Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access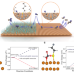 Ligand-modified nanoparticle surfaces influence CO electroreduction selectivity
Ligand-modified nanoparticle surfaces influence CO electroreduction selectivity
Enhancing the kinetics and selectivity of CO2/CO electroreduction towards valuable multi-carbon products poses a scientific challenge and is imperative for practical applicability. Here the authors report that modifying copper catalysts with surface thiol ligands significantly improves acetate selectivity.
- Erfan Shirzadi
- , Qiu Jin
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access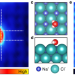 Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
Controlled dissolution of a single ion from a salt interface
The strong ionic bond in salt is broken by electrostatic interactions with water, but direct observation at the level of a single ion is challenging. Here, the authors have visualized the preferential dissolution of an anion by manipulating a single water molecule.
- Huijun Han
- , Yunjae Park
- & Hyung-Joon Shin
-
Article
| Open Access A Ce-CuZn catalyst with abundant Cu/Zn-OV-Ce active sites for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol
A Ce-CuZn catalyst with abundant Cu/Zn-OV-Ce active sites for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol
Carbon dioxide hydrogenation is an important industrial reaction. Here, the authors design a CeCuZn catalyst through a metal organic framework template for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol with excellent methanol yield and stability.
- Runping Ye
- , Lixuan Ma
- & Jian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access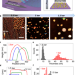 Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Molecules arranged in close proximity to a surface form molecular layers, exhibiting distinct properties. However, the creation of these layers is challenging. Here, the authors present a technique for generating molecular layers through crystallization induced by gas blowing onto a surface.
- Jincheng Tong
- , Nathan de Bruyn
- & Cinzia Casiraghi
-
Article
| Open Access Janus microparticles-based targeted and spatially-controlled piezoelectric neural stimulation via low-intensity focused ultrasound
Janus microparticles-based targeted and spatially-controlled piezoelectric neural stimulation via low-intensity focused ultrasound
Wireless and localized stimulation of neural cells remains challenging. Here, the authors propose piezoelectric magnetic Janus microparticles that can target and stimulate neurons under low-intensity ultrasound through voltage-gated ion channels.
- Mertcan Han
- , Erdost Yildiz
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface cyclization of vinyl groups on poly-para-phenylene involving an unusual pentagon to hexagon transformation
On-surface synthesis relies on carefully designed molecular precursors that are thermally activated to afford desired, covalently coupled architectures. Here, the authors study the intramolecular reactions of vinyl groups in a poly-para-phenylene-based model system and provide a comprehensive description of the reaction steps taking place on the Au(111) surface under ultrahigh vacuum conditions.
- Marco Di Giovannantonio
- , Zijie Qiu
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article
| Open Access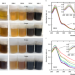 Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Transient chemical and structural changes in graphene oxide during ripening
Graphene oxide is in demand for various applications - however, this is complicated by changing physicochemical properties over time. Here, the authors show the intrinsic, metastable, and transient states of graphene oxide colloids upon ripening.
- Hayato Otsuka
- , Koki Urita
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
The efficiency of upconversion electroluminescence remains very low for single-molecule emitters. Here, the authors report over one order of magnitude improvement in the emission efficiency via engineering energy-level alignments for triplet relayed upconversion involving only carrier injection.
- Yang Luo
- , Fan-Fang Kong
- & Zhen-Chao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access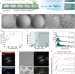 Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
Observing growth and interfacial dynamics of nanocrystalline ice in thin amorphous ice films
In-situ cryo-electron microscopy in thin amorphous ice films and ice-dynamics simulations reveal polymorph-dependent growth kinetics of nanoscale ice crystals. Hetero-crystalline ice exhibits anisotropic growth: fast-growing facets are associated with low-density interfaces, driving tetrahedral ordering of interfacial H2O molecules and accelerating ice growth.
- Minyoung Lee
- , Sang Yup Lee
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access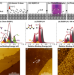 EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
Scanning tunnelling microscopy-based H desorption lithography is used for atomic-scale patterning of quantum devices in Si, but its time-consuming nature hinders scalability. Here the authors report H desorption from Si(001):H surface using extreme-UV light and explore implications for patterning.
- Procopios Constantinou
- , Taylor J. Z. Stock
- & Steven R. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Investigating the role of undercoordinated Pt sites at the surface of layered PtTe2 for methanol decomposition
Methanol on under-coordinated Pt sites at surface Te vacancies on layered PtTe2 decomposes at a probability >90 % which ultimately produces gaseous molecular hydrogen, methane, water and formaldehyde.
