Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Antisite occupation induced single anionic redox chemistry and structural stabilization of layered sodium chromium sulfide
Antisite occupation induced single anionic redox chemistry and structural stabilization of layered sodium chromium sulfide
The rational design of intercalation electrodes is largely confined to the optimization of redox chemistry of transition metals and oxygen. Here, the authors report the single anionic redox process in NaCrS2 where it is sulfur rather than chromium that works as the electrochemical active species.
- Zulipiya Shadike
- , Yong-Ning Zhou
- & Zheng-Wen Fu
-
Article
| Open Access A chip-integrated coherent photonic-phononic memory
A chip-integrated coherent photonic-phononic memory
Optical storage implementations based on optomechanical resonator are limited to one wavelength. Here, exploiting stimulated Brillouin scattering, the authors demonstrate a coherent optical memory based on a planar integrated waveguide, which can operate at different wavelengths without cross-talk.
- Moritz Merklein
- , Birgit Stiller
- & Benjamin J. Eggleton
-
Article
| Open Access Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Coalbeds produce natural gas, which has been observed to be enhanced by in situ microbes. Here, the authors add plant-derived carbohydrates (monosaccharides) to coal seams to be converted by indigenous microbes into natural gas, thus demonstrating a potential low carbon renewable natural gas resource.
- Zaixing Huang
- , Christine Sednek
- & Shengpin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tricritical wings and modulated magnetic phases in LaCrGe3 under pressure
Tricritical wings and modulated magnetic phases in LaCrGe3 under pressure
The study of phase transitions in quantum ferromagnets has shown that the approach to a continuous quantum ferromagnetic transition is typically interrupted by either a tricritical point or a new magnetic phase. Here the authors show that LaCrGe3 exhibits both these features in its phase diagram.
- Udhara S. Kaluarachchi
- , Sergey L. Bud’ko
- & Valentin Taufour
-
Article
| Open Access Direct measurement of strain-dependent solid surface stress
Direct measurement of strain-dependent solid surface stress
Solid surface stress is a fundamental property of solid interfaces. Here authors measure the solid surface stress of a gel, and show its dependence on surface strain through a surface modulus.
- Qin Xu
- , Katharine E. Jensen
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article
| Open Access Taming active turbulence with patterned soft interfaces
Taming active turbulence with patterned soft interfaces
Active nematics consist of self-driven components that develop orientational order and turbulent flow. Here Guillamat et al. investigate an active nematic constrained in a quasi-2D geometrical setup and show that there exists an intrinsic length scale that determines the geometry in all forcing regimes.
- P. Guillamat
- , J. Ignés-Mullol
- & F. Sagués
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature 2D semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
Room-temperature 2D semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
Two-dimensional materials have recently emerged as interesting materials for optoelectronic applications. Here, Shang et al. demonstrate two-dimensional semiconductor activated vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers where both the gain material and the lasing characteristics are two-dimensional.
- Jingzhi Shang
- , Chunxiao Cong
- & Ting Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible supercapacitor electrodes based on real metal-like cellulose papers
Flexible supercapacitor electrodes based on real metal-like cellulose papers
With ligand-mediated layer-by-layer assembly between metal nanoparticles and small organic molecules, the authors prepare metallic paper electrodes for supercapacitors with high power and energy densities. This approach could be extended to various electrodes for portable/wearable electronics.
- Yongmin Ko
- , Minseong Kwon
- & Jinhan Cho
-
Article
| Open Access A rechargeable iodine-carbon battery that exploits ion intercalation and iodine redox chemistry
A rechargeable iodine-carbon battery that exploits ion intercalation and iodine redox chemistry
Carbon-based electrodes able to intercalate Li+ and Na+ ions have been exploited for high performing energy storage devices. Here, the authors combine the ion intercalation properties of porous graphitic carbons with the redox chemistry of iodine to produce iodine–carbon batteries with high reversible capacities.
