Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding spatiotemporal transcriptional dynamics and epithelial fibroblast crosstalk during gastroesophageal junction development through single cell analysis
Decoding spatiotemporal transcriptional dynamics and epithelial fibroblast crosstalk during gastroesophageal junction development through single cell analysis
Elucidating the gastroesophageal junction’s development is key to comprehending its disease susceptibility. Here, the authors mapped its development, uncovering cellular diversity and interaction dynamics using advanced spatiotemporal single-cell analysis.
- Naveen Kumar
- , Pon Ganish Prakash
- & Cindrilla Chumduri
-
Article
| Open Access ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of IL-11 drives macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and pathological cardiac fibrosis in mice
ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of IL-11 drives macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition and pathological cardiac fibrosis in mice
Cardiac macrophage contributes to the onset of cardiac fibrosis, but the underneath mechanisms remain unclear. Here the authors show that mouse cardiac macrophages from circulating monocytes may trans-differentiate into myofibroblast under hypertensive conditions for fibrosis development, with an AKLBH5/IL11 molecular axis modulating this macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition.
- Tao Zhuang
- , Mei-Hua Chen
- & Cheng-Chao Ruan
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell and spatial multi-omics highlight effects of anti-integrin therapy across cellular compartments in ulcerative colitis
Single-cell and spatial multi-omics highlight effects of anti-integrin therapy across cellular compartments in ulcerative colitis
Anti-integrin therapy inhibits lymphocyte trafficking in ulcerative colitis. Here Mennillo et al. use single-cell and spatial -omics to show modulation of mononuclear phagocytes and other networks, identifying gene sets related to treatment response.
- Elvira Mennillo
- , Yang Joon Kim
- & Michael G. Kattah
-
Article
| Open Access Disrupting cellular memory to overcome drug resistance
Disrupting cellular memory to overcome drug resistance
Identifying memory and state switching in single cells remains elusive. Here, the authors develop a method, scMemorySeq, by combining cell barcoding and scRNA-seq and apply it to human melanoma cells to track lineages as they switch states between a drug-susceptible state and a state primed for drug resistance.
- Guillaume Harmange
- , Raúl A. Reyes Hueros
- & Sydney M. Shaffer
-
Comment
| Open Access Epichaperomics reveals dysfunctional chaperone protein networks
Epichaperomics reveals dysfunctional chaperone protein networks
Molecular chaperones establish essential protein-protein interaction networks. Modified versions of these assemblies are generally enriched in certain maladies. A study published in Nature Communications used epichaperomics to identify unique changes occurring in chaperone-formed protein networks during mitosis in cancer cells.
- Mark R. Woodford
- , Dimitra Bourboulia
- & Mehdi Mollapour
-
Article
| Open Access Chronic inflammation, neutrophil activity, and autoreactivity splits long COVID
Chronic inflammation, neutrophil activity, and autoreactivity splits long COVID
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) has heterogenous presentation and complex etiology. Here the authors profile peripheral blood of patients with PASC and analyze by machine-learning to identify immune and serology features that allow the stratification of PASC into inflammatory and non-inflammatory types for better diagnosis and therapy-planning.
- Matthew C. Woodruff
- , Kevin S. Bonham
- & Ignacio Sanz
-
Article
| Open Access Functional decomposition of metabolism allows a system-level quantification of fluxes and protein allocation towards specific metabolic functions
Functional decomposition of metabolism allows a system-level quantification of fluxes and protein allocation towards specific metabolic functions
Quantifying the contribution of individual molecular components to complex cellular processes is a grand challenge in systems biology. Here, the authors present a general theoretical framework (Functional Decomposition of Metabolism, FDM) to quantify the contribution of every metabolic reaction to metabolic functions, e.g. the synthesis of biomass building blocks.
- Matteo Mori
- , Chuankai Cheng
- & Terence Hwa
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell Hi-C identifies plastic chromosome conformations underlying the gastrulation enhancer landscape
Single cell Hi-C identifies plastic chromosome conformations underlying the gastrulation enhancer landscape
Here the authors use single-cell Hi-C to investigate chromosome conformation in post-gastrulation mouse embryos. They find a distinct genome organization in primitive erythrocytes and conformations matching the mesodermal and ectodermal lineages.