- Jing-Wen Hsueh
- , Lai-Hsiang Kuo
- & Meng-Fan Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Surface-confined alternating copolymerization with molecular precision by stoichiometric control
Surface-confined alternating copolymerization with molecular precision by stoichiometric control
Conventional sequence-controlled copolymerization often suffers from strict requirements on reaction kinetics of comonomer pairs and tedious synthetic processes. Here, the authors demonstrate a sequence-controlled alternating copolymerization with molecular precision on a Ag(111) surface under thermodynamic control of the polymerization selectivity.
- Lingbo Xing
- , Jie Li
- & Kai Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
Nanotexture-sensitive fracture focusing during magma fragmentation determines the surface chemistry of volcanic ash particles, thereby modifying the reactive interface and subsequent environmental impacts
- Adrian J. Hornby
- , Paul M. Ayris
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access Heparin-network-mediated long-lasting coatings on intravascular catheters for adaptive antithrombosis and antibacterial infection
Heparin-network-mediated long-lasting coatings on intravascular catheters for adaptive antithrombosis and antibacterial infection
Catheter-related infection and thrombosis are serious complications, and preventative coatings are not always suitable. Here, the authors report a heparin mediated coating for to address both infections and thrombosis from catheters simultaneously.
- Lin Liu
- , Huan Yu
- & Hengchong Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Controlling site-selectivity and reactivity in chemical reactions continues to be a key challenge in modern synthetic chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate the assembly of amino-substituted porphyrins on a water surface into J-aggregate structures in the presence of charged surfactants.
- Anupam Prasoon
- , Xiaoqing Yu
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Chemical identification of the building blocks of biopolymers often considerably relies on the presence of markers, extensive simulations, or is not possible at all. Here, the authors report a molecular probe-sensitisation approach addressing the identification of a specific amino acid within different peptides.
- Xu Wu
- , Bogdana Borca
- & Uta Schlickum
-
Article
| Open Access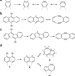 Local probe-induced structural isomerization in a one-dimensional molecular array
Local probe-induced structural isomerization in a one-dimensional molecular array
Achieving unit-by-unit isomerization within a molecular array poses a significant challenge in chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate tip-induced stereoisomerization of dehydroazulene and diradical units in three-dimensional organometallic compounds on Ag(111).
- Shigeki Kawai
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Adam S. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Supported CoOx catalysts display higher reactivities towards CO oxidation, yet, corresponding catalytically active phases are still unclear, especially under reaction conditions. Here, by means of in-situ APXPS and ResPES, the authors demonstrate that the topographic restructuring and chemical restructuring occur on these CoOx working catalysts, and also highlight the unique catalytic properties of Co3+ sites.
- Hao Chen
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Miquel Salmeron
-
Article
| Open Access Porphene and porphite as porphyrin analogs of graphene and graphite
Porphene and porphite as porphyrin analogs of graphene and graphite
Here the authors report Zn porphene, a member of a new organic metalloporphene family. Similar to graphene, these also are fully conjugated 2D polymers, but are composed of fused metalloporphyrin rings.
- Thomas F. Magnera
- , Paul I. Dron
- & Josef Michl
-
Article
| Open Access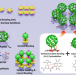 Extending on-surface synthesis from 2D to 3D by cycloaddition with C60
Extending on-surface synthesis from 2D to 3D by cycloaddition with C60
On-surface synthesis (OSS) defines a special opportunity to investigate intermolecular coupling at. sub-molecular level and has delivered many appealing polymers but so-far OSS is limited to the. lateral covalent bonding of molecular precursors. Here, the authors demonstrate cycloaddition. between C60 and an aromatic compound allowing covalent coupling perpendicular to the surface and multiple non-planar covalent coupling of C60.
- Pengcheng Ding
- , Shaoshan Wang
- & Miao Yu
-
Article
| Open Access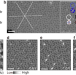 Strong signature of electron-vibration coupling in molecules on Ag(111) triggered by tip-gated discharging
Strong signature of electron-vibration coupling in molecules on Ag(111) triggered by tip-gated discharging
Electron-vibration coupling is driving advances in molecular electronics, spintronics, and quantum technology. Here, the authors succeeded in directly controlling vibronic excitations in tetrabromotetraazapyrene (TBTAP) molecules on the surface of Ag(111).
