Abstract
Caffeine, the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world, is used to promote wakefulness and enhance alertness. Like other wake-promoting drugs (stimulants and modafinil), caffeine enhances dopamine (DA) signaling in the brain, which it does predominantly by antagonizing adenosine A2A receptors (A2AR). However, it is unclear if caffeine, at the doses consumed by humans, increases DA release or whether it modulates the functions of postsynaptic DA receptors through its interaction with adenosine receptors, which modulate them. We used positron emission tomography and [11C]raclopride (DA D2/D3 receptor radioligand sensitive to endogenous DA) to assess if caffeine increased DA release in striatum in 20 healthy controls. Caffeine (300 mg p.o.) significantly increased the availability of D2/D3 receptors in putamen and ventral striatum, but not in caudate, when compared with placebo. In addition, caffeine-induced increases in D2/D3 receptor availability in the ventral striatum were associated with caffeine-induced increases in alertness. Our findings indicate that in the human brain, caffeine, at doses typically consumed, increases the availability of DA D2/D3 receptors, which indicates that caffeine does not increase DA in the striatum for this would have decreased D2/D3 receptor availability. Instead, we interpret our findings to reflect an increase in D2/D3 receptor levels in striatum with caffeine (or changes in affinity). The association between increases in D2/D3 receptor availability in ventral striatum and alertness suggests that caffeine might enhance arousal, in part, by upregulating D2/D3 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance.1 Its behavioral arousing pharmacological effects are similar to those of stimulant drugs (amphetamine and methylphenidate) and modafinil, which are drugs that increase dopamine (DA) signaling by blocking DA transporters and/or enhancing DA release from the terminals.2, 3, 4 The DA-enhancing effects of these drugs underlie their arousing5, 6 and reinforcing effects.7, 8, 9, 10 In contrast, preclinical studies indicate that caffeine’s pharmacological effects are mediated by its antagonism of adenosine receptors (A1 and A2A subtypes).11 In particular, its antagonism of A2A receptors (A2AR) in striatum has been implicated in its dopaminergic effects.12 Similarly, caffeine-induced increases in locomotor activity13 and arousal14 appear to be mediated by A2AR as they are absent in A2AR knockout mice, and silencing the expression of A2AR with short-hairpin RNA in the nucleus accumbens interferes with caffeine’s effects on wakefulness.15
The striatum expresses high levels of A2AR where they are co-expressed with postsynaptic D2 receptors (D2R) forming A2AR-D2R heteromers.16, 17, 18 Through allosteric and second-messenger interactions adenosine inhibits D2R signaling. Thus, in striatal neurons, A2AR agonists decrease D2R agonist binding.19 Caffeine, by blocking A2AR, could enhance DA signaling through the unopposed D2R.20 Though it was initially postulated that caffeine antagonism of adenosine A1 receptors resulted in DA increases in the nucleus accumbens,21 this finding was only obtained after very high doses of caffeine and was not corroborated by others.22, 23 Furthermore, a brain imaging study with [11C]raclopride, which is a radioligand that competes with endogenous DA for binding to D2 and D3 receptors (D2/D3R), showed that oral caffeine (200 mg) increased its binding in striatum,24 which is inconsistent with DA increases. However, the small sample size from the study (n=8) precludes its generalizability. Thus, the question of whether caffeine increases striatal DA and the mechanism(s) of action for caffeine’s alerting effects in the human brain remain unclear.
To assess whether caffeine increases DA in the human brain, we used positron emission tomography (PET) and [11C]raclopride25 and tested 20 healthy controls once with placebo and once with oral caffeine. A 300-mg dose of caffeine was selected to reflect the average amount of caffeine in 2–3 cups of coffee. We hypothesized that caffeine would not increase DA in striatum but instead would enhance striatal DA signaling by increasing D2R.
Materials and methods
Subjects
This study included 20 healthy male controls (38±8 years of age, body mass index 26±3; years of education 14±2) recruited through advertisements in local newspapers. Exclusion criteria included consumption of more than two caffeine beverages per day, current or past psychiatric disease as per DSM IV including any substance use disorder (smokers were excluded); past or present history of neurological, cardiovascular or endocrinological disease; history of head trauma with loss of consciousness greater than 30 min; and current medical illness. Seventeen of the participants reported that they did not drink coffee (or caffeinated beverages), one reported one cup a day and two reported two cups a day. Written informed consent was obtained from all the subjects and the studies were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board at Stony Brook University Medical Center.