- Nimrod Rappoport
- , Elad Chomsky
- & Amos Tanay
-
Article
| Open Access Systems-level analyses of protein-protein interaction network dysfunctions via epichaperomics identify cancer-specific mechanisms of stress adaptation
Systems-level analyses of protein-protein interaction network dysfunctions via epichaperomics identify cancer-specific mechanisms of stress adaptation
Epichaperomics allow the study of protein-protein interactions and their alterations, but probes have been limited to capturing HSP90 epichaperomes. Here, the authors introduce and validate a toolset of HSP70 epichaperome ligands, and use them in epichaperomics to identify a mechanism with which cancer cells can enhance the fitness of mitotic protein networks.
- Anna Rodina
- , Chao Xu
- & Gabriela Chiosis
-
Article
| Open Access Learning perturbation-inducible cell states from observability analysis of transcriptome dynamics
Learning perturbation-inducible cell states from observability analysis of transcriptome dynamics
A major challenge in biotechnology and biomanufacturing is the identification of a set of biomarkers for perturbations and metabolites of interest. Here, the authors develop a data-driven, transcriptome-wide approach to rank perturbation-inducible genes from time-series RNA sequencing data for the discovery of analyte-responsive promoters.
- Aqib Hasnain
- , Shara Balakrishnan
- & Enoch Yeung
-
Article
| Open Access NetBID2 provides comprehensive hidden driver analysis
NetBID2 provides comprehensive hidden driver analysis
It’s challenging to capture “hidden” drivers that may not be genetically-altered or differentially-expressed from omics data. Here the authors developed NetBID2, a comprehensive network-based toolbox with versatile features, enabling the integration of multi-omics data to expose such hidden drivers.
- Xinran Dong
- , Liang Ding
- & Jiyang Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleocytoplasmic transport of active HER2 causes fractional escape from the DCIS-like state
Nucleocytoplasmic transport of active HER2 causes fractional escape from the DCIS-like state
HER2 receptor aberrations are more common in breast DCIS premalignancy than in breast cancer. Here the authors identify a feedback circuit involving HER2 nucleocytoplasmic transport that may explain why some DCIS lesions progress and others do not.
- Lixin Wang
- , B. Bishal Paudel
- & Kevin A. Janes
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated proteomic and transcriptomic landscape of macrophages in mouse tissues
Integrated proteomic and transcriptomic landscape of macrophages in mouse tissues
Macrophage is located in different tissue to serve diverse functions. Here the authors use mass spectrometry and bulk RNA-sequencing to profile 11 mouse macrophage populations from 8 tissues, and combine their de novo data with public datasets to report an integrated proteomic and transcriptomic landscape of mouse macrophage as a valuable resource.
- Jingbo Qie
- , Yang Liu
- & Chen Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating and formatting biomedical data as pre-calculated knowledge graph embeddings in the Bioteque
Integrating and formatting biomedical data as pre-calculated knowledge graph embeddings in the Bioteque
Biomedical data is accumulating at a fast pace and integrating it into a unified framework is a major challenge. Here, the authors present a resource that contains pre-calculated biomedical descriptors derived from a very large knowledge graph.
- Adrià Fernández-Torras
- , Miquel Duran-Frigola
- & Patrick Aloy
-
Article
| Open Access Proteotoxicity caused by perturbed protein complexes underlies hybrid incompatibility in yeast
Proteotoxicity caused by perturbed protein complexes underlies hybrid incompatibility in yeast
Hybrid incompatibility can be an important element of reproductive isolation and speciation. Using chromosome replacement lines of yeast, the authors show that perturbed proteostasis caused by destabilized hybrid protein complexes may represent a general mechanism of hybrid incompatibility.
- Krishna B. S. Swamy
- , Hsin-Yi Lee
- & Jun-Yi Leu
-
Article
| Open Access Selective activation and expansion of regulatory T cells using lipid encapsulated mRNA encoding a long-acting IL-2 mutein
Selective activation and expansion of regulatory T cells using lipid encapsulated mRNA encoding a long-acting IL-2 mutein
IL-2 has been used to expand regulatory T (Treg) cells for treating inflammatory disorders. Here the authors test an engineered IL-2 mutein, delivered subcutaneously as mRNA, to show its increased specificity for activating and expanding Treg cells in both rodents and non-human primates, and to demonstrate its ability to suppress autoimmunity in mouse models.