- Chao Li
- , Christoph Kaspar
- & Rémy Pawlak
-
Article
| Open Access Methyl radical chemistry in non-oxidative methane activation over metal single sites
Methyl radical chemistry in non-oxidative methane activation over metal single sites
Understanding of the direct methane conversion mechanism is essential for further development of efficient catalysts. Here, authors demonstrate a general methyl radical chemistry for metal single site catalysis regardless of the support (either zeolite or SiO2) in non-oxidative methane activation.
- Xin Huang
- , Daniel Eggart
- & Xinhe Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the role of interfacial water and key intermediates at ruthenium surfaces in the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction
Revealing the role of interfacial water and key intermediates at ruthenium surfaces in the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction
Here, the authors simultaneously capture dynamic Raman spectral evidence of Ru surfaces, interfacial water, *H and *OH intermediates, and the interactions between them, demonstrating the regulation of Ru valence state on interfacial water and intermediates for catalytic activity improvement.
- Xing Chen
- , Xiao-Ting Wang
- & Jian-Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access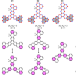 Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Orbital-symmetry effects on magnetic exchange in open-shell nanographenes
Nanographenes, as their name suggests, are small sections of graphene. They offer a diverse array of magnetic behaviors; for example, sublattice imbalances in the nanographene lead to unpaired spins. Here, Du et al uncover a large variation in the exchange energy in nanographenes, due to changes in the frontier orbital symmetries.
- Qingyang Du
- , Xuelei Su
- & Ping Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative study of Co3O4(111), CoFe2O4(111), and Fe3O4(111) thin film electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Comparative study of Co3O4(111), CoFe2O4(111), and Fe3O4(111) thin film electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Cobalt-based oxidic anodes with added iron are good electrocatalysts for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction, but the role of iron is still unclear. Here the authors investigate oxygen evolution reaction activity of three well-defined epitaxial thin-film electrodes to address this issue.
- Earl Matthew Davis
- , Arno Bergmann
- & Beatriz Roldan Cuenya
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality control of a single carbene molecule by tip-induced van der Waals interactions
Chirality control of a single carbene molecule by tip-induced van der Waals interactions
The control of molecular chirality is of great interest in stereochemistry and biochemistry. Here, the authors show how to alter the chirality dynamics of a single molecule through tip-induced van der Waals interactions.
- Yunjun Cao
- , Joel Mieres-Perez
- & Karina Morgenstern
-
Article
| Open Access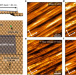 Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Revealing CO2 dissociation pathways at vicinal copper (997) interfaces
Catalytic CO2 dissociation pathways are selectively determined by surface geometry in heterogeneous catalysis. The authors find that the stepped Cu surfaces effectively affect CO2 activation in elementary reaction steps at the atomic level
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Youngseok Yu
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine plays an important role in living system. Here, the authors investigated the effect of the molecular chirality of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine on the improved structural and thermal stability of self-assembled films by tyrosinase-induced oxidative polymerization.
- Yuhe Shen
- , Rongxin Su
- & Wei Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Nonthermal acceleration of protein hydration by sub-terahertz irradiation
Nonthermal acceleration of protein hydration by sub-terahertz irradiation
The collective intermolecular dynamics of protein and water molecules, which overlap in subterahertz frequencies, are relevant for protein function expressions. Here the authors develop highly sensitive dielectric measurements, revealing that protein hydration is nonthermally accelerated by sub-terahertz irradiation.
- Jun-ichi Sugiyama
- , Yuji Tokunaga
- & Masahiko Imashimizu
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the reactivity of carbon surfaces with oxygen-containing functional groups
Tuning the reactivity of carbon surfaces with oxygen-containing functional groups
Distinguishing the influence of oxygen functional groups in carbon materials is important but elusive. Here, the authors combine experimental and machine learning techniques and reveal that phenolic groups are more acidic than carboxylic groups.
- Jiahua Zhou
- , Piaoping Yang
- & Dionisios G. Vlachos
-
Article
| Open Access Condensation and asymmetric amplification of chirality in achiral molecules adsorbed on an achiral surface
Condensation and asymmetric amplification of chirality in achiral molecules adsorbed on an achiral surface
The origin of homochirality in nature is an important but open question. Here, the authors provide insight into the physicochemical origin of homochirality through surface adsorption on the model of adlayers of achiral carbon monoxide molecules on an achiral Au(111) surface.
