Abstract
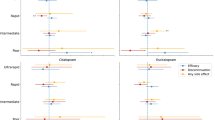
The cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) isoenzyme metabolizes about 25% of clinically used drugs. The impact of CYP2D6 metabolizer status on therapeutic outcome was assessed in 365 psychiatric in-patients treated with neuroleptics or antidepressants. Length of hospitalization and response onset were prolonged for patients receiving CYP2D6 drugs. Intermediate metabolizers (IMs) receiving CYP2D6 doses above the population median had more side effects after 4 weeks than extensive metabolizers with above-median doses (9/13, 69% vs 4/23, 17%, P=0.003), than IMs with below-median doses (5/22, 23%, P=0.012) and IMs with other medication (24/84, 29%, P=0.009). The Clinical Global Impression scale response was lower for IMs treated with CYP2D6 drugs (3/42, 7%) than for IMs with other medication (21/84, 25%, P=0.017) probably due to increased side effects. Identification of IM status (38% of study population) may help to reduce side effects and length/cost of hospitalization. Thus, not only poor and ultrarapid metabolizer but also IMs may benefit from CYP2D6 genotyping. This is of paramount interest since it greatly improves cost/benefit estimations for pretreatment CYP2D6 screening.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingelman-Sundberg M, Rodriguez-Antona C . Pharmacogenetics of drug-metabolizing enzymes: implications for a safer and more effective drug therapy. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2005; 360: 1563–1570.
Nebert DW . Polymorphisms in drug-metabolizing enzymes: what is their clinical relevance and why do they exist? Am J Hum Genet 1997; 60: 265–271.
Ingelman-Sundberg M . Human drug metabolising cytochrome P450 enzymes: properties and polymorphisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2004; 369: 89–104.
Bradford LD . CYP2D6 allele frequency in European Caucasians, Asians, Africans and their descendants. Pharmacogenomics 2002; 3: 229–243.
Raimundo S, Toscano C, Klein K, Fischer J, Griese EU, Eichelbaum M et al. A novel intronic mutation, 2988G>A, with high predictivity for impaired function of cytochrome P450 2D6 in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 76: 128–138.
Wuttke H, Rau T, Heide R, Bergmann K, Bohm M, Weil J et al. Increased frequency of cytochrome P450 2D6 poor metabolizers among patients with metoprolol-associated adverse effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 72: 429–437.
Chou WH, Yan FX, de Leon J, Barnhill J, Rogers T, Cronin M et al. Extension of a pilot study: impact from the cytochrome P450 2D6 polymorphism on outcome and costs associated with severe mental illness. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2000; 20: 246–251.
Rau T, Wohlleben G, Wuttke H, Thuerauf N, Lunkenheimer J, Lanczik M et al. CYP2D6 genotype: impact on adverse effects and nonresponse during treatment with antidepressants—a pilot study. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 75: 386–393.
Brockmoller J, Kirchheiner J, Schmider J, Walter S, Sachse C, Muller-Oerlinghausen B et al. The impact of the CYP2D6 polymorphism on haloperidol pharmacokinetics and on the outcome of haloperidol treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 72: 438–452.
Kawanishi C, Lundgren S, Agren H, Bertilsson L . Increased incidence of CYP2D6 gene duplication in patients with persistent mood disorders: ultrarapid metabolism of antidepressants as a cause of nonresponse. A pilot study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2004; 59: 803–807.
Kirchheiner J, Brosen K, Dahl ML, Gram LF, Kasper S, Roots I et al. CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotype-based dose recommendations for antidepressants: a first step towards subpopulation-specific dosages. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2001; 104: 173–192.
de Leon J . The crucial role of the therapeutic window in understanding the clinical relevance of the poor versus the ultrarapid metabolizer phenotypes in subjects taking drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 or CYP2C19. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2007; 27: 241–245.
Flockhart DA . Drug interactions: cytochrome P450 drug interaction table (version 4.0). Indiana University School of Medicine (2007) (cited 2009); Available from: http://medicine.iupui.edu/flockhart/table.htm.
Kirchheiner J, Meineke I, Muller G, Roots I, Brockmoller J . Contributions of CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 to the biotransformation of E- and Z-doxepin in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenetics 2002; 12: 571–580.
World Health Organization. Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) index 2008 including defined daily doses (DDD). Available from: http://www.whocc.no/atcddd/. Accessed 2008 [updated Accessed 2008; cited 2008].
