Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of single-stranded DNA annealing by RAD52–RPA complex
Mechanism of single-stranded DNA annealing by RAD52–RPA complex
Single-stranded DNA annealing is driven by RAD52 open rings in association with RPA.
- Chih-Chao Liang
- , Luke A. Greenhough
- & Stephen C. West
-
News & Views |
 Charles Darwin investigates: the curious case of primrose punishment
Charles Darwin investigates: the curious case of primrose punishment
Birds emerge as top suspects for unexplained flower mutilation, and reflections from 1974 mark the 21st anniversary of the discovery of the DNA double helix, in the weekly dip into Nature’s archive.
-
Article |
 Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor
Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor
We propose a model for a sequential, multistep activation mechanism of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5, including a series of structures in lipid nanodiscs, from inactive to fully active, with agonist-bound intermediate states.
- Kaavya Krishna Kumar
- , Haoqing Wang
- & Brian K. Kobilka
-
Article
| Open Access Streptomyces umbrella toxin particles block hyphal growth of competing species
Streptomyces umbrella toxin particles block hyphal growth of competing species
Streptomyces are discovered to produce antibacterial protein complexes that selectively inhibit the hyphal growth of related species, a function distinct from that of the small-molecule antibiotics they are known for.
- Qinqin Zhao
- , Savannah Bertolli
- & Joseph D. Mougous
-
Article |
 Promiscuous G-protein activation by the calcium-sensing receptor
Promiscuous G-protein activation by the calcium-sensing receptor
Structures of the human calcium-sensing receptor can be bound into complex with G proteins from three different Gα subtypes while maintaining G-protein-binding specificity.
- Hao Zuo
- , Jinseo Park
- & Qing R. Fan
-
News & Views |
 A step along the path towards AlphaFold — 50 years ago
A step along the path towards AlphaFold — 50 years ago
Paring down the astronomical complexity of the protein-folding problem, plus Isaac Newton’s ambiguous use of the word ‘axiom’, in the weekly dip into Nature’s archive.
-
News & Views |
 A bitter taste receptor activated in a surprising way
A bitter taste receptor activated in a surprising way
The sensing of bitter taste results from the complex interplay of many chemical cues and a range of receptors. It emerges that this complexity might be built-in even at the level of individual receptors.
- Antonella Di Pizio
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of fractal geometries in the evolution of a metabolic enzyme
Emergence of fractal geometries in the evolution of a metabolic enzyme
Citrate synthase from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus is shown to self-assemble into Sierpiński triangles, a finding that opens up the possibility that other naturally occurring molecular-scale fractals exist.
- Franziska L. Sendker
- , Yat Kei Lo
- & Georg K. A. Hochberg
-
Article |
 Bitter taste receptor activation by cholesterol and an intracellular tastant
Bitter taste receptor activation by cholesterol and an intracellular tastant
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the type 2 taste receptor TAS2R14 in complex with Ggust and Gi1 identify cholesterol as an orthosteric agonist and the bitter tastant cmpd28.1 as a positive allosteric modulator and agonist.
- Yoojoong Kim
- , Ryan H. Gumpper
- & Bryan L. Roth
-
Review Article |
 Bridging structural and cell biology with cryo-electron microscopy
Bridging structural and cell biology with cryo-electron microscopy
The interplay between cryo-electron microscopy and cryo-electron tomography to define complex macromolecular assemblies and visualize them in situ is explored.
- Eva Nogales
- & Julia Mahamid
-
Article |
 Mechanical activation opens a lipid-lined pore in OSCA ion channels
Mechanical activation opens a lipid-lined pore in OSCA ion channels
The molecular basis of OSCA/TMEM63 channel mechanosensitivity was investigated by determining 44 cryogenic electron microscopy structures of channels in different environments, expanding understanding of channel-mediated mechanotransduction and pore formation, with implications for two protein families.
- Yaoyao Han
- , Zijing Zhou
- & Yixiao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Integrator-dependent RNA polymerase II termination
Structural basis of Integrator-dependent RNA polymerase II termination
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human Integrator complex in three different functional states shed light on how Integrator terminates RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription by disengaging Pol II from the DNA template.
- Isaac Fianu
- , Moritz Ochmann
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Nature Podcast |
 How climate change is affecting global timekeeping
How climate change is affecting global timekeeping
Melting polar ice could delay major time adjustment, and the strange connection between brain inflammation and memory.
