Abstract
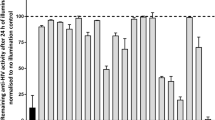
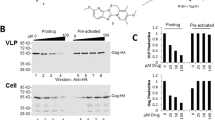
Lens epithelium–derived growth factor (LEDGF/p75) is a cellular cofactor of HIV-1 integrase that promotes viral integration by tethering the preintegration complex to the chromatin. By virtue of its crucial role in the early steps of HIV replication, the interaction between LEDGF/p75 and integrase represents an attractive target for antiviral therapy. We have rationally designed a series of 2-(quinolin-3-yl)acetic acid derivatives (LEDGINs) that act as potent inhibitors of the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction and HIV-1 replication at submicromolar concentration by blocking the integration step. A 1.84-Å resolution crystal structure corroborates the binding of the inhibitor in the LEDGF/p75-binding pocket of integrase. Together with the lack of cross-resistance with two clinical integrase inhibitors, these findings define the 2-(quinolin-3-yl)acetic acid derivatives as the first genuine allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Our work demonstrates the feasibility of rational design of small molecules inhibiting the protein-protein interaction between a viral protein and a cellular host factor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Summa, V. et al. Discovery of raltegravir, a potent, selective orally bioavailable HIV-integrase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV-AIDS infection. J. Med. Chem. 51, 5843–5855 (2008).
Murray, J.M. et al. Antiretroviral therapy with the integrase inhibitor raltegravir alters decay kinetics of HIV, significantly reducing the second phase. AIDS 21, 2315–2321 (2007).
Malet, I. et al. Mutations associated with failure of raltegravir treatment affect integrase sensitivity to the inhibitor in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 1351–1358 (2008).
Van Maele, B., Busschots, K., Vandekerckhove, L., Christ, F. & Debyser, Z. Cellular co-factors of HIV-1 integration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2, 98–105 (2006).
Greene, W.C. et al. Novel targets for HIV therapy. Antiviral Res. 80, 251–265 (2008).
Ganapathy, V., Daniels, T. & Casiano, C.A. LEDGF/p75: a novel nuclear autoantigen at the crossroads of cell survival and apoptosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2, 290–297 (2003).
Ge, H., Si, Y. & Roeder, R.G. Isolation of cDNAs encoding novel transcription coactivators p52 and p75 reveals an alternate regulatory mechanism of transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 17, 6723–6729 (1998).
Singh, D.P. et al. Lens epithelium-derived growth factor: effects on growth and survival of lens epithelial cells, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 267, 373–381 (2000).
Cherepanov, P. et al. HIV-1 integrase forms stable tetramers and associates with LEDGF/p75 protein in human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 372–381 (2003).
De Rijck, J. et al. Overexpression of the lens epithelium-derived growth factor/p75 integrase binding domain inhibits human immunodeficiency virus replication. J. Virol. 80, 11498–11509 (2006).
Emiliani, S. et al. Integrase mutants defective for interaction with LEDGF/p75 are impaired in chromosome tethering and HIV-1 replication. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 25517–25523 (2005).
Hombrouck, A. et al. Virus evolution reveals an exclusive role for LEDGF/p75 in chromosomal tethering of HIV. PLoS Pathog. 3, e47 (2007).
Llano, M. et al. An essential role for LEDGF/p75 in HIV integration. Science 314, 461–464 (2006).
Shun, M.C. et al. LEDGF/p75 functions downstream from preintegration complex formation to effect gene-specific HIV-1 integration. Genes Dev. 21, 1767–1778 (2007).
Vandekerckhove, L. et al. Transient and stable knockdown of the integrase cofactor LEDGF/p75 reveals its role in the replication cycle of human immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 80, 1886–1896 (2006).
Busschots, K. et al. Identification of the LEDGF/p75 binding site in HIV-1 integrase. J. Mol. Biol. 365, 1480–1492 (2007).
Shun, M.C., Daigle, J.E., Vandegraaff, N. & Engelman, A. Wild-type levels of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity in the absence of cellular emerin protein. J. Virol. 81, 166–172 (2007).
Maertens, G., Cherepanov, P., Debyser, Z., Engelborghs, Y. & Engelman, A. Identification and characterization of a functional nuclear localization signal in the HIV-1 integrase interactor LEDGF/p75. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 33421–33429 (2004).
Vanegas, M. et al. Identification of the LEDGF/p75 HIV-1 integrase-interaction domain and NLS reveals NLS-independent chromatin tethering. J. Cell Sci. 118, 1733–1743 (2005).
Ciuffi, A. et al. A role for LEDGF/p75 in targeting HIV DNA integration. Nat. Med. 11, 1287–1289 (2005).
Cherepanov, P., Ambrosio, A.L., Rahman, S., Ellenberger, T. & Engelman, A. Structural basis for the recognition between HIV-1 integrase and transcriptional coactivator p75. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 17308–17313 (2005).
Molteni, V. et al. Identification of a small-molecule binding site at the dimer interface of the HIV integrase catalytic domain. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 57, 536–544 (2001).
Maignan, S., Guilloteau, J.P., Zhou-Liu, Q., Clement-Mella, C. & Mikol, V. Crystal structures of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 integrase free and complexed with its metal cofactor: high level of similarity of the active site with other viral integrases. J. Mol. Biol. 282, 359–368 (1998).
Jones, G., Willett, P., Glen, R.C., Leach, A.R. & Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 267, 727–748 (1997).
Gohlke, H., Hendlich, M. & Klebe, G. Knowledge-based scoring function to predict protein-ligand interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 295, 337–356 (2000).