- Ke Lu
- , Ziyu Hu
- & Jintao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mergeable nervous systems for robots
Mergeable nervous systems for robots
Robots that can self-assemble into different morphologies are desired to perform tasks that require different physical capabilities. Mathews et al. design robots whose bodies and control systems can merge and split to form new robots that retain full sensorimotor control and act as a single entity.
- Nithin Mathews
- , Anders Lyhne Christensen
- & Marco Dorigo
-
Article
| Open Access Giant magnetoelectric effects achieved by tuning spin cone symmetry in Y-type hexaferrites
Giant magnetoelectric effects achieved by tuning spin cone symmetry in Y-type hexaferrites
Control of the electrical properties of materials by means of magnetic fields or vice versa may facilitate next-generation spintronic devices, but is still limited by their intrinsically weak magnetoelectric effect. Here, the authors report the existence of an enhanced magnetoelectric effect in a Y-type hexaferrite, and reveal its underlining mechanism.
- Kun Zhai
- , Yan Wu
- & Young Sun
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D magnetic tissue stretcher for remote mechanical control of embryonic stem cell differentiation
A 3D magnetic tissue stretcher for remote mechanical control of embryonic stem cell differentiation
The development of embryoid bodies that are responsive to external stimuli is of great interest in tissue engineering. Here, the authors culture embryonic stem cells with magnetic nanoparticles and show that the presence of magnetic fields could affect their aggregation and differentiation.
- Vicard Du
- , Nathalie Luciani
- & Claire Wilhelm
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of charge density waves and a pseudogap in single-layer TiTe2
Emergence of charge density waves and a pseudogap in single-layer TiTe2
Due to reduced dimensionality, the properties of 2D materials are often different from their 3D counterparts. Here, the authors identify the emergence of a unique charge density wave (CDW) order in monolayer TiTe2 that challenges the current understanding of CDW formation.
- P. Chen
- , Woei Wu Pai
- & T.-C. Chiang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular analogue of the perovskite repeating unit and evidence for direct MnIII-CeIV-MnIII exchange coupling pathway
Molecular analogue of the perovskite repeating unit and evidence for direct MnIII-CeIV-MnIII exchange coupling pathway
Perovskite manganites exhibit intriguing but poorly understood properties, including multiferroicity. Here, the authors synthesize a Ce3Mn8 cluster that structurally resembles a perovskite repeat unit, and use this molecular analogue to elucidate mechanisms driving bulk perovskite properties.
- Annaliese E. Thuijs
- , Xiang-Guo Li
- & George Christou
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent long-distance displacement of individual electron spins
Coherent long-distance displacement of individual electron spins
The spin states of electrons in quantum dots have well-established potential for use as qubits but some proposed developments require the ability to move the quantum spin state across a larger device. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate coherent shuttling of spins in a ring of three dots.
- H. Flentje
- , P.-A. Mortemousque
- & T. Meunier
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling selectivities in CO2 reduction through mechanistic understanding
Controlling selectivities in CO2 reduction through mechanistic understanding
Understanding the mechanism of CO2 reduction on a catalyst surface is essential for achieving the desired product selectivity. Here, the authors show an operando kinetic analysis of CO2 hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst in order to address the factors governing the selectivity of the process.
- Xiang Wang
- , Hui Shi
- & János Szanyi
-
Article
| Open Access Dichotomy between in-plane magnetic susceptibility and resistivity anisotropies in extremely strained BaFe2As2
Dichotomy between in-plane magnetic susceptibility and resistivity anisotropies in extremely strained BaFe2As2
Interplay between lattice, orbital, magnetic and nematic degrees of freedom is crucial for the superconductivity in Fe-based materials. Here, the authors demonstrate the subdominant roles of pure lattice distortions and/or orbital ordering in BaFe2As2 by characterizing the in-plane magnetic susceptibility anisotropy.