Self-reports and scales and cardiovascular measures
To study the behavioral effects of caffeine, we assessed self-reports for subjective perception of ‘alertness’, ‘tiredness’, ‘sleepiness’ and ‘mood’ using analog scales (rated from 1 to 10) that were obtained before and at 30 and 120 min after placebo or caffeine administration, as previously described.26 The use of analog scales to assess self-reports of drug effects have been shown to be reproducible and to predict drug responses.27 For the correlation analysis, we used the measures obtained 120 min after caffeine administration (at the end of the [11C]raclopride scan), which is within the time for peak caffeine effects (60–120 min).28
Heart rate and blood pressure were recorded three times at five-minute intervals before the administration of placebo or caffeine and periodically thereafter until 120 min post placebo or post caffeine. The measures taken before placebo or caffeine were averaged (pre-drug measures) and those taken 60–120 min post administration were averaged as post-drug measures. Effects of the drug were evaluated as paired t-test comparisons between the pre- and the post-drug measures.
Measures of caffeine in plasma
Venous blood was drawn before and at 30, 60 and 120 min after caffeine administration. Caffeine in plasma was quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography.29
PET scan
We used an HR+ tomography (resolution 4.5 × 4.5 × 4.5 mm full width at half maximum, 63 slices) with [11C]raclopride 4–8 mCi (specific activity 0.5–1.5 Ci μM−1 at the end of bombardment). The procedures for imaging were as previously described.30 Briefly, 20 dynamic emission scans were obtained immediately after injection for a total of 54 min. The participants were scanned with [11C]raclopride twice, once with placebo and once with caffeine; the placebo scans were done 2 h before the caffeine scan. Caffeine (300 mg) and placebo (sugar tablet) were administered orally 60 min before the [11C]raclopride injection. We chose 60 min as peak effects from oral caffeine occur at ~60 min when it is administered as a tablet.28 The half life of caffeine in plasma is ~3–5 h,31 so this time point ensured high plasma caffeine levels during the PET measurements (60–120 min post caffeine).
PET image analysis
We analyzed the nondisplaceable binding potential (BPND) images using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM8; Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, London, UK), which enabled us to make comparisons on a pixel-by-pixel basis.32 Specifically, we estimated for each voxel the distribution volume ratio, which corresponds to the equilibrium measurement of the ratio of the radiotracer’s tissue concentration in the striatum to that in the cerebellum, which is used as a reference region.33 These images were then spatially normalized to the stereotactic space of the Montreal Neurological Institute using a 12-parameter affine transformation and 2-mm isotropic voxels. A custom Montreal Neurological Institute template, which was previously developed using images from 34 healthy subjects acquired with [11C]raclopride and the same PET scanning sequence,34 was used for the spatial normalization of the distribution volume ratio images. The voxels of the distribution volume ratio images correspond to BPND +1.
An independent region-of-interest (ROI) analysis was performed using preselected ROIs in caudate, putamen and ventral striatum (VS) as previously described25 to corroborate the SPM findings. The ROI measures were used for the correlation analysis with the behavioral measures that were significantly affected by caffeine and to assess the correlations with the levels of caffeine in plasma.
Statistical analyses
The brain maps (BPND) were spatially smoothed in SPM8 using an 8-mm isotropic Gaussian kernel to minimize the effects associated with the variability of the brain anatomy across subjects. A striatal mask (dorsal striatum and VS) was created using the digital anatomical brain atlases provided with the MRIcro software (www.cabiatl.com/mricro/). Specifically, the voxels corresponding to striatum (caudate, putamen and VS) were defined in the Montreal Neurological Institute stereotactic space using the Automated Anatomical Labeling atlas.35 One-way (within-subjects) analysis of variance was used to assess drug effects (placebo vs caffeine) on BPND with SPM8. Statistical significance was set by the stringent threshold PFWE<0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons at the voxel level (within a striatal mask) using the random field theory with a family-wise error correction. For visualization purposes regarding the MRI location of the regions that differed significantly between placebo and caffeine, we used an uncorrected threshold of P<0.01.
For the independent ROI analysis, statistical significance was set at P<0.05, if it corroborated the SPM findings.