Spina E, Scordo MG, D'Arrigo C . Metabolic drug interactions with new psychotropic agents. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2003; 17: 517–538.
Sjoqvist F, Eliasson E . The convergence of conventional therapeutic drug monitoring and pharmacogenetic testing in personalized medicine: focus on antidepressants. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 81: 899–902.
de Leon J, Barnhill J, Rogers T, Boyle J, Chou WH, Wedlund PJ . Pilot study of the cytochrome P450-2D6 genotype in a psychiatric state hospital. Am J Psychiatry 1998; 155: 1278–1280.
Schillevoort I, de Boer A, van der Weide J, Steijns LS, Roos RA, Jansen PA et al. Antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal syndromes and cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype: a case–control study. Pharmacogenetics 2002; 12: 235–240.
Ellingrod VL, Schultz SK, Arndt S . Abnormal movements and tardive dyskinesia in smokers and nonsmokers with schizophrenia genotyped for cytochrome P450 2D6. Pharmacotherapy 2002; 22: 1416–1419.
Furman KD, Grimm DR, Mueller T, Holley-Shanks RR, Bertz RJ, Williams LA et al. Impact of CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizer alleles on single-dose desipramine pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 279–284.
Mihara K, Otani K, Tybring G, Dahl ML, Bertilsson L, Kaneko S . The CYP2D6 genotype and plasma concentrations of mianserin enantiomers in relation to therapeutic response to mianserin in depressed Japanese patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1997; 17: 467–471.
Zanger UM, Fischer J, Raimundo S, Stuven T, Evert BO, Schwab M et al. Comprehensive analysis of the genetic factors determining expression and function of hepatic CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 573–585.
Raimundo S, Fischer J, Eichelbaum M, Griese EU, Schwab M, Zanger UM . Elucidation of the genetic basis of the common ‘intermediate metabolizer’ phenotype for drug oxidation by CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 2000; 10: 577–581.
Hamelin BA, Dorson PG, Pabis D, Still D, Bouchard RH, Pourcher E et al. CYP2D6 mutations and therapeutic outcome in schizophrenic patients. Pharmacotherapy 1999; 19: 1057–1063.
Steimer W, Zopf K, von Amelunxen S, Pfeiffer H, Bachofer J, Popp J et al. Amitriptyline or not, that is the question: pharmacogenetic testing of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 identifies patients with low or high risk for side effects in amitriptyline therapy. Clin Chem 2005; 51: 376–385.
Guy W . ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. DHEW publication no. 76-338 US National Institute of Mental Health: Bethesda (MD), 1976.
Muller B, Zopf K, Bachofer J, Steimer W . Optimized strategy for rapid cytochrome P450 2D6 genotyping by real-time long PCR. Clin Chem 2003; 49: 1624–1631.
Steimer W, Muller T, Popp J, Heres S, Kissling W, Leucht S . Rapid detection of the intermediate metabolizer associated CYP2D6 polymorphisms*9 and*17 with real time PCR. Ther Drug Monit 2005; 27: 242–243.
Ji L, Pan S, Marti-Jaun J, Hanseler E, Rentsch K, Hersberger M . Single-step assays to analyze CYP2D6 gene polymorphisms in Asians: allele frequencies and a novel *14B allele in mainland Chinese. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 983–988.
Sachse C, Brockmoller J, Bauer S, Roots I . Cytochrome P450 2D6 variants in a Caucasian population: allele frequencies and phenotypic consequences. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 60: 284–295.
Steimer W, Zopf K, von Amelunxen S, Pfeiffer H, Bachofer J, Popp J et al. Allele-specific change of concentration and functional gene dose for the prediction of steady-state serum concentrations of amitriptyline and nortriptyline in CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 extensive and intermediate metabolizers. Clin Chem 2004; 50: 1623–1633.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laika, B., Leucht, S., Heres, S. et al. Intermediate metabolizer: increased side effects in psychoactive drug therapy. The key to cost-effectiveness of pretreatment CYP2D6 screening?. Pharmacogenomics J 9, 395–403 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2009.23
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2009.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Meta-analysis of probability estimates of worldwide variation of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Challenges in pharmacogenetics
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2013)
-
Assessment of Activity Levels for CYP2D6*1, CYP2D6*2, and CYP2D6*41 Genes by Population Pharmacokinetics of Dextromethorphan
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2010)
-
The promises of personalized medicine
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2010)