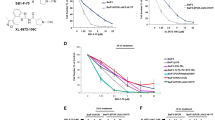
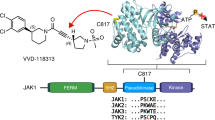
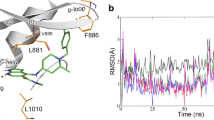
Abstract
Janus kinases (JAKs) are required for cytokine receptor signaling. Since the discovery of the highly prevalent JAK2 V617F mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), JAK2 became a prime target for inhibition. Only one approved JAK2 inhibitor exists, with positive, but not curative effects in MPNs, and promising effects in autoimmune diseases and cancer. On the basis of recent advances in the structural features regulating both normal and mutant JAKs, as well as in small-molecule targeting, we review the current state of JAK2 inhibitor development and present novel avenues of selecting JAK2 inhibitors, with broad and narrow specificities and extend these approaches to other JAKs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vainchenker W, Constantinescu SN . JAK/STAT signaling in hematological malignancies. Oncogene 2013; 32: 2601–2613.
Briscoe J, Rogers NC, Witthuhn BA, Watling D, Harpur AG, Wilks AF et al. Kinase-negative mutants of JAK1 can sustain interferon-gamma-inducible gene expression but not an antiviral state. EMBO J 1996; 15: 799–809.
Drachman JG, Millett KM, Kaushansky K . Thrombopoietin signal transduction requires functional JAK2, not TYK2. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 13480–13484.
Witthuhn BA, Quelle FW, Silvennoinen O, Yi T, Tang B, Miura O et al. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell 1993; 74: 227–236.
Royer Y, Staerk J, Costuleanu M, Courtoy PJ, Constantinescu SN . Janus kinases affect thrombopoietin receptor cell surface localization and stability. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 27251–27261.
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005; 365: 1054–1061.
James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005; 434: 1144–1148.
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1779–1790.
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 387–397.
Pietra D, Brisci A, Rumi E, Boggi S, Elena C, Pietrelli A et al. Deep sequencing reveals double mutations in cis of MPL exon 10 in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Haematologica 2011; 96: 607–611.
Nangalia J, Massie CE, Baxter EJ, Nice FL, Gundem G, Wedge DC et al. Somatic CALR mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms with nonmutated JAK2. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2391–2405.
Klampfl T, Gisslinger H, Harutyunyan AS, Nivarthi H, Rumi E, Milosevic JD et al. Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 2379–2390.
Chachoua I, Pecquet C, El-Khoury M, Nivarthi H, Albu RI, Marty C et al. Thrombopoietin receptor activation by myeloproliferative neoplasm associated calreticulin mutants. Blood 2016; 127: 1325–1335.
Rampal R, Al-Shahrour F, Abdel-Wahab O, Patel JP, Brunel JP, Mermel CH et al. Integrated genomic analysis illustrates the central role of JAK-STAT pathway activation in myeloproliferative neoplasm pathogenesis. Blood 2014; 123: e123–e133.
Passamonti F, Caramazza D, Maffioli M . JAK inhibitor in CALR-mutant myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 1168–1169.
Guglielmelli P, Biamonte F, Rotunno G, Artusi V, Artuso L, Bernardis I et al. Impact of mutational status on outcomes in myelofibrosis patients treated with ruxolitinib in the COMFORT-II study. Blood 2014; 123: 2157–2160.
Badrinarayan P, Sastry GN . Rational approaches towards lead optimization of kinase inhibitors: the issue of specificity. Curr Pharm Des 2013; 19: 4714–4738.
Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 787–798.
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 799–807.
Vannucchi AM . Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1670–1671.
Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Mesa RA, Pardanani AD, Cortes-Franco J, Thomas DA et al. Safety and efficacy of INCB018424, a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 1117–1127.
Meyer SC, Keller MD, Woods BA, LaFave LM, Bastian L, Kleppe M et al. Genetic studies reveal an unexpected negative regulatory role for Jak2 in thrombopoiesis. Blood 2014; 124: 2280–2284.
Schepers H, Wierenga AT, Vellenga E, Schuringa JJ . STAT5-mediated self-renewal of normal hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells. JAKSTAT 2012; 1: 13–22.
Wierenga AT, Schepers H, Moore MA, Vellenga E, Schuringa JJ . STAT5-induced self-renewal and impaired myelopoiesis of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells involves down-modulation of C/EBPalpha. Blood 2006; 107: 4326–4333.
Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Diamond S, Boer J, Harris JJ, Li Y et al. The Janus kinase 2 inhibitor fedratinib inhibits thiamine uptake: a putative mechanism for the onset of Wernicke's encephalopathy. Drug Metab Dispos 2014; 42: 1656–1662.