- Elizabeth Gibney
- & Nick Petrić Howe
-
Article |
 Structural basis of exoribonuclease-mediated mRNA transcription termination
Structural basis of exoribonuclease-mediated mRNA transcription termination
A study presents two cryo-EM structures of yeast Pol II pre-termination transcription complexes bound to Rat1–Rai1, and provides the mechanisms for termination of mRNA transcription in yeast and other eukaryotes.
- Yuan Zeng
- , Hong-Wei Zhang
- & Yu Zhang
-
News Feature |
 These ‘movies’ of proteins in action are revealing the hidden biology of cells
These ‘movies’ of proteins in action are revealing the hidden biology of cells
A burgeoning technique called time-resolved cryo-EM is granting insights into the tiny motors and devices that power life.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article |
 Structure and assembly of a bacterial gasdermin pore
Structure and assembly of a bacterial gasdermin pore
Cryo-electron microscopy and molecular dynamics studies of a Vitiosangium gasdermin pore reveal insights into the assembly of this large and diverse family of membrane pore-forming proteins.
- Alex G. Johnson
- , Megan L. Mayer
- & Philip J. Kranzusch
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of RAD51 assembled on nucleosomes containing a DSB site
Cryo-EM structures of RAD51 assembled on nucleosomes containing a DSB site
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of human RAD51 in complex with the nucleosome show that RAD51 can adopt two conformations—rings and filaments—and reveal how RAD51 binds to the nucleosome through its N-terminal lobe domain.
- Takuro Shioi
- , Suguru Hatazawa
- & Hitoshi Kurumizaka
-
News |
 ‘A landmark moment’: scientists use AI to design antibodies from scratch
‘A landmark moment’: scientists use AI to design antibodies from scratch
Modified protein-design tool could make it easier to tackle challenging drug targets — but AI antibodies are still a long way from reaching the clinic.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article
| Open Access Blueprinting extendable nanomaterials with standardized protein blocks
Blueprinting extendable nanomaterials with standardized protein blocks
A study describes an approach using designed building blocks that are far more regular in geometry than natural proteins to construct modular multicomponent protein assemblies.
- Timothy F. Huddy
- , Yang Hsia
- & David Baker
-
Article |
 Time-resolved cryo-EM of G-protein activation by a GPCR
Time-resolved cryo-EM of G-protein activation by a GPCR
Time-resolved cryo-EM is used to capture structural transitions during G-protein activation stimulated by a G-protein-coupled receptor.
- Makaía M. Papasergi-Scott
- , Guillermo Pérez-Hernández
- & Georgios Skiniotis
-
News |
 Could AI-designed proteins be weaponized? Scientists lay out safety guidelines
Could AI-designed proteins be weaponized? Scientists lay out safety guidelines
AI tools that can come up with protein structures at the push of a button should be used safely and ethically, say researchers in the field.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular basis of sugar detection by an insect taste receptor
The molecular basis of sugar detection by an insect taste receptor
A study reports structures of an insect taste receptor in the absence and presence of different sugars, providing details on the molecular basis of sugar detection and selectivity in insects.
- João Victor Gomes
- , Shivinder Singh-Bhagania
- & Joel A. Butterwick
-
Article |
 Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Structures of the yeast replisome associated with the FACT complex and an evicted histone hexamer offer insights into the mechanism of replication-coupled histone recycling for maintaining epigenetic inheritance.
- Ningning Li
- , Yuan Gao
- & Yuanliang Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Automated model building and protein identification in cryo-EM maps
Automated model building and protein identification in cryo-EM maps
ModelAngelo builds atomic models and identifies proteins with unknown sequences in cryo-EM maps.
- Kiarash Jamali
- , Lukas Käll
- & Sjors H. W. Scheres
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted protein degradation via intramolecular bivalent glues
Targeted protein degradation via intramolecular bivalent glues
Studies using genetic screening, biophysical characterization and structural reconstitution elucidate the mechanism of action and enable rational design of a new class of functional compounds that glue target proteins to E3 ligases via intramolecularly bridging two domains to enhance intrinsic protein–protein interactions and promote target ubiquitination and degradation.
- Oliver Hsia
- , Matthias Hinterndorfer
- & Alessio Ciulli
-
Article |
 UFM1 E3 ligase promotes recycling of 60S ribosomal subunits from the ER
UFM1 E3 ligase promotes recycling of 60S ribosomal subunits from the ER
Structural and biochemical analyses reveal details of how UFM1 conjugation and deconjugation mediate ribosome recycling and quality control.