- Seymour de Picciotto
- , Nicholas DeVita
- & Eric Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Lsm7 phase-separated condensates trigger stress granule formation
Lsm7 phase-separated condensates trigger stress granule formation
Stress granules are non-membranous organelles connected to stress responses and age-related disease. Here, the authors identify a conserved yeast protein, Lsm7, that facilitates stress granule formation through dynamic liquid-liquid phase separation condensates upon 2-deoxy-D-glucose-induced stress.
- Michelle Lindström
- , Lihua Chen
- & Beidong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial cell heterogeneity and microglia regulons revealed by a pig cell landscape at single-cell level
Endothelial cell heterogeneity and microglia regulons revealed by a pig cell landscape at single-cell level
Pigs are important large animal models for biomedical research. Here, the authors construct a single-cell landscape of pig tissues, unravelling the phenotypic heterogeneity of blood endothelial cells in adipose tissues and the evolutionally conserved regulons of microglia in brains.
- Fei Wang
- , Peiwen Ding
- & Yonglun Luo
-
Article
| Open Access RNase III CLASH in MRSA uncovers sRNA regulatory networks coupling metabolism to toxin expression
RNase III CLASH in MRSA uncovers sRNA regulatory networks coupling metabolism to toxin expression
Regulatory small RNA (sRNA) interact with mRNAs to regulate their stability, transcription, and translation via diverse mechanisms. Here, McKellar et al. apply RNase IIICLASH of multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus under different culture conditions to link the network of RNA-RNA interactions to environmental conditions and find that the production of small membrane-permeabilizing toxins is strongly regulated by sRNAs.
- Stuart W. McKellar
- , Ivayla Ivanova
- & Sander Granneman
-
Article
| Open Access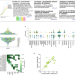 A genome-wide atlas of antibiotic susceptibility targets and pathways to tolerance
A genome-wide atlas of antibiotic susceptibility targets and pathways to tolerance
A lack of understanding in the development and emergence of antimicrobial resistance presents as a problem for accurate infection diagnosis and treatment. Here, authors utilize Streptococcus pneumoniae and build a genome-wide atlas to understand the genes and interactions that contribute to altered drug susceptibility.
- Dmitry Leshchiner
- , Federico Rosconi
- & Tim van Opijnen
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome allocations change linearly with the specific growth rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under glucose limitation
Proteome allocations change linearly with the specific growth rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under glucose limitation
Understanding how yeast organizes its functional proteome is a fundamental task in systems biology. Here, the authors conduct a multiomics analysis on yeast cells cultured with different growth rates, identifying a linear dependence of the functional proteome on the growth rate.
- Jianye Xia
- , Benjamin J. Sánchez
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access An Artificial Intelligence-guided signature reveals the shared host immune response in MIS-C and Kawasaki disease
An Artificial Intelligence-guided signature reveals the shared host immune response in MIS-C and Kawasaki disease
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome may occur in children following COVID-19 infection. Here, the authors analyze gene signatures to show that MIS-C shares the same host immune response as the pre-pandemic inflammatory syndrome of Kawasaki disease but is further along in the spectrum in disease severity
- Pradipta Ghosh
- , Gajanan D. Katkar
- & Debashis Sahoo
-
Article
| Open Access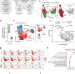 Single-cell characterization of leukemic and non-leukemic immune repertoires in CD8+ T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Single-cell characterization of leukemic and non-leukemic immune repertoires in CD8+ T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (T-LGLL) is a lymphoproliferative disorder involving clonally expanded T cell clones and is not fully understood. Here the authors show that the rest of the immune repertoire is interconnected with the T-LGLL clonotype(s) and is more mature, cytotoxic and clonally restricted than in other cancers and autoimmune disorders.
- Jani Huuhtanen
- , Dipabarna Bhattacharya
- & Satu Mustjoki
-
Article
| Open Access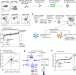 In vivo CRISPR screens reveal a HIF-1α-mTOR-network regulates T follicular helper versus Th1 cells
In vivo CRISPR screens reveal a HIF-1α-mTOR-network regulates T follicular helper versus Th1 cells
T follicular helper (Tfh) and T help type 1 (Th1) cells both arise from naïve CD4 T cells, but detailed knowledge of their differentiation remains incomplete. Here the authors pursue an in vivo CRISPR screen to identify genes, focusing on druggable targets, regulating Tfh versus Th1 to provide a resource for related studies, while also implicating HIF-1α and VHL in this regulation.