Nakaya Y, Shide K, Naito H, Niwa T, Horio T, Miyake J et al. Effect of NS-018, a selective JAK2V617F inhibitor, in a murine model of myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J 2014; 4: e174.
Ma L, Clayton JR, Walgren RA, Zhao B, Evans RJ, Smith MC et al. Discovery and characterization of LY2784544, a small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor of JAK2V617F. Blood Cancer J 2013; 3: e109.
Andraos R, Qian Z, Bonenfant D, Rubert J, Vangrevelinghe E, Scheufler C et al. Modulation of activation-loop phosphorylation by JAK inhibitors is binding mode dependent. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 512–523.
Feng J, Witthuhn BA, Matsuda T, Kohlhuber F, Kerr IM, Ihle JN . Activation of Jak2 catalytic activity requires phosphorylation of Y1007 in the kinase activation loop. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 2497–2501.
Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Ye Q, Viale A, Sander C, Solit DB et al. (V600E)BRAF is associated with disabled feedback inhibition of RAF-MEK signaling and elevated transcriptional output of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 4519–4524.
Hatzivassiliou G, Song K, Yen I, Brandhuber BJ, Anderson DJ, Alvarado R et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature 2010; 464: 431–435.
Koppikar P, Bhagwat N, Kilpivaara O, Manshouri T, Adli M, Hricik T et al. Heterodimeric JAK-STAT activation as a mechanism of persistence to JAK2 inhibitor therapy. Nature 2012; 489: 155–159.
Meyer SC, Keller MD, Chiu S, Koppikar P, Guryanova OA, Rapaport F et al. CHZ868, a type II JAK2 inhibitor, reverses type I JAK inhibitor persistence and demonstrates efficacy in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cancer Cell 2015; 28: 15–28.
Marty C, Saint-Martin C, Pecquet C, Grosjean S, Saliba J, Mouton C et al. Germ-line JAK2 mutations in the kinase domain are responsible for hereditary thrombocytosis and are resistant to JAK2 and HSP90 inhibitors. Blood 2014; 123: 1372–1383.
Liu Y, Gray NS . Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat Chem Biol 2006; 2: 358–364.
Nagar B, Bornmann WG, Pellicena P, Schindler T, Veach DR, Miller WT et al. Crystal structures of the kinase domain of c-Abl in complex with the small molecule inhibitors PD173955 and imatinib (STI-571). Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4236–4243.
Wu SC, Li LS, Kopp N, Montero J, Chapuy B, Yoda A et al. Activity of the type II JAK2 inhibitor CHZ868 in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015; 28: 29–41.
Manley PW, Bruggen J, Floersheimer A, Furet P, Jensen MR, Mestan J et al Chimia2008; 62.
Ma DL, Chan DS, Wei G, Zhong HJ, Yang H, Leung LT et al. Virtual screening and optimization of type II inhibitors of JAK2 from a natural product library. Chem Commun (Camb) 2014; 50: 13885–13888.
Losdyck E, Hornakova T, Springuel L, Degryse S, Gielen O, Cools J et al. Distinct acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)-associated Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) mutants exhibit different cytokine-receptor requirements and JAK inhibitor specificities. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 29022–29034.
Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS . Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 28–39.
Cowan-Jacob SW, Mobitz H, Fabbro D . Structural biology contributions to tyrosine kinase drug discovery. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21: 280–287.
Cowan-Jacob SW, Jahnke W, Knapp S . Novel approaches for targeting kinases: allosteric inhibition, allosteric activation and pseudokinases. Future Med Chem 2014; 6: 541–561.
Adrian FJ, Ding Q, Sim T, Velentza A, Sloan C, Liu Y et al. Allosteric inhibitors of Bcr-abl-dependent cell proliferation. Nat Chem Biol 2006; 2: 95–102.
Jatiani SS, Cosenza SC, Reddy MV, Ha JH, Baker SJ, Samanta AK et al. A Non-ATP-competitive dual inhibitor of JAK2 and BCR-ABL kinases: elucidation of a novel therapeutic spectrum based on substrate competitive inhibition. Genes Cancer 2010; 1: 331–345.
Lipka DB, Hoffmann LS, Heidel F, Markova B, Blum MC, Breitenbuecher F et al. LS104, a non-ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of JAK2, is potently inducing apoptosis in JAK2V617F-positive cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 1176–1184.
Samanta AK, Chakraborty SN, Wang Y, Schlette E, Reddy EP, Arlinghaus RB . Destabilization of Bcr-Abl/Jak2 network by a Jak2/Abl kinase inhibitor ON044580 overcomes drug resistance in blast crisis chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Genes Cancer 2010; 1: 346–359.