For the behavioral and cardiovascular measures, we compared each time point between the placebo and caffeine scores using repeated analysis of variance. Correlation analyses were done to assess the relationship between the regions where caffeine changed BPND and the behavioral measures that were significantly affected by caffeine. Significance was set at P <0.05.
Results
Effects of caffeine on self-reports and on cardiovascular measures
Comparisons between caffeine and placebo for the corresponding time measures showed significantly higher self-reports of ‘alertness’ both at 30’ (P=0.05) and at 120’ (P=0.01) and lower scores in ‘sleepiness’ at 120’ (P=0.04) than placebo. Differences between caffeine and placebo for scores on mood and tiredness only reached trend effects (P>0.06<0.09; Figure 1).
The average cardiovascular measures were not significantly affected by caffeine (pre vs post). Specifically, for heart rate, pre vs post placebo (70±10 vs 64±9) or pre vs post caffeine (66±9 vs 65±11); for systolic pressure, pre vs post placebo (124±6 vs 122±7) or pre vs post caffeine (128±11 vs 129±9); or for diastolic pressure, pre vs post placebo (67±10 vs 65±9) or pre vs post caffeine measures (71±12 vs 69±11); none of which differ significantly from one another.
Measures of caffeine in plasma
There were no detectable levels of caffeine on the plasma samples taken before caffeine administration. Measures of caffeine concentration in plasma were 4.7±2 μg ml−1 at 30 min, 5.2±1 μg ml−1 at 60 min and 4.8±0.6 μg ml−1 at 120 min. This corroborated that we had peak levels of caffeine in plasma at the time of [11C]raclopride injection (60 min post caffeine) and high levels at the time of the behavioral measures (30 and 120 min post caffeine).
Effects of caffeine on D2/D3R availability
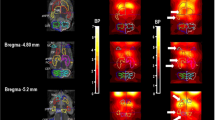
SPM revealed that caffeine increased D2/D3R availability (observed as increases in BPND) in right and left striatum (including dorsal putamen and VS) as shown both by the averaged statistical maps as well as the individual values extracted from the center of the significant clusters (Figure 2, Table 1).
(a) Brain maps obtained with Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) showing significant differences in D2/D3R availability, which was quantified as nondisplaceable binding potential (BPND), between placebo and caffeine for the contrast caffeine >placebo. Threshold for significance corresponds to Pu<0.01, clusters >100 voxels. (b) Individual values for BPND from measures extracted in dorsal putamen and in ventral striatum after placebo and after caffeine.
The independent ROI analyses, corroborated that caffeine when compared with placebo induced small but significant increases in BPND, in putamen (placebo: 2.84±0.37 vs caffeine: 2.97±0.35; P=0.05) and in VS (placebo: 2.69±0.31 vs caffeine: 2.84±0.39, P=0.05) but not in caudate.
Correlations between caffeine-induced changes in D2/D3R availability and behavior and plasma levels
The correlation analysis with the striatal ROI and the behavioral measures showed a significant positive correlation between VS and alertness (r=0.56, P=0.01) such that increases in D2/D3R availability with caffeine were associated with increases in alertness.
The correlation analysis between caffeine-induced changes in D2/D3R availability in striatum and levels of caffeine in plasma were not significant.
Discussion
Here we show that caffeine increases D2/D3R availability in striatum (evidenced as increases in BPND in dorsal putamen and VS) in a group of healthy controls with low levels of daily caffeine intake. These findings are consistent with findings from a prior PET [11C]raclopride study done in a small group of subjects (eight habitual coffee drinkers) that also reported increases in D2/D3R availability in striatum with caffeine (200 mg).24 The findings from these two studies thus suggest that caffeine at doses typically consumed by humans might enhance DA signaling by increasing D2/D3R levels or their affinity rather than by increasing DA release in the striatum.