- Paul A. DaRosa
- , Ivan Penchev
- & Ron R. Kopito
-
Article |
 Activation of Thoeris antiviral system via SIR2 effector filament assembly
Activation of Thoeris antiviral system via SIR2 effector filament assembly
A study reports that the Theoris anti-phage defence system is activated through helical filament assembly of the ThsA effector and details the activation mechanism.
- Giedre Tamulaitiene
- , Dziugas Sabonis
- & Virginijus Siksnys
-
Article
| Open Access The UFM1 E3 ligase recognizes and releases 60S ribosomes from ER translocons
The UFM1 E3 ligase recognizes and releases 60S ribosomes from ER translocons
Attachment of the ubiquitin-like modifier UFM1 to 60S ribosomes has a critical function in the release and recycling of stalled or terminated ribosomes from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
- Linda Makhlouf
- , Joshua J. Peter
- & Yogesh Kulathu
-
News & Views Forum |
 Energetic laser pulses alter outcomes of X-ray studies of proteins
Energetic laser pulses alter outcomes of X-ray studies of proteins
Cutting-edge X-ray sources have enabled the structural dynamics of proteins to be tracked during biochemical processes, but the findings have been questioned. Two experts discuss the implications of a study that digs into this issue.
- Richard Neutze
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access A new family of bacterial ribosome hibernation factors
A new family of bacterial ribosome hibernation factors
A study identifies a new bacterial ribosome hibernation factor, Balon, and describes its association with EF-Tu and its initiation of mRNA-independent hibernation during protein synthesis.
- Karla Helena-Bueno
- , Mariia Yu. Rybak
- & Sergey V. Melnikov
-
Article |
 Structure of human phagocyte NADPH oxidase in the activated state
Structure of human phagocyte NADPH oxidase in the activated state
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human phagocyte NADPH oxidase in the activated state provides insight into how cytosolic factors bind to and promote the activating conformational changes of NOX2, facilitating its efficient electron transfer.
- Xiaoyu Liu
- , Yiting Shi
- & Lei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of pump laser fluence on ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics
Influence of pump laser fluence on ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics
Ultrafast time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography is used to investigate a photodissociation reaction in a protein, revealing the strong impact of the pump laser fluence on the structural changes and the reaction mechanism.
- Thomas R. M. Barends
- , Alexander Gorel
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Article |
 Allosteric modulation and G-protein selectivity of the Ca2+-sensing receptor
Allosteric modulation and G-protein selectivity of the Ca2+-sensing receptor
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human calcium-sensing receptor in complex with Gi and Gq proteins reveal how this receptor activates distinct G protein subtypes and how its function is modulated by a variety of ligands.
- Feng He
- , Cheng-Guo Wu
- & Georgios Skiniotis
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of ribosomal 30S subunit degradation by RNase R
Structural basis of ribosomal 30S subunit degradation by RNase R
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of intermediates formed during the degradation of the 30S ribosomal unit shed light on how the 3′ to 5′ exonuclease ribonuclease R controls the ribosomal degradation process.
- Lyudmila Dimitrova-Paternoga
- , Sergo Kasvandik
- & Helge Paternoga
-
Article |
 Conformational ensembles of the human intrinsically disordered proteome
Conformational ensembles of the human intrinsically disordered proteome
A computational model generates conformational ensembles of 28,058 intrinsically disordered proteins and regions (IDRs) in the human proteome and sheds light on the relationship between sequence, conformational properties and functions of IDRs.
- Giulio Tesei
- , Anna Ida Trolle
- & Kresten Lindorff-Larsen
-
Technology Feature |
 Seven technologies to watch in 2024
Seven technologies to watch in 2024
Advances in artificial intelligence are at the heart of many of this year’s most exciting areas of technological innovation
- Michael Eisenstein
-
News & Views |
 Snapshots of genetic copy-and-paste machinery in action
Snapshots of genetic copy-and-paste machinery in action
LINE-1 DNA elements self-duplicate, inserting the copy into new regions of the genome — a key process in chromosome evolution. Structures of the machinery that performs this process in humans are now reported.
