Abstract
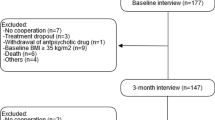
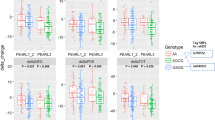
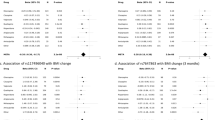
The use of antipsychotics is associated with an increased risk of obesity. This consideration makes it important to search for determinants that can predict the risk for antipsychotic-induced obesity. In this cross-sectional study, we investigated whether polymorphisms in the HTR2C gene were associated with obesity (body mass index >30 kg/m2) in patients using antipsychotics. We examined polymorphisms in the promoter region of the HTR2C gene ((HTR2C:c.1–142948(GT)n, rs3813928 (−997 G/A), rs3813929 (−759 C/T), rs518147 (−697 G/C)) and an intragenic polymorphism (rs1414334:C>G). The results of the logistic regression were expressed as adjusted odds ratios (OR). In total, we included 127 patients mainly diagnosed with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder (89%). The results indicate that a combined genotype carrying the variant HTR2C:c.1–142948(GT)n 13 repeat allele, the common allele rs3813929 C, the variant allele rs518147 C and the variant allele rs1414334 C is significantly related to an increased risk of obesity (OR 3.71 (95% confidence interval: 1.24–11.12)).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison DB, Casey DE . Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a review of the literature. J Clin Psychiatry 2001; 62 (Suppl 7): 22–31.
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH . The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 1999; 282: 1523–1529.
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, VanItallie TB . Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA 1999; 282: 1530–1538.
Muller DJ, Muglia P, Fortune T, Kennedy JL . Pharmacogenetics of antipsychotic-induced weight gain. Pharmacol Res 2004; 49: 309–329.
Hugenholtz GW, Heerdink ER, Meijer WE, Stolker JJ, Egberts AC, Nolen WA . Reasons for switching between antipsychotics in daily clinical practice. Pharmacopsychiatry 2005; 38: 122–124.
Yuan X, Yamada K, Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Koyama W, Nonaka K . Identification of polymorphic loci in the promoter region of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor gene and their association with obesity and type II diabetes. Diabetologia 2000; 43: 373–376.
Reynolds GP, Zhang ZJ, Zhang XB . Association of antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain with a 5-HT2C receptor gene polymorphism. Lancet 2002; 359: 2086–2087.
Reynolds GP, Zhang Z, Zhang X . Polymorphism of the promoter region of the serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptor gene and clozapine-induced weight gain. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 677–679.
Templeman LA, Reynolds GP, Arranz B, San L . Polymorphisms of the 5-HT2C receptor and leptin genes are associated with antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain in Caucasian subjects with a first-episode psychosis. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2005; 15: 195–200.
Ellingrod VL, Perry PJ, Ringold JC, Lund BC, Bever-Stille K, Fleming F et al. Weight gain associated with the −759C/T polymorphism of the 5HT2C receptor and olanzapine. Am J Med Genet B 2005; 134: 76–78.
Miller dD, Ellingrod VL, Holman TL, Buckley PF, Arndt S . Clozapine-induced weight gain associated with the 5HT2C receptor −759C/T polymorphism. Am J Med Genet B 2005; 133: 97–100.
Theisen FM, Hinney A, Bromel T, Heinzel-Gutenbrunner M, Martin M, Krieg JC et al. Lack of association between the −759C/T polymorphism of the 5-HT2C receptor gene and clozapine-induced weight gain among German schizophrenic individuals. Psychiatr Genet 2004; 14: 139–142.
Ellingrod VL, Miller D, Ringold JC, Perry PJ . Distribution of the serotonin 2C (5HT2C) receptor gene −759C/T polymorphism in patients with schizophrenia and normal controls. Psychiatr Genet 2004; 14: 93–95.
Tsai SJ, Hong CJ, Yu YW, Lin CH . 759C/T genetic variation of 5HT(2C) receptor and clozapine-induced weight gain. Lancet 2002; 360: 1790.
Basile VS, Masellis M, De Luca V, Meltzer HY, Kennedy JL . 759C/T genetic variation of 5HT(2C) receptor and clozapine-induced weight gain. Lancet 2002; 360: 1790–1791.
Reynolds GP, Templeman LA, Zhang ZJ . The role of 5-HT2C receptor polymorphisms in the pharmacogenetics of antipsychotic drug treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2005; 29: 1021–1028.
Pooley EC, Fairburn CG, Cooper Z, Sodhi MS, Cowen PJ, Harrison PJ . A 5-HT2C receptor promoter polymorphism (HT). Am J Med Genet B 2004; 126: 124–127.
McCarthy S, Mottagui-Tabar S, Mizuno Y, Sennblad B, Hoffstedt J, Arner P et al. Complex HTR2C linkage disequilibrium and promoter associations with body mass index and serum leptin. Hum Genet 2005; 117: 545–557.
Perneger TV . What's wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. BMJ 1998; 316: 1236–1238.
Blin O, Micallef J . Antipsychotic-associated weight gain and clinical outcome parameters. J Clin Psychiatry 2001; 62 (Suppl 7): 11–21.
Ronaghi M, Uhlen M, Nyren P . A sequencing method based on real-time pyrophosphate. Science 1998; 281: 363–365.
Pacey-Miller T, Henry R . Single-nucleotide polymorphism detection in plants using a single-stranded pyrosequencing protocol with a universal biotinylated primer. Anal Biochem 2003; 317: 166–170.
Anonymous. Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification Index: Including Defined Daily Doses (DDDs) for Plain Substances. World Health Organization: Oslo, Norway, 1997.
Vanina Y, Podolskaya A, Sedky K, Shahab H, Siddiqui A, Munshi F et al. Body weight changes associated with psychopharmacology. Psychiatr Serv 2002; 53: 842–847.
Wirshing DA, Boyd JA, Meng LR, Ballon JS, Marder SR, Wirshing WC . The effects of novel antipsychotics on glucose and lipid levels. J Clin Psychiatry 2002; 63: 856–865.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Maldonado G, Greenland S . Simulation study of confounder-selection strategies. Am J Epidemiol 1993; 138: 923–936.
Acknowledgements
This study was kindly supported financially by the Mental Health Services Drenthe, Assen, The Netherlands and the Arijan Porsius foundation, Utrecht, The Netherlands. We thank Cees Slooff and Wim van Oven for establishing initial contacts and stimulating discussions and Annet Derks for careful assistance. We are thankful for the help of Marc Bijen in setting up and carrying out the genotyping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of Interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulder, H., Franke, B., Aart van der – Beek van der, A. et al. The association between HTR2C polymorphisms and obesity in psychiatric patients using antipsychotics: a cross-sectional study. Pharmacogenomics J 7, 318–324 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500422
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500422
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
From evidence based medicine to mechanism based medicine. Reviewing the role of pharmacogenetics
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy (2013)
-
Gene-microRNA interactions associated with antipsychotic mechanisms and the metabolic side effects of olanzapine
Psychopharmacology (2013)
-
Pharmacogenetics of antipsychotic-induced weight gain: review and clinical implications
Molecular Psychiatry (2012)
-
From evidence based medicine to mechanism based medicine. Reviewing the role of pharmacogenetics
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy (2011)
-
Association of genetic variants of the histamine H1 and muscarinic M3 receptors with BMI and HbA1c values in patients on antipsychotic medication
Psychopharmacology (2011)