle Schleich
- , Katrin Strassburger
- & Aurelio A. Teleman
-
Letter |
 Generation of inner ear sensory epithelia from pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture
Generation of inner ear sensory epithelia from pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture
A new approach has been developed in order to achieve the stepwise differentiation of inner ear sensory epithelia from mouse embryonic stem cells in a three-dimensional culture: this process, which mimics normal development and produces cells that have functional characteristics of mechanosensitive hair cells, is hoped to provide further insights into inner ear development and disorder.
- Karl R. Koehler
- , Andrew M. Mikosz
- & Eri Hashino
-
Research Highlights |
 Salamanders heal like embryos grow
Salamanders heal like embryos grow
-
Research Highlights |
Blood vessel directs cells
-
Letter |
 Independent evolution of striated muscles in cnidarians and bilaterians
Independent evolution of striated muscles in cnidarians and bilaterians
This phylogenomic study shows that core muscle proteins were already present in unicellular organisms before the origin of multicellular animals, and supports a convergent evolutionary model for striated muscles in which new proteins are added to ancient contractile apparatus during independent evolution of bilaterians and some non-bilaterians, resulting in very similar ultrastructures.
- Patrick R. H. Steinmetz
- , Johanna E. M. Kraus
- & Ulrich Technau
-
News |
 Rudimentary liver grown in vitro
Rudimentary liver grown in vitro
Japanese scientists coax pluripotent cells to form functional liver tissue.
- David Cyranoski
-
News |
 Biologists grow human-eye precursor from stem cells
Biologists grow human-eye precursor from stem cells
Achievement raises hopes for optic repair in the clinic.
- David Cyranoski
-
News & Views |
 Heart under construction
Heart under construction
Developing organs adapt dynamically to meet the changing needs of a growing organism. A study in zebrafish reveals surprising patterns of muscle growth that reshape the heart as it matures. See Article p.479
- Deborah Yelon
-
Letter |
 Spalt mediates an evolutionarily conserved switch to fibrillar muscle fate in insects
Spalt mediates an evolutionarily conserved switch to fibrillar muscle fate in insects
- Cornelia Schönbauer
- , Jutta Distler
- & Frank Schnorrer
-
News & Views |
 Skin-cancer stem cells outwitted
Skin-cancer stem cells outwitted
Skin-cancer stem cells secrete a factor that organizes a blood-supply system to fuel tumour growth. But the same factor has another sinister function — it stimulates the stem cells to propagate uncontrollably. See Letter p.399
- Salvador Aznar Benitah
-
Article |
 Distinct stem cells contribute to mammary gland development and maintenance
Distinct stem cells contribute to mammary gland development and maintenance
- Alexandra Van Keymeulen
- , Ana Sofia Rocha
- & Cédric Blanpain
-
Letter |
 Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts
Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts
- Massimiliano Caiazzo
- , Maria Teresa Dell’Anno
- & Vania Broccoli
-
Letter |
 Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration
Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration
These authors describe a molecular pathway by which endothelial cells sustain liver regeneration after surgical resection. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor-A receptor-2 in a defined subpopulation of liver endothelial cells leads to the upregulation of the endothelial-specific transcription factor Id1, which in turn induces Wnt2 and hepatocyte growth factor, which are secreted from the endothelial cells and trigger hepatocyte proliferation.
- Bi-Sen Ding
- , Daniel J. Nolan
- & Shahin Rafii
-
News |
 A direct hit for thalidomide
A direct hit for thalidomide
The drug stunts limb development in zebrafish and chicks by binding to a protein called cereblon.
- Janet Fang

 The sex of organ geometry
The sex of organ geometry