Dusa A, Mouton C, Pecquet C, Herman M, Constantinescu SN . JAK2 V617F constitutive activation requires JH2 residue F595: a pseudokinase domain target for specific inhibitors. PLoS One 2010; 5: e11157.
Toms AV, Deshpande A, McNally R, Jeong Y, Rogers JM, Kim CU et al. Structure of a pseudokinase-domain switch that controls oncogenic activation of Jak kinases. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013; 20: 1221–1223.
Hammaren HM, Ungureanu D, Grisouard J, Skoda RC, Hubbard SR, Silvennoinen O . ATP binding to the pseudokinase domain of JAK2 is critical for pathogenic activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015; 112: 4642–4647.
Leroy E, Dusa A, Colau D, Motamedi A, Cahu X, Mouton C et al. Uncoupling JAK2 V617F activation from cytokine-induced signalling by modulation of JH2 alphaC helix. Biochem J 2016; 473: 1579–1591.
Saharinen P, Silvennoinen O . The pseudokinase domain is required for suppression of basal activity of Jak2 and Jak3 tyrosine kinases and for cytokine-inducible activation of signal transduction. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 47954–47963.
Yeh TC, Dondi E, Uze G, Pellegrini S . A dual role for the kinase-like domain of the tyrosine kinase Tyk2 in interferon-alpha signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000; 97: 8991–8996.
Chen M, Cheng A, Candotti F, Zhou YJ, Hymel A, Fasth A et al. Complex effects of naturally occurring mutations in the JAK3 pseudokinase domain: evidence for interactions between the kinase and pseudokinase domains. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 947–956.
Shan Y, Gnanasambandan K, Ungureanu D, Kim ET, Hammaren H, Yamashita K et al. Molecular basis for pseudokinase-dependent autoinhibition of JAK2 tyrosine kinase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2014; 21: 579–584.
Lupardus PJ, Ultsch M, Wallweber H, Bir Kohli P, Johnson AR, Eigenbrot C . Structure of the pseudokinase-kinase domains from protein kinase TYK2 reveals a mechanism for Janus kinase (JAK) autoinhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 8025–8030.
Bandaranayake RM, Ungureanu D, Shan Y, Shaw DE, Silvennoinen O, Hubbard SR . Crystal structures of the JAK2 pseudokinase domain and the pathogenic mutant V617F. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2012; 19: 754–759.
Ungureanu D, Wu J, Pekkala T, Niranjan Y, Young C, Jensen ON et al. The pseudokinase domain of JAK2 is a dual-specificity protein kinase that negatively regulates cytokine signaling. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011; 18: 971–976.
Hasan S, Lacout C, Marty C, Cuingnet M, Solary E, Vainchenker W et al. JAK2V617F expression in mice amplifies early hematopoietic cells and gives them a competitive advantage that is hampered by IFNalpha. Blood 2013; 122: 1464–1477.
Bhagwat N, Koppikar P, Keller M, Marubayashi S, Shank K, Rampal R et al. Improved targeting of JAK2 leads to increased therapeutic efficacy in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2014; 123: 2075–2083.
Tokarski JS, Zupa-Fernandez A, Tredup JA, Pike K, Chang C, Xie D et al. Tyrosine kinase 2-mediated signal transduction in T lymphocytes is blocked by pharmacological stabilization of its pseudokinase domain. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 11061–11074.
Davis MI, Hunt JP, Herrgard S, Ciceri P, Wodicka LM, Pallares G et al. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 2011; 29: 1046–1051.
Min X, Ungureanu D, Maxwell S, Hammaren H, Thibault S, Hillert EK et al. Structural and functional characterization of the JH2 pseudokinase domain of JAK family tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2). J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 27261–27270.
Dusa A, Staerk J, Elliott J, Pecquet C, Poirel HA, Johnston JA et al. Substitution of pseudokinase domain residue Val-617 by large non-polar amino acids causes activation of JAK2. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 12941–12948.
Zhao L, Dong H, Zhang CC, Kinch L, Osawa M, Iacovino M et al. A JAK2 interdomain linker relays Epo receptor engagement signals to kinase activation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 26988–26998.
Liu Q, Sabnis Y, Zhao Z, Zhang T, Buhrlage SJ, Jones LH et al. Developing irreversible inhibitors of the protein kinase cysteinome. Chem Biol 2013; 20: 146–159.