- Bonnie Huang
- , James D. Phelan
- & Pamela L. Schwartzberg
-
Article
| Open Access The mouse metallomic landscape of aging and metabolism
The mouse metallomic landscape of aging and metabolism
The metallome is crucial for normal cell functioning but remains largely overlooked in mammals. Here the authors analyze the metallome and copper and zinc isotope compositions in aging mice and show networks of interactions that are organ-specific, age-dependent, isotopically-typified and associated with a wealth of clinical and molecular traits.
- Jean-David Morel
- , Lucie Sauzéat
- & Vincent Balter
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell multi-omics reveals dyssynchrony of the innate and adaptive immune system in progressive COVID-19
Single-cell multi-omics reveals dyssynchrony of the innate and adaptive immune system in progressive COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to progressive pathology in patients with COVID-19, but information for this disease progression is sparse. Here the authors use multi-omics approach to profile the immune responses of patients, assessing immune repertoire and effects of tocilizumab treatments, to find a dyssynchrony between innate and adaptive immunity in progressive COVID-19.
- Avraham Unterman
- , Tomokazu S. Sumida
- & Charles S. Dela Cruz
-
Article
| Open Access Postmortem high-dimensional immune profiling of severe COVID-19 patients reveals distinct patterns of immunosuppression and immunoactivation
Postmortem high-dimensional immune profiling of severe COVID-19 patients reveals distinct patterns of immunosuppression and immunoactivation
Postmortem analyses provide useful information for COVID-19 etiology. Here the authors profile 22 deceased severe COVID-19 patients with transcriptomic and histological approaches to find correlations between the presence of viral antigens with lymphocyte suppression yet myeloid activation, hinting distinct functions of these cells during pathogenesis.
- Haibo Wu
- , Peiqi He
- & Cheng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic drug survey highlights cancer cell dependencies and vulnerabilities
Metabolic drug survey highlights cancer cell dependencies and vulnerabilities
Metabolic reprogramming contributes to cancer development and progression. Here, the authors show the utility of a metabolic drug library to uncover metabolic vulnerabilities and obtain functional insights into myeloid leukemia biology.
- Tea Pemovska
- , Johannes W. Bigenzahn
- & Giulio Superti-Furga
-
Article
| Open Access The composition of human vaginal microbiota transferred at birth affects offspring health in a mouse model
The composition of human vaginal microbiota transferred at birth affects offspring health in a mouse model
Exposure at birth to maternal microbiota has significant effects on offspring health and development. Here, the authors validate a model where inoculation of mice at birth with human vaginal microbiota produces significant effects on offspring health that are further amplified by an unhealthy prenatal environment.
- Eldin Jašarević
- , Elizabeth M. Hill
- & Tracy L. Bale
-
Article
| Open Access OTULIN maintains skin homeostasis by controlling keratinocyte death and stem cell identity
OTULIN maintains skin homeostasis by controlling keratinocyte death and stem cell identity
OTULIN is a deubiquitinase for linear ubiquitin chains. Here the authors show, using genetic mouse models and single-cell RNA-sequencing, that deficiency of OTULIN in keratinocytes causes skin inflammation and verrucous carcinoma via the induction of keratinocyte death, thereby implicating a function of OTULIN in keratinocyte homeostasis.
- Esther Hoste
- , Kim Lecomte
- & Geert van Loo
-
Article
| Open Access CD177 modulates the function and homeostasis of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells
CD177 modulates the function and homeostasis of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells
Regulatory T (Treg) cells are important modulators of the tumor microenvironment. Here the authors perform transcriptome profiling of immune cells from patients with renal clear cell carcinoma to find a Treg signature that correlates with poorer prognosis, with CD177 being implicated as the main mediator for related alterations in Treg activity and tumor outcome.
- Myung-Chul Kim
- , Nicholas Borcherding
- & Weizhou Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access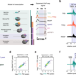 Promoter-proximal elongation regulates transcription in archaea
Promoter-proximal elongation regulates transcription in archaea
Transcription in archaea is known to be regulated through the recruitment of RNA polymerase to promoters. Here, the authors show that the archaeon Saccharolobus solfataricus regulates transcription globally through a rate-limiting promoter-proximal elongation step.
- Fabian Blombach
- , Thomas Fouqueau
- & Finn Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Complex biomolecular networks are fundamental to the functioning of living systems, both at the cellular level and beyond. In this paper, the authors develop a systems framework to elucidate the interplay of networks and the spatial localisation of network components.
