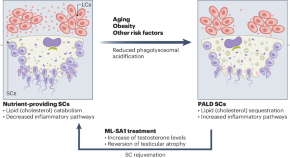
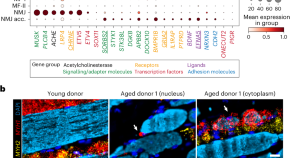
Featured

Announcements
-
-
-
-

Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
Open for submissions
Advertisement
-
-
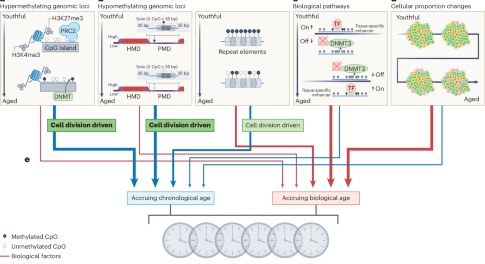
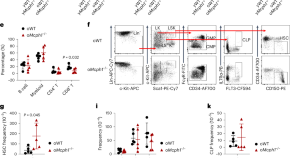
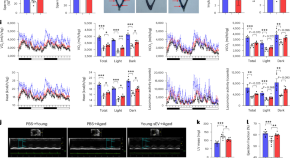
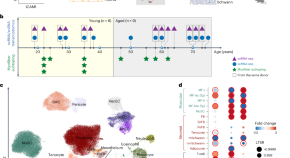
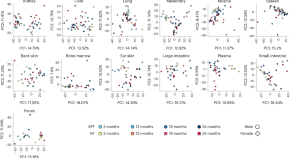
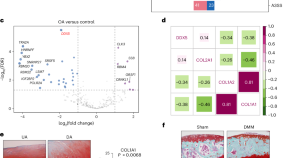
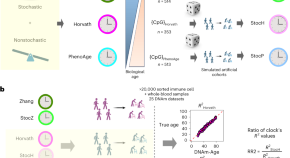
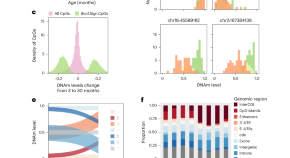
Quantifying stochasticity in the aging DNA methylome
Aging-related DNA methylation changes are numerous. Their precise measurement has opened new avenues to explore aging-related disease pathology, including the construction of chronological and biological age predictors (termed DNA methylation ‘clocks’). Three studies investigate the substantial stochastic contribution to these epigenetic changes and further our understanding of aging biology, as well as of these predictors.
-
-

Aging, longevity and age-related diseases
Trending - Altmetric
-
Aging clocks based on accumulating stochastic variation
-
Influence of grandchildren on COVID-19 vaccination uptake among older adults in China: a parallel-group, cluster-randomized controlled trial
-
PD1 blockade improves survival and CD8+ cytotoxic capacity, without increasing inflammation, during normal microbial experience in old mice
-
The killifish germline regulates longevity and somatic repair in a sex-specific manner