Leproult E, Barluenga S, Moras D, Wurtz JM, Winssinger N . Cysteine mapping in conformationally distinct kinase nucleotide binding sites: application to the design of selective covalent inhibitors. J Med Chem 2011; 54: 1347–1355.
Tan L, Akahane K, McNally R, Reyskens KM, Ficarro SB, Liu S et al. Development of selective covalent janus kinase 3 inhibitors. J Med Chem 2015; 58: 6589–6606.
Goedken ER, Argiriadi MA, Banach DL, Fiamengo BA, Foley SE, Frank KE et al. Tricyclic covalent inhibitors selectively target Jak3 through an active site thiol. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 4573–4589.
Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV, Woo MS, Greulich H, Wong KK et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 2070–2075.
Zhang J, Adrian FJ, Jahnke W, Cowan-Jacob SW, Li AG, Iacob RE et al. Targeting Bcr-Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors. Nature 2010; 463: 501–506.
Lu X, Levine R, Tong W, Wernig G, Pikman Y, Zarnegar S et al. Expression of a homodimeric type I cytokine receptor is required for JAK2V617F-mediated transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18962–18967.
Lu X, Huang LJ, Lodish HF . Dimerization by a cytokine receptor is necessary for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5258–5266.
Staerk J, Defour JP, Pecquet C, Leroy E, Antoine-Poirel H, Brett I et al. Orientation-specific signalling by thrombopoietin receptor dimers. EMBO J 2011; 30: 4398–4413.
Matthews EE, Thevenin D, Rogers JM, Gotow L, Lira PD, Reiter LA et al. Thrombopoietin receptor activation: transmembrane helix dimerization, rotation, and allosteric modulation. FASEB J 2011; 25: 2234–2244.
Seubert N, Royer Y, Staerk J, Kubatzky KF, Moucadel V, Krishnakumar S et al. Active and inactive orientations of the transmembrane and cytosolic domains of the erythropoietin receptor dimer. Mol Cell 2003; 12: 1239–1250.
Moraga I, Wernig G, Wilmes S, Gryshkova V, Richter CP, Hong WJ et al. Tuning cytokine receptor signaling by re-orienting dimer geometry with surrogate ligands. Cell 2015; 160: 1196–1208.
Ferrao R, Wallweber HJ, Ho H, Tam C, Franke Y, Quinn J et al. The structural basis for class II cytokine receptor recognition by JAK1. Structure 2016; 24: 897–905.
Wallweber HJ, Tam C, Franke Y, Starovasnik MA, Lupardus PJ . Structural basis of recognition of interferon-alpha receptor by tyrosine kinase 2. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2014; 21: 443–448.
Frank SJ, Yi W, Zhao Y, Goldsmith JF, Gilliland G, Jiang J et al. Regions of the JAK2 tyrosine kinase required for coupling to the growth hormone receptor. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 14776–14785.
Haan C, Is'harc H, Hermanns HM, Schmitz-Van De Leur H, Kerr IM, Heinrich PC et al. Mapping of a region within the N terminus of Jak1 involved in cytokine receptor interaction. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 37451–37458.
Kohlhuber F, Rogers NC, Watling D, Feng J, Guschin D, Briscoe J et al. A JAK1/JAK2 chimera can sustain alpha and gamma interferon responses. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 695–706.
Zhao Y, Wagner F, Frank SJ, Kraft AS . The amino-terminal portion of the JAK2 protein kinase is necessary for binding and phosphorylation of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor beta c chain. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 13814–13818.
Wernig G, Gonneville JR, Crowley BJ, Rodrigues MS, Reddy MM, Hudon HE et al. The Jak2V617F oncogene associated with myeloproliferative diseases requires a functional FERM domain for transformation and for expression of the Myc and Pim proto-oncogenes. Blood 2008; 111: 3751–3759.
Zhao L, Ma Y, Seemann J, Huang LJ . A regulating role of the JAK2 FERM domain in hyperactivation of JAK2(V617F). Biochem J 2010; 426: 91–98.
McNally R, Toms AV, Eck MJ . Crystal structure of the FERM-SH2 module of human Jak2. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0156218.
Cacalano NA, Migone TS, Bazan F, Hanson EP, Chen M, Candotti F et al. Autosomal SCID caused by a point mutation in the N-terminus of Jak3: mapping of the Jak3-receptor interaction domain. EMBO J 1999; 18: 1549–1558.
O'Sullivan JM, McLornan DP, Harrison CN . Safety considerations when treating myelofibrosis. Expert Opin Drug Safety 2016; 15: 1185–1192.
Genovese MC, Kremer J, Zamani O, Ludivico C, Krogulec M, Xie L et al. Baricitinib in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 1243–1252.
