Abstract
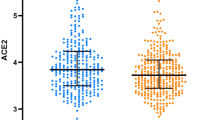
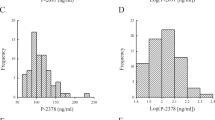
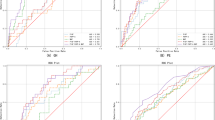
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 is a major endogenous inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9, which may affect the responsiveness to therapy in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. We examined whether TIMP-1 polymorphism (g.–9830T>G, rs2070584) modifies plasma MMP-9 and TIMP-1 levels and the response to antihypertensive therapy in 596 pregnant: 206 patients with preeclampsia (PE), 183 patients with gestational hypertension (GH) and 207 healthy pregnant controls. We also studied the TIMP-3 polymorphism (g.–1296T>C, rs9619311). Plasma MMP-9 and TIMP-1 levels were measured by ELISA. GH patients with the GG genotype for the TIMP-1 polymorphism had lower MMP-9 levels and MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratios than those with the TT genotype. PE patients with the TG genotype had higher TIMP-1 levels. The G allele and the GG genotype were associated with PE and responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in PE, but not in GH. Our results suggest that the TIMP-1 g.–9830T>G polymorphism not only promotes PE but also decreases the responses to antihypertensive therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hutcheon JA, Lisonkova S, Joseph KS . Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2011; 25: 391–403.
Palei AC, Spradley FT, Warrington JP, George EM, Granger JP . Pathophysiology of hypertension in pre-eclampsia: a lesson in integrative physiology. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2013; 208: 224–233.
Warrington JP, George EM, Palei AC, Spradley FT, Granger JP . Recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2013; 62: 666–673.
Visse R, Nagase H . Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 2003; 92: 827–839.
Karthikeyan VJ, Lane DA, Beevers DG, Lip GY, Blann AD . Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in hypertension-related pregnancy complications. J Hum Hypertens 2013; 27: 72–78.
Palei AC, Granger JP, Tanus-Santos JE . Matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets in preeclampsia. Curr Drug Targets 2013; 14: 325–334.
Sankaralingam S, Arenas IA, Lalu MM, Davidge ST . Preeclampsia: current understanding of the molecular basis of vascular dysfunction. Expert Rev Mol Med 2006; 8: 1–20.
Isaka K, Usuda S, Ito H, Sagawa Y, Nakamura H, Nishi H et al. Expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in human trophoblasts. Placenta 2003; 24: 53–64.
Shimonovitz S, Hurwitz A, Dushnik M, Anteby E, Geva-Eldar T, Yagel S . Developmental regulation of the expression of 72 and 92 kd type IV collagenases in human trophoblasts: a possible mechanism for control of trophoblast invasion. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994; 171: 832–838.
Zhang B, Ye S, Herrmann SM, Eriksson P, de Maat M, Evans A et al. Functional polymorphism in the regulatory region of gelatinase B gene in relation to severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 1999; 99: 1788–1794.
Shimajiri S, Arima N, Tanimoto A, Murata Y, Hamada T, Wang KY et al. Shortened microsatellite d(CA)21 sequence down-regulates promoter activity of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene. FEBS Lett 1999; 455: 70–74.
Fraser R, Walker JJ, Ekbote UV, Martin KL, McShane P, Orsi NM . Interleukin-4 -590 (C>T), toll-like receptor-2 +2258 (G>A) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 -1562 (C>T) polymorphisms in pre-eclampsia. BJOG 2008; 115: 1052–1056, discussion 1056.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Amaral LM, Machado JS, Cavalli RC, Lacchini R et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 polymorphisms affect plasma MMP-9 levels and antihypertensive therapy responsiveness in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Pharmacogenomics J 2012; 12: 489–498.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Duarte G, Cavalli RC, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE . Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 genotypes and haplotypes in preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Clin Chim Acta 2010; 411: 874–877.
Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Opdenakker G . Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2002; 37: 375–536.
Luizon MR, Amaral LM, Palei AC . Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of MMPs genetic polymorphisms and plasma levels in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Hum Hypertens 2013; 27: 278–279.
Pradhan-Palikhe P, Vesterinen T, Tarkkanen J, Leivo I, Sorsa T, Salo T et al. Plasma level of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 but not that of matrix metalloproteinase-8 predicts survival in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Oral Oncol 2010; 46: 514–518.
Ogata T, Shibamura H, Tromp G, Sinha M, Goddard KA, Sakalihasan N et al. Genetic analysis of polymorphisms in biologically relevant candidate genes in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 2005; 41: 1036–1042.
Armstrong C, Abilleira S, Sitzer M, Markus HS, Bevan S . Polymorphisms in MMP family and TIMP genes and carotid artery intima-media thickness. Stroke 2007; 38: 2895–2899.
Report of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on high blood pressure in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000; 183: S1–S22.
Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Luizon MR, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Cavalli RC, Tanus-Santos JE . eNOS haplotypes affect the responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in preeclampsia but not in gestational hypertension. Pharmacogenomics J 2010; 10: 40–45.