- Huiru Liu
- , Heping Li
- & Lan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable biomimetic nanochannels for on-demand SO2 detection by light-controlled photochromism
Switchable biomimetic nanochannels for on-demand SO2 detection by light-controlled photochromism
Conventional nanochannel sensors are passively responsive and may be slowly damaged by analytes present in the environment before detection. Here, authors developed a light-controlled inert/active-switchable biomimetic nanochannel sensor to achieve SO2 on-demand detection and long-term preservation.
- Dan Zhang
- , Yongjie Sun
- & Xuanjun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of electron orbital signatures of single atoms within metal-phthalocyanines using atomic force microscopy
Observation of electron orbital signatures of single atoms within metal-phthalocyanines using atomic force microscopy
Resolving the orbital structure of single atoms is challenging and of great importance for understanding basic chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate that the orbital occupation difference of single Fe/Co atoms within molecules can be distinguished with high resolution AFM imaging and spectroscopy.
- Pengcheng Chen
- , Dingxin Fan
- & Nan Yao
-
Article
| Open Access General approach to surface-accessible plasmonic Pickering emulsions for SERS sensing and interfacial catalysis
General approach to surface-accessible plasmonic Pickering emulsions for SERS sensing and interfacial catalysis
The preparation of Pickering emulsions from nanoparticles commonly requires modification of the particles’ surface chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate a chemical modifier-free approach for the preparation of long-term stable Pickering emulsions for SERS sensing and catalytic applications.
- Yingrui Zhang
- , Ziwei Ye
- & Yikai Xu
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of enetriynes
On-surface synthesis of enetriynes
Enetriynes, which belong to the enyne family, are characterized by a distinct electron-rich carbon-bonding scheme. Here, the authors report the formation of enetriynes with high selectivity by tetramerization of terminal alkynes on Ag(100).
- Nan Cao
- , Biao Yang
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article
| Open Access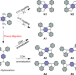 Real-space imaging of a phenyl group migration reaction on metal surfaces
Real-space imaging of a phenyl group migration reaction on metal surfaces
On-surface synthesis allows fabrication of nanostructures with atomic precision and may follow different routes compared to in-solution chemistry. Here the authors, using scanning probe microscopy techniques, observe a phenyl group migration reaction on three different metal surfaces forming polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which cannot be accessed by in-solution chemistry.
- Zilin Ruan
- , Baijin Li
- & Jinming Cai
-
Article
| Open Access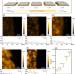 Steering carbon dioxide reduction toward C–C coupling using copper electrodes modified with porous molecular films
Steering carbon dioxide reduction toward C–C coupling using copper electrodes modified with porous molecular films
This study explores how the activity and selectivity of Cu electrodes for CO2 reduction can be tuned with organic films of different porosity and thickness. As a result, the films increase the local CO partial pressures and surface coverages.
- Siqi Zhao
- , Oliver Christensen
- & Kim Daasbjerg
-
Article
| Open Access Weak CO binding sites induced by Cu–Ag interfaces promote CO electroreduction to multi-carbon liquid products
Weak CO binding sites induced by Cu–Ag interfaces promote CO electroreduction to multi-carbon liquid products
Here, the authors demonstrate a Cu-based catalyst with Cu–Ag interfacial sites, which favor oxygenate over alcohol production in CO2 electroreduction. Near 80% selectivity for multi-carbon liquid products in a 100 cm2 membrane electrode assembly electrolyzer is exhibited over 100 h.
- Jing Li
- , Haocheng Xiong
- & Qi Lu
-
Article
| Open Access New insights in polydopamine formation via surface adsorption
New insights in polydopamine formation via surface adsorption
Polydopamine is a biomimetic self-adherent polymer, which can be easily deposited on a wide variety of materials but the polymerization mechanism and the key intermediate species formed during the deposition process are still controversial. Here, the authors report a systematic investigation of polydopamine formation on halloysite nanotubes.
- Hamoon Hemmatpour
- , Oreste De Luca
- & Petra Rudolf
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of accelerating hydrogen spillover via surface-lattice-confinement effect
Direct observation of accelerating hydrogen spillover via surface-lattice-confinement effect
Hydrogen spillover is a surface phenomenon encountered in catalytic reactions. Here the authors show that the surface-lattice-confinement effect can regulate the hydrogen spillover directions and accelerate spillover rates. It is intrinsically related to the local surface geometries and coordination numbers of surface O sites.