Eldridge, M.D., Murray, C.W., Auton, T.R., Paolini, G.V. & Mee, R.P. Empirical scoring functions: I. The development of a fast empirical scoring function to estimate the binding affinity of ligands in receptor complexes. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 11, 425–445 (1997).
Bartholomeeusen, K. et al. Differential interaction of HIV-1 integrase and JPO2 with the C terminus of LEDGF/p75. J. Mol. Biol. 372, 407–421 (2007).
Bartholomeeusen, K. et al. Lens epithelium derived growth factor/p75 interacts with the transposase derived DDE domain of pogZ. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 11467–11477 (2009).
Maertens, G.N., Cherepanov, P. & Engelman, A. Transcriptional co-activator p75 binds and tethers the Myc-interacting protein JPO2 to chromatin. J. Cell Sci. 119, 2563–2571 (2006).
Sato, M. et al. Novel HIV-1 integrase inhibitors derived from quinolone antibiotics. J. Med. Chem. 49, 1506–1508 (2006).
Debyser, Z., Cherepanov, P., Van Maele, B., De Clercq, E. & Witvrouw, M. In search of authentic inhibitors of HIV-1 integration. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 13, 1–15 (2002).
Hazuda, D.J. Inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type I integration. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 1, 212–217 (2006).
Johnson, V.A. et al. Update of the drug resistance mutations in HIV-1: 2007. Top. HIV Med. 15, 119–125 (2007).
Hazuda, D.J. et al. Inhibitors of strand transfer that prevent integration and inhibit HIV-1 replication in cells. Science 287, 646–650 (2000).
Dyda, F. et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 integrase: similarity to other polynucleotidyl transferases. Science 266, 1981–1986 (1994).
Arkin, M.R. & Wells, J.A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: progressing towards the dream. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 301–317 (2004).
Ryan, D.P. & Matthews, J.M. Protein-protein interactions in human disease. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 15, 441–446 (2005).
Vassilev, L.T. MDM2 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 13, 23–31 (2007).
Chi, S.W. et al. Structural details on mdm2-p53 interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 38795–38802 (2005).
Kussie, P.H. et al. Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science 274, 948–953 (1996).
Vassilev, L.T. et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303, 844–848 (2004).
Du, L. et al. D77, one benzoic acid derivative, functions as a novel anti-HIV-1 inhibitor targeting the interaction between integrase and cellular LEDGF/p75. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 375, 139–144 (2008).
De Luca, L. et al. Pharmacophore-based discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions between HIV-1 integrase and cellular cofactor LEDGF/p75. Chem. Med. Chem. 4, 1311–1316 (2009).
Yu, F. et al. HIV-1 integrase preassembled on donor DNA is refractory to activity stimulation by LEDGF/p75. Biochemistry 46, 2899–2908 (2007).
Tsantrizos, Y.S. et al. Inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus replication. PCT CA2007, (2007).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 50, 760–763 (1994.).
Delelis, O., et al. The G140S mutation in HIV integrases from raltegravir-resistant patients rescues catalytic defect due to the resistance Q148H mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1193–1201 (2009).
Larder, B.A. & Kemp, S.D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science 246, 1155–1158 (1989).
Nunberg, J.H. et al. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J. Virol. 65, 4887–4892 (1991).
de Vreese, K. et al. The molecular target of bicyclams, potent inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus replication. J. Virol. 70, 689–696 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge A. Calleja for performing analytical chemistry on the compounds, M. Michiels for macrophage and integrase assays and L. Desender for performing large-scale protein purifications. We thank A. Jonckheer for information and communication technology support. X-ray diffraction data collection was done at the X06DA beamline of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen, Switzerland. We thank R. Clayton of Tibotec for providing raltegravir and elvitegravir as well as HXB2D-INN155H E92Q Q148H. Research was funded by the CellCoVir SBO grant (60813) of the Flemish Agentschap voor Innovatie door Wetenschap en Technologie, the FWO grant G.0530.08, the EC grant THINC (HEALTH-F3-2008-201032), the Research Fund and the Industrieel Onderzoeksfonds Program of the K.U. Leuven. A.V. is supported by a grant from the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders. F.C. is funded by an Industrieel Onderzoeksfonds mandate, and B.A.D. is funded by a Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds-PhD scholarship for international cooperation with non-EEA countries outside the EEA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.C. established the specific high-throughput screening tools for the LEDGF/p75-IN interaction, purified proteins and designed and guided the biological characterization of the compounds; A.V. designed and executed the modeling strategy; A.M. and P.C. guided and coordinated the medicinal chemistry; D.M. and D.B. performed organic synthesis; S.N. performed the cocrystallization studies; B.A.D. performed Q-PCR analysis, resistance selection and, together with B.V.R., antiviral testing; B.V.R. performed antiviral testing in T cells and primary cells; N.J.V.d.V. performed AlphaScreen assays; S.V.S. guided the crystallography; M.D.M. guided the modeling; Z.D. coordinated the project and designed experiments; F.C. and Z.D. prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Results (PDF 596 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christ, F., Voet, A., Marchand, A. et al. Rational design of small-molecule inhibitors of the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction and HIV replication. Nat Chem Biol 6, 442–448 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.370
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.370
This article is cited by
-
Structure and function of retroviral integrase
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2022)
-
HIV-1 integrase binding to genomic RNA 5′-UTR induces local structural changes in vitro and in virio
Retrovirology (2021)
-
Structure, function and inhibition of critical protein–protein interactions involving mixed lineage leukemia 1 and its fusion oncoproteins
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
The KT Jeang Retrovirology prize 2021: Peter Cherepanov
Retrovirology (2021)
-
Suppression of HIV-1 Integration by Targeting HIV-1 Integrase for Degradation with A Chimeric Ubiquitin Ligase
Virologica Sinica (2021)