Here we interpret our results of increases in BPND (in BPND availability) with caffeine to suggest that they reflect increases in D2/D3R levels rather than reflecting decreases in endogenous DA, which is the way that typically increases in BPND are interpreted (reduced competition from DA to bind to D2/D3R). The reasons for this interpretation follow. First, it is recognized that alerting drugs (amphetamine, methylphenidate and modafinil) increase DA release in the striatum.3, 25, 36 Second, clinical studies have shown that the DA increases in striatum induced by stimulant drugs are associated with increases in alertness.5 Finally, preclinical studies have shown that the increases in striatal DA induced by stimulants and modafinil is necessary for their wake-promoting actions.6 Thus, if caffeine had reduced DA in the striatum, this would have resulted in an increase in tiredness and sleepiness instead of the increases in alertness observed after caffeine administration. Our interpretation that the increases in striatal D2/D3R availability in VS with caffeine reflect an increase in D2/D3R levels is also consistent with our findings that downregulation of D2/D3R in VS after sleep deprivation is associated with reduced alertness.5
Striato-pallidal neurons adjust their excitability by changing D2R levels in the membrane.37 Thus, D2R downregulate with DA stimulation38 and upregulate with reduced DA signaling.39, 40 DA stimulation of D2R triggers their internalization,38 which can then be recycled or degraded.38, 41 Internalization of D2R is regulated by A2AR,42 agonists facilitate its internalization through the binding of β-arrestin 2 to A2AR-D2R receptor heteromers43 whereas A2AR antagonists interfere with D2R internalization in striatal neurons.44 Thus, caffeine might interfere with a tonic A2AR-dependent internalization of D2R mediated by endogenous adenosine, which could contribute to its psychostimulant effects.14, 19, 45, 46 Indeed, our findings along with those previously reported showing that caffeine increased D2R availability in striatum,24 support this interpretation. As caffeine modulates DA signaling, in part, by its antagonism of A2AR,47 caffeine-induced D2R increases in striatum would be consistent with caffeine's antagonism of A2A-mediated D2R internalization. Indeed, A2A receptor knockout mice show increased D2R levels in striatum;48 though we cannot necessarily equate the chronic state of a knockout with the effects from acute caffeine exposure.
However, regardless of the mechanism responsible for the increases in striatal D2/D3R availability, our results indicate that in humans, caffeine at the doses typically consumed, does not increase DA in the striatum. This is consistent with findings from microdialysis studies in rodent showing that caffeine (0.25–5 mg kg−1 intravenously or 1.5 to 30 mg kg−1 intraperitoneally) did not increase DA in the nucleus accumbens,22, 23 though a study reported increases with a large (10 mg kg−1 intraperitoneally) but not a lower caffeine dose (3 mg kg−1 intraperitoneally).21 Thus, on the basis of the current and prior findings24 and the preclinical results, caffeine at doses that are relevant to human consumption does not appear to increase DA in the nucleus accumbens. As the ability of drugs of abuse to increase DA is necessary for their rewarding effects and for the neuroadaptations associated with the addiction phenotype,49 this could explain why caffeine does not produce the compulsive administration and the loss of control that characterizes addiction.50
Caffeine-induced increases in D2/D3R in VS were associated with increases in alertness. This association between alertness and D2/D3R replicates our previous findings with sleep deprivation but in the opposite direction, in which we showed that the decreases in D2/D3R availability in VS with sleep deprivation were associated with reductions in alertness.5 In the prior PET study, caffeine-induced increases in striatal D2/D3R availability were associated with reduced tiredness.24 Thus this provides evidence that enhanced signaling through D2/D3R in striatal regions might enhance alertness or decrease tiredness, whereas reduced signaling might decrease alertness or increase fatigue.
Study limitations
Traditionally, increases in D2/D3R availability with [11C]raclopride, as observed here, have been interpreted to reflect decreases in DA release. Instead, our model leads us to interpret them as increases in D2/D3R levels and/or increases in affinity. However, our model cannot rule out the potential confound that more than one factor could be affecting the binding of [11C]raclopride. In this respect, preclinical experiments that use more selective compounds should be performed to investigate whether caffeine’s effects on [11C]raclopride binding reflect changes in the expression or in the affinity of D2/D3R and whether these effects reflect caffeine’s antagonism at A2AR. Also because [11C]raclopride binds to both D2R and D3R,51 we cannot distinguish whether caffeine-induced increases in striatal BPND reflects only increases in D2R or also in D3R. However, in putamen where the relative density of D3R is much lower than that of D2R,52 the effects of caffeine are likely to reflect D2R. Another potential confound in our study is that caffeine significantly reduces cerebral blood flow,53 which could interfere with the BPND measures as cerebral blood flow effects differ between cerebellum and striatum.54 However, because caffeine decreases cerebral blood flow in striatum to a greater extent than in cerebellum,54 this would lead to decreases in striatal BPND, whereas we showed the opposite; that is increases in striatal BPND with caffeine, indicating that our findings are not due to caffeine-induced changes in cerebral blood flow. Though the raclopride PET method cannot distinguish between presynaptic and postsynaptic D2/D3R, the fact that caffeine is an antagonist at A2A receptors, which are expressed in medium spiny neurons expressing D2R but not in DA neurons lead us to presume that the effects are postsynaptic. Another confound in our studies is the order effect as placebo was always given 2 h before caffeine. However, studies that have evaluated test–retest reproducibility for raclopride binding (including ours)55, 56 have reported no significant differences between measures even when the repeated measures were performed on the same day57 as per the current study, indicating that the order effect is unlikely to account for our findings. We are unable to assess if the participants were able to determine if they received caffeine or placebo as we did not query them at the end of the study. Finally, we did not collect blood samples for epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are increased by caffeine.58 Thus, we cannot rule out the contribution of caffeine’s effects in the autonomic system on the behavioral effects of caffeine. Nonetheless, the significant association between increases in D2R availability in VS and alertness indicates that caffeine’s effects on D2R signaling contribute to its alerting effects.
