Abstract
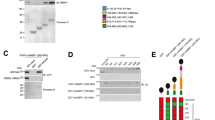
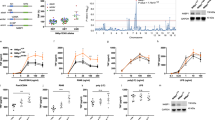
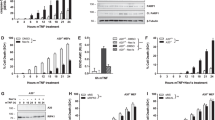
In response to stimulation with proinflammatory cytokines, the deubiquitinase A20 inducibly interacts with the regulatory molecules TAX1BP1, Itch and RNF11 to form the A20 ubiquitin-editing complex. However, the molecular signal that coordinates the assembly of this complex has remained elusive. Here we demonstrate that TAX1BP1 was inducibly phosphorylated on Ser593 and Ser624 in response to proinflammatory stimuli. The kinase IKKα, but not IKKβ, was required for phosphorylation of TAX1BP1 and directly phosphorylated TAX1BP1 in response to stimulation with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interleukin 1 (IL-1). TAX1BP1 phosphorylation was pivotal for cytokine-dependent interactions among TAX1BP1, A20, Itch and RNF11 and downregulation of signaling by the transcription factor NF-κB. IKKα therefore serves a key role in the negative feedback of NF-κB canonical signaling by orchestrating assembly of the A20 ubiquitin-editing complex to limit inflammatory gene activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grivennikov, S.I., Greten, F.R. & Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140, 883–899 (2010).
Vallabhapurapu, S. & Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 693–733 (2009).
Ghosh, S. & Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 837–848 (2008).
Zandi, E., Rothwarf, D.M., Delhase, M., Hayakawa, M. & Karin, M. The IκB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKα and IKKβ, necessary for IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Cell 91, 243–252 (1997).
Yamaoka, S. et al. Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IκB kinase complex essential for NF-κB activation. Cell 93, 1231–1240 (1998).
Hacker, H. & Karin, M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci. STKE 2006, re13 (2006).
Coope, H.J. et al. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100 to p52. EMBO J. 21, 5375–5385 (2002).
Claudio, E., Brown, K., Park, S., Wang, H. & Siebenlist, U. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-κB2 in maturing B cells. Nat. Immunol. 3, 958–965 (2002).
Senftleben, U. et al. Activation by IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κB signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 (2001).
Xiao, G., Harhaj, E.W. & Sun, S.C.N.F. -κB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100. Mol. Cell 7, 401–409 (2001).
Sun, S.C., Ganchi, P.A., Ballard, D.W. & Greene, W.C.N.F. -κB controls expression of inhibitor IκBα: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 259, 1912–1915 (1993).
Sun, S.C. Deubiquitylation and regulation of the immune response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 501–511 (2008).
Harhaj, E.W. & Dixit, V.M. Deubiquitinases in the regulation of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21, 22–39 (2011).
Trompouki, E. et al. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-κB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 424, 793–796 (2003).
Kovalenko, A. et al. The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-κB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 424, 801–805 (2003).
Boone, D.L. et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1052–1060 (2004).
Reiley, W.W. et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates the ubiquitin-dependent kinase Tak1 and prevents abnormal T cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1475–1485 (2007).
Jin, W. et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates RANK signaling and osteoclastogenesis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 1858–1866 (2008).
Turer, E.E. et al. Homeostatic MyD88-dependent signals cause lethal inflammation in the absence of A20. J. Exp. Med. 205, 451–464 (2008).
Sass, G. et al. TNF pretreatment interferes with mitochondrial apoptosis in the mouse liver by A20-mediated down-regulation of Bax. J. Immunol. 179, 7042–7049 (2007).
Coornaert, B., Carpentier, I. & Beyaert, R. A20: Central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 8217–8221 (2008).
Lee, E.G. et al. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-κB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289, 2350–2354 (2000).
Compagno, M. et al. Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-κB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 459, 717–721 (2009).
Kato, M. et al. Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature 459, 712–716 (2009).
Wertz, I.E. et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-κB signalling. Nature 430, 694–699 (2004).
Shembade, N., Ma, A. & Harhaj, E.W. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 327, 1135–1139 (2010).
Shembade, N. & Harhaj, E.W. A20 inhibition of NF-κB and inflammation: Targeting E2:E3 ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Cell Cycle 9, 2481–2482 (2010).
Shembade, N., Parvatiyar, K., Harhaj, N.S. & Harhaj, E.W. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 requires RNF11 to downregulate NF-κB signalling. EMBO J. 28, 513–522 (2009).
Shembade, N., Harhaj, N.S., Liebl, D.J. & Harhaj, E.W. Essential role for TAX1BP1 in the termination of TNF-α-, IL-1- and LPS-mediated NF-κB and JNK signaling. EMBO J. 26, 3910–3922 (2007).
Iha, H. et al. Inflammatory cardiac valvulitis in TAX1BP1-deficient mice through selective NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J. 27, 629–641 (2008).
Matsuoka, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I and adult T-cell leukemia. Oncogene 22, 5131–5140 (2003).
Robek, M.D. & Ratner, L. Immortalization of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants expressed in a functional molecular clone. J. Virol. 73, 4856–4865 (1999).
Sun, S.C. & Yamaoka, S. Activation of NF-κB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation. Oncogene 24, 5952–5964 (2005).