- Yijing Liu
- , Rankun Zhang
- & Qiang Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Structure sensitivity in gas sorption and conversion on metal-organic frameworks
Structure sensitivity in gas sorption and conversion on metal-organic frameworks
Probing gas sorption on defects and facets of porous materials at the nanoscale is challenging. Here, we visualize nano-domains of preferred formaldehyde sorption on (defective) ZIF-8 microcrystals using in situ Photo-induced Force Microscopy (PiFM).
- Guusje Delen
- , Matteo Monai
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical reaction-mediated covalent localization of bacteria
Chemical reaction-mediated covalent localization of bacteria
Transplantation of helpful bacteria has been used to treat disease through modulating host microbiota. Here, the authors report a strategy to control bacteria localization in the jejunum, via an in vivo in-situ thiol-disulfide exchange reaction between surface-reactive bacteria and mucous.
- Huilong Luo
- , Yanmei Chen
- & Jinyao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of long-range chirality transfer in a self-assembled supramolecular monolayer at interface in situ
Direct observation of long-range chirality transfer in a self-assembled supramolecular monolayer at interface in situ
Unravelling the mechanism of chirality transfer in supramolecular assemblies is important to understand the relationship between molecular chirality and supramolecular chirality. Here, the authors use nonlinear spectroscopy and molecular dynamic simulations to study the long-range chirality transfer in a self-assembled supramolecular system.
- Yuening Zhang
- , Xujin Qin
- & Zhen Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
Ba+2 ion trapping using organic submonolayer for ultra-low background neutrinoless double beta detector
One of the possible events signaling a neutrinoless double beta decay is a Xe atom decaying into a Ba ion and two electrons. Aiming at the realisation of a detector for such a process, the authors show that Ba ions can be efficiently trapped (chelated) in vacuum by an organic molecule layer on a surface.
- P. Herrero-Gómez
- , J. P. Calupitan
- & J. T. White
-
Article
| Open Access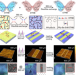 Photo-induced stress relaxation in reconfigurable disulfide-crosslinked supramolecular films visualized by dynamic wrinkling
Photo-induced stress relaxation in reconfigurable disulfide-crosslinked supramolecular films visualized by dynamic wrinkling
The mechanics of reconfigurable supramolecular polymer networks are governed by their dynamic crosslinking chemistry and the resulting stress relaxations. Here, the authors use reversible wrinkling patterns to visualize localized stress relaxations, due to molecular network rearrangements.
- Shuzhen Yan
- , Kaiming Hu
- & Xuesong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule binding to surface-supported single-site transition-metal reaction centres
Small molecule binding to surface-supported single-site transition-metal reaction centres
Surface-supported metalorganics promise the best of homogenous and heterogeneous catalysts. Here the authors show that small molecules bind to an iron-terpyridine site on silver via surface bound intermediates by following molecules one at a time.
- M. DeJong
- , A. J. A. Price
- & S. A. Burke
-
Article
| Open Access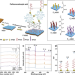 Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Fouling is a continuous challenge for the effective application of membranes in oily wastewater treatment. Here, the authors present a hydrophobic chain engineering strategy to regulate the surface of graphene oxide-based membranes at a molecular scale for increased antifouling even at high permeance.
- Chao Yang
- , Mengying Long
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access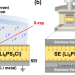 Effect of current density on the solid electrolyte interphase formation at the lithium∣Li6PS5Cl interface
Effect of current density on the solid electrolyte interphase formation at the lithium∣Li6PS5Cl interface
The interface between the Li metal electrode and inorganic solid electrolyte is crucial for developing reliable all-solid-state Li batteries. Here, the authors show that the Li plating current density distinctly affects the chemistry and morphology of interphase components formed at the interface.
- Sudarshan Narayanan
- , Ulderico Ulissi
- & Mauro Pasta
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Graphitic carbon nitride has long been considered a poor oxygen evolution catalyst. Here, the authors report a simple fluorination strategy to prevent the accumulation of inert C=O on carbon nitride to break through this bottleneck.
- Ji Wu
- , Zhonghuan Liu
- & Yongsheng Yan

 Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping
Topology selectivity of a conformationally flexible precursor through selenium doping