Plimack ER, Lorusso PM, McCoon P, Tang W, Krebs AD, Curt G et al. AZD1480: a phase I study of a novel JAK2 inhibitor in solid tumors. Oncologist 2013; 18: 819–820.
Seavey MM, Lu LD, Stump KL, Wallace NH, Hockeimer W, O'Kane TM et al. Therapeutic efficacy of CEP-33779, a novel selective JAK2 inhibitor, in a mouse model of colitis-induced colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 984–993.
Baffert F, Regnier CH, De Pover A, Pissot-Soldermann C, Tavares GA, Blasco F et al. Potent and selective inhibition of polycythemia by the quinoxaline JAK2 inhibitor NVP-BSK805. Mol Cancer Ther 2010; 9: 1945–1955.
Duan Y, Chen L, Chen Y, Fan XG . c-Src binds to the cancer drug Ruxolitinib with an active conformation. PLoS One 2014; 9: e106225.
Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B et al. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature 1998; 395: 511–516.
Li Q, Wong YL, Yueqi Lee M, Li Y, Kang C . Solution structure of the transmembrane domain of the mouse erythropoietin receptor in detergent micelles. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 13586.
Abdelrahman RA, Begna KH, Al-Kali A, Hogan WJ, Litzow MR, Pardanani A et al. Momelotinib treatment-emergent neuropathy: prevalence, risk factors and outcome in 100 patients with myelofibrosis. Br J Haematol 2015; 169: 77–80.
Purandare AV, McDevitt TM, Wan H, You D, Penhallow B, Han X et al. Characterization of BMS-911543, a functionally selective small-molecule inhibitor of JAK2. Leukemia 2012; 26: 280–288.
Hexner EO, Mascarenhas J, Prchal J, Roboz GJ, Baer MR, Ritchie EK et al. Phase I dose escalation study of lestaurtinib in patients with myelofibrosis. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56: 2543–2551.
Verstovsek S, Hoffman R, Mascarenhas J, Soria JC, Bahleda R, McCoon P et al. A phase I, open-label, multi-center study of the JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 in patients with myelofibrosis. Leuk Res 2015; 39: 157–163.
Komrokji RS, Seymour JF, Roberts AW, Wadleigh M, To LB, Scherber R et al. Results of a phase 2 study of pacritinib (SB1518), a JAK2/JAK2(V617F) inhibitor, in patients with myelofibrosis. Blood 2015; 125: 2649–2655.
Verstovsek S, Tam CS, Wadleigh M, Sokol L, Smith CC, Bui LA et al. Phase I evaluation of XL019, an oral, potent, and selective JAK2 inhibitor. Leuk Res 2014; 38: 316–322.
Ringel F, Kaeda J, Schwarz M, Oberender C, Grille P, Dorken B et al. Effects of Jak2 type 1 inhibitors NVP-BSK805 and NVP-BVB808 on Jak2 mutation-positive and Bcr-Abl-positive cell lines. Acta Haematol 2014; 132: 75–86.
Geissler K, Jager E, Barna A, Sliwa T, Knobl P, Schwarzinger I et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of JAK2 inhibition in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Eur J Haematol 2016; 97: 562–567.
Miyamoto N, Sugita K, Goi K, Inukai T, Lijima K, Tezuka T et al. The JAK2 inhibitor AG490 predominantly abrogates the growth of human B-precursor leukemic cells with 11q23 translocation or Philadelphia chromosome. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1758–1768.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Andrew K. Shiau, Leila Varghese and Thomas Radimerski for critical comments. We acknowledge FRIA PhD and Salus Sanguinis fellowships to EL. Support to SNC was from Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, the Fondation contre le cancer (Grant Number F/2004/266), from Actions de Recherche Concertées of the communauté Française de Belgique (Grant Number ARC10/15-027) and the PAI program Belgian Medical Genetics Initiative (Grant Number IAP-P7/43).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leroy, E., Constantinescu, S. Rethinking JAK2 inhibition: towards novel strategies of more specific and versatile janus kinase inhibition. Leukemia 31, 1023–1038 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.43
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.43
This article is cited by
-
A multitask GNN-based interpretable model for discovery of selective JAK inhibitors
Journal of Cheminformatics (2022)
-
A computationally affordable approach for accurate prediction of the binding affinity of JAK2 inhibitors
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2022)
-
Role of JAK inhibitors in myeloproliferative neoplasms: current point of view and perspectives
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Targeted therapies for myeloproliferative neoplasms
Biomarker Research (2019)
-
Targeting nuclear β-catenin as therapy for post-myeloproliferative neoplasm secondary AML
Leukemia (2019)