- Govind Menon
- & J. Krishnan
-
Article
| Open Access Downregulation of exhausted cytotoxic T cells in gene expression networks of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children
Downregulation of exhausted cytotoxic T cells in gene expression networks of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) onsets in COVID-19 patients with manifestations similar to Kawasaki disease (KD). Here the author probe the peripheral blood transcriptome of MIS-C patients to find signatures related to natural killer (NK) cell activation and CD8+ T cell exhaustion that are shared with KD patients.
- Noam D. Beckmann
- , Phillip H. Comella
- & Alexander W. Charney
-
Article
| Open Access The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19
The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19
COVID-19 is a critical public health threat, but molecular characterizations of patients’ immunity is still lacking. Here the authors collected blood from patients with various disease severity, and prefiltered to exclude selected comorbidity, to obtain genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic and lipidomic profiles to report a trans-omics landscape.
- Peng Wu
- , Dongsheng Chen
- & Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access The geometry of clinical labs and wellness states from deeply phenotyped humans
The geometry of clinical labs and wellness states from deeply phenotyped humans
Longitudinal multi-omics measurements are highly valuable in studying heterogeneity in health and disease phenotypes. Here, the authors apply Pareto Task Inference to analyze the clinical lab tests of 3094 individuals and find three wellness states, and one aberrant health state defining this cohort.
- Anat Zimmer
- , Yael Korem
- & Nathan D. Price
-
Article
| Open Access Clinical and molecular characteristics of COVID-19 patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection
Clinical and molecular characteristics of COVID-19 patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection
Some patients with COVID-19 fail to clear the viral infection quickly, yet our understanding for the underlying immune characteristics is still lacking. Here the authors use single-cell RNA sequencing and other data form such patients to show that persistent infection is associated with immune suppression and reduced expression of ribosomal protein genes.
- Bin Yang
- , Junpeng Fan
- & Chaoyang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access The landscape of molecular chaperones across human tissues reveals a layered architecture of core and variable chaperones
The landscape of molecular chaperones across human tissues reveals a layered architecture of core and variable chaperones
Tissue-specific differences in protein folding capacities are poorly understood. Here, the authors show that the human chaperone system consists of ubiquitous core chaperones and tissue-specific variable chaperones, perturbation of which leads to tissue-specific phenotypes.
- Netta Shemesh
- , Juman Jubran
- & Esti Yeger-Lotem
-
Article
| Open Access Differential controls of MAIT cell effector polarization by mTORC1/mTORC2 via integrating cytokine and costimulatory signals
Differential controls of MAIT cell effector polarization by mTORC1/mTORC2 via integrating cytokine and costimulatory signals
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are key in immunity and diseases, but how their effector polarization is controlled is still unclear. Here, the authors show that an IL-1β/IL-23/mTORC2 axis is essential for the induction of IL-17-producing MAIT17, while an IL-2/IL-15/mTORC1 axis is important for the homeostasis of IFN-γ-producing MAIT1.
- Huishan Tao
- , Yun Pan
- & Xiao-Ping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analyses of Crohn’s disease tissues reveal intestinal intraepithelial T cells heterogeneity and altered subset distributions
Single-cell analyses of Crohn’s disease tissues reveal intestinal intraepithelial T cells heterogeneity and altered subset distributions
Crohn’s disease results from transmural inflammation in the gut, but analyses of local immune populations are still lacking. Here, the authors show, by combining multiple single-cell approaches, that intraepithelial and lamina propria T cells are heterogenous, show unique phenotypes, and exhibit altered subsets upon inflammation.
- Natalia Jaeger
- , Ramya Gamini
- & Marco Colonna
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell transcriptional profiling of human thymic stroma uncovers novel cellular heterogeneity in the thymic medulla
Single-cell transcriptional profiling of human thymic stroma uncovers novel cellular heterogeneity in the thymic medulla
The thymus supports T cell immunity by providing the environment for thymocyte differentiation. Here the authors profile human thymic stroma at the single cell level, identifying ionocytes as a new medullary population and defining tissue specific antigen expression in multiple stromal cell types.
- Jhoanne L. Bautista
- , Nathan T. Cramer
- & Audrey V. Parent
-
Article
| Open Access Co-stimulation with opposing macrophage polarization cues leads to orthogonal secretion programs in individual cells
Co-stimulation with opposing macrophage polarization cues leads to orthogonal secretion programs in individual cells
Macrophages can be polarized by in vitro culture stimuli into M1 or M2 cells, but microenvironments in vivo are more complex. Here the authors analyze cultured macrophages stimulated with a combination of M1 and M2 stimuli by single-cell RNA sequencing, machine learning, and single-cell secretion profiling to show a surprising level of heterogeneity of response.