Conclusion
We show a significant increase in D2/D3R availability in striatum with caffeine administration, which indicates that caffeine at doses consumed by humans does not increase DA in striatum. Instead we interpret our findings to indicate that caffeine’s DA-enhancing effects in the human brain are indirect and mediated by an increase in D2/D3R levels and/or changes in D2/D3R affinity.
References
Mitchell DC, Knight CA, Hockenberry J, Teplansky R, Hartman TJ . Beverage caffeine intakes in the U.S. Food Chem Toxicol 2014; 63: 136–142.
Cardenas L, Houle S, Kapur S, Busto UE . Oral D-amphetamine causes prolonged displacement of [11C]raclopride as measured by PET. Synapse 2004; 51: 27–31.
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F et al. Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA 2009; 301: 1148–1154.
Volkow ND, Wang G, Fowler JS, Logan J, Gerasimov M, Maynard L et al. Therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate significantly increase extracellular dopamine in the human brain. J Neurosci 2001; 21: RC121.
Volkow ND, Tomasi D, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Logan J et al. Evidence that sleep deprivation downregulates dopamine D2R in ventral striatum in the human brain. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 6711–6717.
Wisor JP, Nishino S, Sora I, Uhl GH, Mignot E, Edgar DM . Dopaminergic role in stimulant-induced wakefulness. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 1787–1794.
Abi-Dargham A, Kegeles LS, Martinez D, Innis RB, Laruelle M . Dopamine mediation of positive reinforcing effects of amphetamine in stimulant naive healthy volunteers: results from a large cohort. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2003; 13: 459–468.
Nguyen TL, Tian YH, You IJ, Lee SY, Jang CG . Modafinil-induced conditioned place preference via dopaminergic system in mice. Synapse 2011; 65: 733–741.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Gatley SJ, Wong C et al. Reinforcing effects of psychostimulants in humans are associated with increases in brain dopamine and occupancy of D(2) receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999; 291: 409–415.
Wuo-Silva R, Fukushiro DF, Borcoi AR, Fernandes HA, Procopio-Souza R, Hollais AW et al. Addictive potential of modafinil and cross-sensitization with cocaine: a pre-clinical study. Addict Biol 2011; 16: 565–579.
Banerjee D, Vitiello MV, Grunstein RR . Pharmacotherapy for excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep Med Rev 2004; 8: 339–354.
Chen JF, Xu K, Petzer JP, Staal R, Xu YH, Beilstein M et al. Neuroprotection by caffeine and A(2 A) adenosine receptor inactivation in a model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 2001; 21: RC143.
El Yacoubi M, Ledent C, Menard JF, Parmentier M, Costentin J, Vaugeois JM . The stimulant effects of caffeine on locomotor behaviour in mice are mediated through its blockade of adenosine A(2A) receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2000; 129: 1465–1473.
Huang ZL, Qu WM, Eguchi N, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Fredholm BB et al. Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 858–859.
Lazarus M, Shen HY, Cherasse Y, Qu WM, Huang ZL, Bass CE et al. Arousal effect of caffeine depends on adenosine A2A receptors in the shell of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 10067–10075.