Motsinger AA, Ritchie MD . Multifactor dimensionality reduction: an analysis strategy for modelling and detecting gene-gene interactions in human genetics and pharmacogenomics studies. Hum Genomics 2006; 2: 318–328.
Gui J, Andrew AS, Andrews P, Nelson HM, Kelsey KT, Karagas MR et al. A robust multifactor dimensionality reduction method for detecting gene-gene interactions with application to the genetic analysis of bladder cancer susceptibility. Ann Hum Genet 2011; 75: 20–28.
Silva PS, Fontana V, Luizon MR, Lacchini R, Silva WA Jr, Biagi C et al. eNOS and BDKRB2 genotypes affect the antihypertensive responses to enalapril. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2013; 69: 167–177.
Ab Hamid J, Mohtarrudin N, Osman M, Andi Asri AA, Wan Hassan WH, Aziz R . Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 as potential biomarkers for gestational hypertension. Singapore Med J 2012; 53: 681–683.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Cavalli RC, Tanus-Santos JE . Comparative assessment of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, and their inhibitors, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 in preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Clin Biochem 2008; 41: 875–880.
Kolben M, Lopens A, Blaser J, Ulm K, Schmitt M, Schneider KT et al. Proteases and their inhibitors are indicative in gestational disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996; 68: 59–65.
Montagnana M, Lippi G, Albiero A, Scevarolli S, Salvagno GL, Franchi M et al. Evaluation of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their inhibitors in physiologic and pre-eclamptic pregnancy. J Clin Lab Anal 2009; 23: 88–92.
Belo VA, Souza-Costa DC, Luizon MR, Lanna CM, Carneiro PC, Izidoro-Toledo TC et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 genetic variations affect MMP-9 levels in obese children. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012; 36: 69–75.
Demacq C, Vasconcellos VB, Marcaccini AM, Gerlach RF, Machado AA, Tanus-Santos JE . A genetic polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) affects the changes in circulating MMP-9 levels induced by highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV patients. Pharmacogenomics J 2009; 9: 265–273.
Marson BP, Lacchini R, Belo V, Mattos SG, da Costa BP, Poli-de-Figueiredo CE et al. Functional matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 genetic variants modify the effects of hemodialysis on circulating MMP-9 levels. Clin Chim Acta 2012; 414: 46–51.
Muniz JJ, Lacchini R, Belo VA, Nobre YT, Tucci S Jr, Martins AC et al. Circulating matrix metalloproteinases and their endogenous inhibitors in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2012; 24: 38–43.
Lee HJ, Lee GH, Nah S, Lee KH, Yang H, Kim YM et al. Association of TIMP-4 gene polymorphism with the risk of osteoarthritis in the Korean population. Rheumatol Int 2008; 28: 845–850.
Boyle AP, Hong EL, Hariharan M, Cheng Y, Schaub MA, Kasowski M et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res 2012; 22: 1790–1797.
O'Mara TA, Clements JA, Spurdle AB . The use of predictive or prognostic genetic biomarkers in endometrial and other hormone-related cancers: justification for extensive candidate gene single nucleotide polymorphism studies of the matrix metalloproteinase family and their inhibitors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009; 18: 2352–2365.
Podymow T, August P . Update on the use of antihypertensive drugs in pregnancy. Hypertension 2008; 51: 960–969.
Martinez ML, Lopes LF, Coelho EB, Nobre F, Rocha JB, Gerlach RF et al. Lercanidipine reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in patients with hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2006; 47: 117–122.
Zervoudaki A, Economou E, Pitsavos C, Vasiliadou K, Aggeli C, Tsioufis K et al. The effect of Ca2+ channel antagonists on plasma concentrations of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 273–276.
Zervoudaki A, Economou E, Stefanadis C, Pitsavos C, Tsioufis K, Aggeli C et al. Plasma levels of active extracellular matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in patients with essential hypertension before and after antihypertensive treatment. J Hum Hypertens 2003; 17: 119–124.
Luizon MR, Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Lacchini R, Cavalli RC, Duarte G et al. Epistasis among eNOS, MMP-9 and VEGF maternal genotypes in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertens Res 2012; 35: 917–921.
Williams PJ, Broughton Pipkin F . The genetics of pre-eclampsia and other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2011; 25: 405–417.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Amaral LM, Machado JS, Cavalli RC, Duarte G et al. Association between matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 polymorphisms and MMP-2 levels in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Exp Mol Pathol 2012; 92: 217–221.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Amaral LM, Machado JS, Cavalli RC, Lacchini R et al. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 polymorphisms on responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy of women with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2012; 111: 262–267.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Brazil) and the Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP-Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luizon, M., Palei, A., Sandrim, V. et al. Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 polymorphism, plasma TIMP-1 levels, and antihypertensive therapy responsiveness in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Pharmacogenomics J 14, 535–541 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2014.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2014.26
This article is cited by
-
Associations of polymorphisms of CYP2D6 and CYP2C9 with early onset severe pre-eclampsia and response to labetalol therapy
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2018)
-
Gene–gene interactions in the NAMPT pathway, plasma visfatin/NAMPT levels, and antihypertensive therapy responsiveness in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2017)
-
An update on the pharmacogenetics of treating hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2015)