- Mingquan He
- , Liran Wang
- & Christoph Meingast
-
Article
| Open Access Microwaves effectively examine the extent and type of coking over acid zeolite catalysts
Microwaves effectively examine the extent and type of coking over acid zeolite catalysts
Catalyst deactivation by coke deposition is a major drawback in industrial processes. Here, the authors show a non-intrusive microwave cavity perturbation technique as a powerful tool to determine the nature and extent of coke accumulation in industrially-relevant zeolite catalysts.
- B. Liu
- , D. R. Slocombe
- & P. P. Edwards
-
Article
| Open Access 3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
Minerals are rarely explored as building blocks for dynamic inorganic materials. Here, the authors derive inspiration from fish scales to create mutable surfaces based on arrays of calcite crystals, in which one end of each crystal is immobilized in and regenerated from silicone, and the other functional end is left exposed.
- Jaeseok Yi
- , Yucai Wang
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-triggered solvent-free metamorphosis of polymeric materials
Photo-triggered solvent-free metamorphosis of polymeric materials
The design of organic and polymeric soft materials showing isothermal reversible liquid–nonliquid conversion is challenging. Here, the authors show solvent-free repeatable molecular architectural transformation between liquid-star and non-liquid-network polymers by the cleavage and reformation of covalent bonds in the polymer chain.
- Satoshi Honda
- & Taro Toyota
-
Article
| Open Access Observing a scale anomaly and a universal quantum phase transition in graphene
Observing a scale anomaly and a universal quantum phase transition in graphene
When the continuous scale symmetry of a quantum system is broken, anomalies occur which may lead to quantum phase transitions. Here, the authors provide evidence for such a quantum phase transition in the attractive Coulomb potential of vacancies in graphene, and further envision its universality for diverse physical systems.
- O. Ovdat
- , Jinhai Mao
- & E. Akkermans
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable carbon dioxide electroreduction coupled to carbonylation chemistry
Scalable carbon dioxide electroreduction coupled to carbonylation chemistry
Electroreduction of CO2 to CO is a potential valorisation pathway of carbon dioxide for fine chemicals production. Here, the authors show a user-friendly device that couples CO2 electroreduction with carbonylation chemistry for up to gram scale synthesis of pharmaceuticals even under atmospheric CO2.
- Mikkel T. Jensen
- , Magnus H. Rønne
- & Troels Skrydstrup
-
Article
| Open Access The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction
The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction
Nanocrystals display a variety of facets with different catalytic activity. Here the authors identify the most active facet of copper nanocrystals relevant to the low-temperature water gas shift reaction and further design zinc oxide-copper nanocubes with exceptionally high catalytic activity.
- Zhenhua Zhang
- , Sha-Sha Wang
- & Weixin Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent diffractive imaging of single helium nanodroplets with a high harmonic generation source
Coherent diffractive imaging of single helium nanodroplets with a high harmonic generation source
Diffraction imaging studies of free individual nanoparticles have so far been restricted to XUV and X-ray free - electron laser facilities. Here the authors demonstrate the possibility of using table-top XUV laser sources to image prolate shapes of superfluid helium droplets.
- Daniela Rupp
- , Nils Monserud
- & Arnaud Rouzée
-
Article
| Open Access Direct measurement of individual phonon lifetimes in the clathrate compound Ba7.81Ge40.67Au5.33
Direct measurement of individual phonon lifetimes in the clathrate compound Ba7.81Ge40.67Au5.33
Phonon lifetime is a fundamental parameter of thermal transport however its determination is challenging. Using inelastic neutron scattering and the neutron resonant spin-echo technique, Lory et al. determine the acoustic phonon lifetime in a single crystal of clathrate Ba7.81Ge40.67Au5.33.
- Pierre-François Lory
- , Stéphane Pailhès
- & Marc de Boissieu
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a beam loaded nanocoulomb-class laser wakefield accelerator
Demonstration of a beam loaded nanocoulomb-class laser wakefield accelerator
Higher beam quality and stability are desired in laser-plasma accelerators for their applications in compact light sources. Here the authors demonstrate in laser plasma wakefield electron acceleration that the beam loading effect can be employed to improve beam quality by controlling the beam charge.