Ferre S, Ciruela F, Woods AS, Lluis C, Franco R . Functional relevance of neurotransmitter receptor heteromers in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 2007; 30: 440–446.
Azdad K, Gall D, Woods AS, Ledent C, Ferre S, Schiffmann SN . Dopamine D2 and adenosine A2A receptors regulate NMDA-mediated excitation in accumbens neurons through A2A-D2 receptor heteromerization. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009; 34: 972–986.
Trifilieff P, Rives ML, Urizar E, Piskorowski RA, Vishwasrao HD, Castrillon J et al. Detection of antigen interactions ex vivo by proximity ligation assay: endogenous dopamine D2-adenosine A2A receptor complexes in the striatum. Biotechniques 2011; 51: 111–118.
Ferre S . Role of the central ascending neurotransmitter systems in the psychostimulant effects of caffeine. J Alzheimers Dis 2010; 20 (Suppl 1): S35–S49.
Fredholm BB, Battig K, Holmen J, Nehlig A, Zvartau EE . Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol Rev 1999; 51: 83–133.
Solinas M, Ferre S, You ZB, Karcz-Kubicha M, Popoli P, Goldberg SR . Caffeine induces dopamine and glutamate release in the shell of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6321–6324.
Acquas E, Tanda G, Di Chiara G . Differential effects of caffeine on dopamine and acetylcholine transmission in brain areas of drug-naive and caffeine-pretreated rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002; 27: 182–193.
De Luca MA, Bassareo V, Bauer A, Di Chiara G . Caffeine and accumbens shell dopamine. J Neurochem 2007; 103: 157–163.
Kaasinen V, Aalto S, Nagren K, Rinne JO . Dopaminergic effects of caffeine in the human striatum and thalamus. Neuroreport 2004; 15: 281–285.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Schlyer D, Hitzemann R et al. Imaging endogenous dopamine competition with [11C]raclopride in the human brain. Synapse 1994; 16: 255–262.
Wang G-J, Volkow ND, Hitzemann RJ, Wong C, Angrist B, Burr G et al. Behavioral and cardiovascular effects of intravenous methylphenidate in normal subjects and cocaine abusers. Eur Addict Res 1997; 3: 49–54.
Fischman MW, Foltin RW . Utility of subjective-effects measurements in assessing abuse liability of drugs in humans. Br J Addict 1991; 86: 1563–1570.
Liguori A, Hughes JR, Grass JA . Absorption and subjective effects of caffeine from coffee, cola and capsules. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1997; 58: 721–726.
Tanaka E . Simultaneous determination of caffeine and its primary demethylated metabolites in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 1992; 575: 311–314.
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schlyer DJ et al. Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse 1993; 14: 169–177.
Lelo A, Birkett DJ, Robson RA, Miners JO . Comparative pharmacokinetics of caffeine and its primary demethylated metabolites paraxanthine, theobromine and theophylline in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 22: 177–182.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Poline JB, Grasby PJ, Williams SC, Frackowiak RS et al. Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited. Neuroimage 1995; 2: 45–53.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Ding YS, Alexoff DL . Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1996; 16: 834–840.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Tomasi D, Telang F . Addiction: beyond dopamine reward circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 15037–15042.
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002; 15: 273–289.
Martinez D, Slifstein M, Broft A, Mawlawi O, Hwang DR, Huang Y et al. Imaging human mesolimbic dopamine transmission with positron emission tomography. Part II: amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the functional subdivisions of the striatum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2003; 23: 285–300.
Iizuka Y, Sei Y, Weinberger DR, Straub RE . Evidence that the BLOC-1 protein dysbindin modulates dopamine D2 receptor internalization and signaling but not D1 internalization. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 12390–12395.
Bartlett SE, Enquist J, Hopf FW, Lee JH, Gladher F, Kharazia V et al. Dopamine responsiveness is regulated by targeted sorting of D2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 11521–11526.
Ginovart N, Wilson AA, Hussey D, Houle S, Kapur S . D2-receptor upregulation is dependent upon temporal course of D2-occupancy: a longitudinal [11C]-raclopride PET study in cats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009; 34: 662–671.
Xu ZC, Ling G, Sahr RN, Neal-Beliveau BS . Asymmetrical changes of dopamine receptors in the striatum after unilateral dopamine depletion. Brain Res 2005; 1038: 163–170.