- Andrés R. Muñoz-Rojas
- , Ilana Kelsey
- & Kathryn Miller-Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission
Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission
Anecdotal reports suggest potential severity and outcome differences between sexes following infection by SARS-CoV-2. Here, the authors perform meta-analyses of more than 3 million cases collected from global public data to demonstrate that male patients with COVID-19 are 3 times more likely to require intensive care, and have ~40% higher death rate.
- Hannah Peckham
- , Nina M. de Gruijter
- & Claire T. Deakin
-
Article
| Open Access Thymic iNKT single cell analyses unmask the common developmental program of mouse innate T cells
Thymic iNKT single cell analyses unmask the common developmental program of mouse innate T cells
Innate-like T cells such as invariant natural killer T (iNKT) and mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells both develop in the thymus. Here the authors use single-cell RNA sequencing to show that mouse iNKT and MAIT share components of developmental regulation, with a transcription factor, Hivep3, implicated for the maturation of both cell types.
- S. Harsha Krovi
- , Jingjing Zhang
- & Laurent Gapin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative modeling predicts mechanistic links between pre-treatment microbiome composition and metronidazole efficacy in bacterial vaginosis
Quantitative modeling predicts mechanistic links between pre-treatment microbiome composition and metronidazole efficacy in bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is typically caused by a shift in the vaginal microbiota from a Lactobacillus-dominant community to one colonised by strains of Gardenerella vaginalis and treatment with the antibiotic metronidazole (MNZ) often results in failure and recurrence. Here, the authors use modelling and in vitro assays to show that sequestration of MNZ by Lactobacillus is critical in reducing efficacy and women with a higher pre-treatment Lactobacillus/Gardnerella ratio are more likely to recur.
- Christina Y. Lee
- , Ryan K. Cheu
- & Kelly B. Arnold
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic elucidation of neuron-astrocyte interaction in models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using multi-modal integrated bioinformatics workflow
Systematic elucidation of neuron-astrocyte interaction in models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using multi-modal integrated bioinformatics workflow
Neuron-astrocyte communication plays a key role in pathophysiology, however systematic approaches to unveil it are limited. Here, the authors propose SEARCHIN, a multi-modal integrated workflow, as a tool to identify cross-compartment ligand-receptor interactions, applied to ALS models.
- Vartika Mishra
- , Diane B. Re
- & Serge Przedborski
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring and modeling of lymphocytic leukemia cell bioenergetics reveals decreased ATP synthesis during cell division
Monitoring and modeling of lymphocytic leukemia cell bioenergetics reveals decreased ATP synthesis during cell division
ATP drives most cellular processes, although ATP production and consumption levels during mitosis remain unreported. Here, the authors combine metabolic measurements and modeling to quantify ATP levels and synthesis dynamics, revealing that ATP synthesis and consumption are lowered during mitosis.
- Joon Ho Kang
- , Georgios Katsikis
- & Teemu P. Miettinen
-
Article
| Open Access Ontogeny of arterial macrophages defines their functions in homeostasis and inflammation
Ontogeny of arterial macrophages defines their functions in homeostasis and inflammation
Arterial macrophages develop from either yolk sac or bone marrow progenitors. Here, the author show that ageing-induced reduction of arterial macrophages is not replenished by bone marrow-derived cells, but under inflammatory conditions circulating monocytes are recruited to maintain homeostasis, while arterial macrophages of yolk sac origin carry out tissue repair.
- Tobias Weinberger
- , Dena Esfandyari
- & Christian Schulz
-
Article
| Open Access Generation, localization and functions of macrophages during the development of testis
Generation, localization and functions of macrophages during the development of testis
The developmental origins and functions of testis macrophages remain incompletely characterized. Here, the authors show, using histology, high-dimensional mass cytometry and cell fate-mapping data, that interstitial and peritubular macrophages originate from distinct precursors and contribute distinctly to spermatogenesis.
- Emmi Lokka
- , Laura Lintukorpi
- & Marko Salmi

 Cell-type-specific mRNA transcription and degradation kinetics in zebrafish embryogenesis from metabolically labeled single-cell RNA-seq
Cell-type-specific mRNA transcription and degradation kinetics in zebrafish embryogenesis from metabolically labeled single-cell RNA-seq