Harhaj, E.W. & Sun, S.C. IKKγ serves as a docking subunit of the IκB kinase (IKK) and mediates interaction of IKK with the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 22911–22914 (1999).
Shembade, N. et al. The E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates inflammatory signaling pathways by controlling the function of the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20. Nat. Immunol. 9, 254–262 (2008).
Hutti, J.E. et al. IKKβ phosphorylates the K63 deubiquitinase A20 to cause feedback inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 7451–7461 (2007).
Hutti, J.E. et al. Phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor CYLD by the breast cancer oncogene IKKɛ promotes cell transformation. Mol. Cell 34, 461–472 (2009).
Micheau, O. & Tschopp, J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114, 181–190 (2003).
Jin, D.Y. et al. A human suppressor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation by tumor necrosis factor α. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25816–25823 (1997).
Gachon, F. et al. CREB-2, a cellular CRE-dependent transcription repressor, functions in association with Tax as an activator of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 promoter. J. Virol. 72, 8332–8337 (1998).
Journo, C. et al. NRP/Optineurin Cooperates with TAX1BP1 to potentiate the activation of NF-κB by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax protein. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000521 (2009).
Xiao, G. et al. Retroviral oncoprotein Tax induces processing of NF-(B2/p100 in T cells: evidence for the involvement of IKKα. EMBO J. 20, 6805–6815 (2001).
Zarnegar, B., Yamazaki, S., He, J.Q. & Cheng, G. Control of canonical NF-κB activation through the NIK-IKK complex pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3503–3508 (2008).
Razani, B. et al. Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-κB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKα-mediated phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 3, ra41 (2010).
Li, Q. et al. Enhanced NF-κB activation and cellular function in macrophages lacking IκB kinase 1 (IKK1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 12425–12430 (2005).
Lawrence, T., Bebien, M., Liu, G.Y., Nizet, V. & Karin, M. IKKα limits macrophage NF-κB activation and contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature 434, 1138–1143 (2005).
Liu, B. et al. Proinflammatory stimuli induce IKKα-mediated phosphorylation of PIAS1 to restrict inflammation and immunity. Cell 129, 903–914 (2007).
Miura, H., Maeda, M., Yamamoto, N. & Yamaoka, S. Distinct IκB kinase regulation in adult T cell leukemia and HTLV-I-transformed cells. Exp. Cell Res. 308, 29–40 (2005).
Harhaj, N.S., Janic, B., Ramos, J.C., Harrington, W.J. Jr. & Harhaj, E.W. Deregulated expression of CD40 ligand in HTLV-I infection: distinct mechanisms of downregulation in HTLV-I-transformed cell lines and ATL patients. Virology 362, 99–108 (2007).
Kwon, H. et al. Lethal cutaneous disease in transgenic mice conditionally expressing type I human T cell leukemia virus Tax. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 35713–35722 (2005).
Wang, X., Naidu, S.R., Sverdrup, F. & Androphy, E.J. Tax1BP1 interacts with papillomavirus E2 and regulates E2-dependent transcription and stability. J. Virol. 83, 2274–2284 (2009).
Sivaram, M.V., Wadzinski, T.L., Redick, S.D., Manna, T. & Doxsey, S.J. Dynein light intermediate chain 1 is required for progress through the spindle assembly checkpoint. EMBO J. 28, 902–914 (2009).
Shembade, N., Harhaj, N.S., Yamamoto, M., Akira, S. & Harhaj, E.W. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein requires the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 for NF-κB activation. J. Virol. 81, 13735–13742 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Sun (University of Texas MD Anderson) for hemagglutinin-tagged IKKα, IKKα(K44M), IKKβ and IKKγ (NEMO), and IκBα amino acids 1–54 fused to GST; W. Greene (Gladstone Institute of Virology) for Jurkat Tax Tet-on cells; M. Maeda (Kyoto University) for TL-OM1 cells; M. Birnbaum (University of Pennsylvania) for MEFs doubly deficient in both Akt1 and Akt2; M. Karin (University of California San Diego) for Ikka−/−, Ikbkb−/− and Ikbkg−/− MEFs; E. Androphy (University of Massachusetts) for Flag-TAX1BP1 amino acids 1–789; and J. Leszyk for mass spectrometry and analysis. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (RO1GM083143 and RO1CA135362 to E.W.H.). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute, National Institute of General Medical Sciences or the US National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.S., R.P. and N.S.H. did experiments and analyzed data; D.W.A. provided reagents and did bioinformatic analyses; and E.W.H. designed and supervised the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Methods (PDF 4596 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shembade, N., Pujari, R., Harhaj, N. et al. The kinase IKKα inhibits activation of the transcription factor NF-κB by phosphorylating the regulatory molecule TAX1BP1. Nat Immunol 12, 834–843 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2066
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2066
This article is cited by
-
The long non-coding RNA SNHG1 attenuates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation via the miR-195/IKK-α axis
Cell and Tissue Banking (2023)
-
Manifold role of ubiquitin in Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Phosphorylation of the histone demethylase KDM5B and regulation of the phenotype of triple negative breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
SQSTM-1/p62 potentiates HTLV-1 Tax-mediated NF-κB activation through its ubiquitin binding function
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
HUWE1 E3 ligase promotes PINK1/PARKIN-independent mitophagy by regulating AMBRA1 activation via IKKα
Nature Communications (2018)