- Gael Cristofari
-
Article
| Open Access The CRISPR effector Cam1 mediates membrane depolarization for phage defence
The CRISPR effector Cam1 mediates membrane depolarization for phage defence
The prokaryotic non-enzymatic effector protein Cam1 mediates CRISPR immunity by binding tetra-adenylate second messengers and forming a pore in the membrane that induces membrane depolarization and growth arrest.
- Christian F. Baca
- , You Yu
- & Luciano A. Marraffini
-
Article
| Open Access A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter
A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter
A mechanism of lipid transport inhibition has been identified for a class of peptide antibiotics effective against resistant Acinetobacter strains, which may have applications in the inhibition of other Gram-negative pathogens.
- Karanbir S. Pahil
- , Morgan S. A. Gilman
- & Daniel Kahne
-
Article |
 Oldest thylakoids in fossil cells directly evidence oxygenic photosynthesis
Oldest thylakoids in fossil cells directly evidence oxygenic photosynthesis
We report the oldest direct evidence of thylakoid membranes in a parallel-to-contorted arrangement within the enigmatic cylindrical microfossils Navifusa majensis from the McDermott Formation, Tawallah Group, Australia (1.78–1.73 Ga).
- Catherine F. Demoulin
- , Yannick J. Lara
- & Emmanuelle J. Javaux
-
Research Briefing |
 High-resolution structures of two phosphatase–inhibitor complexes
High-resolution structures of two phosphatase–inhibitor complexes
Progression into the final phase of the cell cycle is driven mainly by protein phosphorylation, although it also requires the inhibition of phosphatase proteins, such as the PP2A:B55 complex. The structures reveal how PP2A:B55 binds to two of its inhibitors.
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the promoter-bound respiratory syncytial virus polymerase
Structures of the promoter-bound respiratory syncytial virus polymerase
A study reports cryogenic electron microscopy structures of the respiratory syncytial virus polymerase bound to its genomic and antigenomic viral RNA promoters.
- Dongdong Cao
- , Yunrong Gao
- & Bo Liang
-
Article
| Open Access The PfRCR complex bridges malaria parasite and erythrocyte during invasion
The PfRCR complex bridges malaria parasite and erythrocyte during invasion
Structural studies show how the PfRCR complex of Plasmodium falciparum forms a bridge between erythrocyte and parasite membranes, and how PfCyRPA-binding antibodies neutralize invasion through a steric mechanism, opening the way to new approaches in rational vaccine design.
- Brendan Farrell
- , Nawsad Alam
- & Matthew K. Higgins
-
Article
| Open Access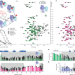 Cryo-EM structures of PP2A:B55–FAM122A and PP2A:B55–ARPP19
Cryo-EM structures of PP2A:B55–FAM122A and PP2A:B55–ARPP19
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the PP2A:B55 holoenzyme bound to its inhibitors ARPP19 and FAM122A show distinct binding modes of the two inhibitors.
- Sathish K. R. Padi
- , Margaret R. Vos
- & Wolfgang Peti
-
News & Views |
 How brine shrimps cope with salt
How brine shrimps cope with salt
Mutant ion pumps help brine shrimp survive highly saline waters.
- Lucia Brunello
-
Article
| Open Access Structures, functions and adaptations of the human LINE-1 ORF2 protein
Structures, functions and adaptations of the human LINE-1 ORF2 protein
X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, structural modelling, biochemistry, cell biology, and evolutionary analysis enable characterization of ORF2p, the reverse transcriptase of the ancient ‘parasitic’ LINE-1 retrotransposon that has written around one-third of the human genome.
- Eric T. Baldwin
- , Trevor van Eeuwen
- & Martin S. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access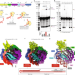 Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Human LINE-1 ORF2p relies on upstream single-stranded target DNA to position the adjacent duplex in the endonuclease active site for nicking of the longer DNA strand, with a single nick generating a staggered DNA break.
- Akanksha Thawani
- , Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza
- & Kathleen Collins
-
News & Views |
 Structures of the amphetamine-binding receptor will aid drug discovery
Structures of the amphetamine-binding receptor will aid drug discovery
High-resolution structures of TAAR1 — the receptor bound by amphetamines and molecules called trace amines — reveal detailed interactions with ligand molecules that will inform efforts to design antipsychotic drugs.
- Harald H. Sitte
-
Article |
 SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB, a lipoprotein in the PhoPQ stress regulon in Gram-negative bacteria, forms stable stress-induced complexes with the outer membrane proteome.
- Arne Janssens
- , Van Son Nguyen
- & Han Remaut
