Optimal conditions for the use of polyrotaxane as a cross-linker in preparing elastomers with high toughnesses
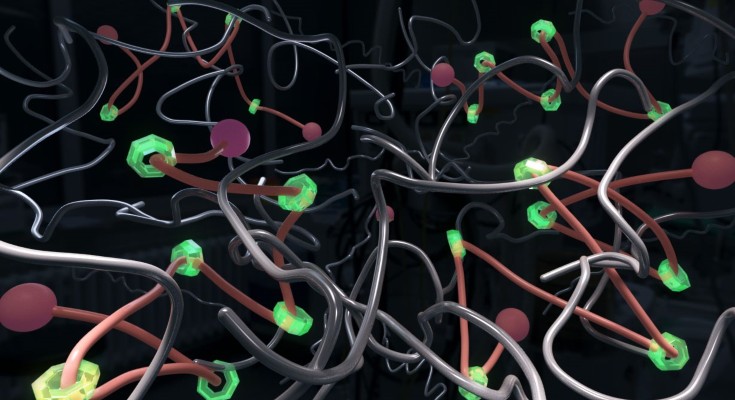
Conceptual diagram of a polymer network using polyrotaxane as a cross-linking agent

Conceptual diagram of a polymer network using polyrotaxane as a cross-linking agent