Li Y, Roy BD, Wang W, Zhang L, Zhang L, Sampson SB et al. Identification of two functionally distinct endosomal recycling pathways for dopamine D(2) receptor. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 7178–7190.
Hillion J, Canals M, Torvinen M, Casado V, Scott R, Terasmaa A et al. Coaggregation, cointernalization, and codesensitization of adenosine A2A receptors and dopamine D2 receptors. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 18091–18097.
Borroto-Escuela DO, Romero-Fernandez W, Tarakanov AO, Ciruela F, Agnati LF, Fuxe K . On the existence of a possible A2A-D2-beta-Arrestin2 complex: A2A agonist modulation of D2 agonist-induced beta-arrestin2 recruitment. J Mol Biol 2011; 406: 687–699.
Huang L, Wu DD, Zhang L, Feng LY . Modulation of A(2)a receptor antagonist on D(2) receptor internalization and ERK phosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 1292–1300.
Biaggioni I, Paul S, Puckett A, Arzubiaga C . Caffeine and theophylline as adenosine receptor antagonists in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1991; 258: 588–593.
Schwierin B, Borbely AA, Tobler I . Effects of N6-cyclopentyladenosine and caffeine on sleep regulation in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 1996; 300: 163–171.
Ferre S, Ciruela F, Borycz J, Solinas M, Quarta D, Antoniou K et al. Adenosine A1-A2A receptor heteromers: new targets for caffeine in the brain. Front Biosci 2008; 13: 2391–2399.
Dassesse D, Massie A, Ferrari R, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Arckens L et al. Functional striatal hypodopaminergic activity in mice lacking adenosine A(2A) receptors. J Neurochem 2001; 78: 183–198.
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Tomasi D . Addiction circuitry in the human brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2012; 52: 321–336.
Dews PB, O'Brien CP, Bergman J . Caffeine: behavioral effects of withdrawal and related issues. Food Chem Toxicol 2002; 40: 1257–1261.
Levant B, Grigoriadis DE, De Souza EB . Relative affinities of dopaminergic drugs at dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1995; 278: 243–247.
Searle G, Beaver JD, Comley RA, Bani M, Tziortzi A, Slifstein M et al. Imaging dopamine D3 receptors in the human brain with positron emission tomography, [11C]PHNO, and a selective D3 receptor antagonist. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 68: 392–399.
Cameron OG, Modell JG, Hariharan M . Caffeine and human cerebral blood flow: a positron emission tomography study. Life Sci 1990; 47: 1141–1146.
Vidyasagar R, Greyling A, Draijer R, Corfield DR, Parkes LM . The effect of black tea and caffeine on regional cerebral blood flow measured with arterial spin labeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33: 963–968.
Kodaka F, Ito H, Kimura Y, Fujie S, Takano H, Fujiwara H et al. Test-retest reproducibility of dopamine D2/3 receptor binding in human brain measured by PET with [11C]MNPA and [11C]raclopride. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013; 40: 574–579.
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Dewey SL, Schlyer D, MacGregor R et al. Reproducibility of repeated measures of carbon-11-raclopride binding in the human brain. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 609–613.
Alakurtti K, Aalto S, Johansson JJ, Nagren K, Tuokkola T, Oikonen V et al. Reproducibility of striatal and thalamic dopamine D2 receptor binding using [11C]raclopride with high-resolution positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2011; 31: 155–165.
Riksen NP, Rongen GA, Smits P . Acute and long-term cardiovascular effects of coffee: implications for coronary heart disease. Pharmacol Ther 2009; 121: 185–191.
Acknowledgements
We thank Colleen Shea, Pauline Carter, Karen Apelskog and Ruben Baler for their contributions. This research was supported by NIH’s Intramural Research Program (NIAAA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Volkow, N., Wang, GJ., Logan, J. et al. Caffeine increases striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor availability in the human brain. Transl Psychiatry 5, e549 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2015.46
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2015.46
This article is cited by
-
Seasonal effect—an overlooked factor in neuroimaging research
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
Brain activity during a working memory task after daily caffeine intake and caffeine withdrawal: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Effect of Pre-Exercise Caffeine Intake on Endurance Performance and Core Temperature Regulation During Exercise in the Heat: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Sports Medicine (2022)
-
Dopamine, behavior, and addiction
Journal of Biomedical Science (2021)
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: caffeine and exercise performance
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (2021)