- J. P. Couperus
- , R. Pausch
- & A. Irman
-
Article
| Open Access Conductance through a helical state in an Indium antimonide nanowire
Conductance through a helical state in an Indium antimonide nanowire
Indium antimonide nanowires have large spin-orbit coupling, which can give rise to helical states that are an important part of proposals for topological quantum computing. Here the authors measure conductance through the helical states and extract a larger spin-orbit energy than obtained before.
- J. Kammhuber
- , M. C. Cassidy
- & L. P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps
Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps
Capturing radioactive organic iodides from nuclear waste is important for safe nuclear energy usage, but remains a significant challenge. Here, Li and co-workers fabricate a stable metal–organic framework functionalized with tertiary amine groups that exhibits high capacities for radioactive organic iodides uptake.
- Baiyan Li
- , Xinglong Dong
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-degradable highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles for bio-medical imaging applications
Bio-degradable highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles for bio-medical imaging applications
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals, but cannot readily be excreted through the renal system. Here the authors show fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units that can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages.
- Tatjana Repenko
- , Anne Rix
- & Alexander J. C. Kuehne
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable inverted gap in monolayer quasi-metallic MoS2 induced by strong charge-lattice coupling
Tunable inverted gap in monolayer quasi-metallic MoS2 induced by strong charge-lattice coupling
MoS2 exhibits multiple electronic properties associated with different crystal structures. Here, the authors observe inverted and fundamental gaps through a designed annealing-based strategy, to induce a semiconductor-to-metal phase transition in monolayer-MoS2 on Au, facilitated by interfacial strain and electron transfer from Au to MoS2.
- Xinmao Yin
- , Qixing Wang
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrawide thermal free-carrier tuning of dielectric antennas coupled to epsilon-near-zero substrates
Ultrawide thermal free-carrier tuning of dielectric antennas coupled to epsilon-near-zero substrates
Achieving large tunability of subwavelength resonators is a central challenge in nanophotonics. Here the authors demonstrate refractive index tuning at mid-infrared wavelengths using temperature-dependent control over the low loss plasma frequency in III-V semiconductors.
- Prasad P. Iyer
- , Mihir Pendharkar
- & Jon A. Schuller
-
Article
| Open Access On the role of initial velocities in pair dispersion in a microfluidic chaotic flow
On the role of initial velocities in pair dispersion in a microfluidic chaotic flow
Elastic turbulence, a random-in-time flow, can drive efficient mixing in microfluidics. Using a 3D particle tracking method, the authors show that the smoothness assumption breaks at scales far smaller than believed and the ballistic pair dispersion holds over much longer distances than expected.
- Eldad Afik
- & Victor Steinberg
-
Article
| Open Access Self-supporting sulfur cathodes enabled by two-dimensional carbon yolk-shell nanosheets for high-energy-density lithium-sulfur batteries
Self-supporting sulfur cathodes enabled by two-dimensional carbon yolk-shell nanosheets for high-energy-density lithium-sulfur batteries
One of the challenges facing lithium-sulfur batteries is to develop cathodes with high mass and high volume loading. Here the authors show that two-dimensional carbon yolk-shell nanosheets are promising sulfur host materials, enabling stable battery cells with high energy density.
- Fei Pei
- , Lele Lin
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo quantitative imaging of tumor pH by nanosonophore assisted multispectral photoacoustic imaging
In vivo quantitative imaging of tumor pH by nanosonophore assisted multispectral photoacoustic imaging
Background optical absorption of several biomolecules impedes an effective in vivo pH imaging in tumors. Here, the authors developed a visible light-based in vivo pH mapping method by coupling photoacoustic imaging and pH-responsive modified nanoparticles that selectively target tumor cells.
- Janggun Jo
- , Chang H. Lee
- & Xueding Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Tunneling anisotropic magnetoresistance driven by magnetic phase transition
Tunneling anisotropic magnetoresistance driven by magnetic phase transition
Tunneling anisotropic magnetoresistance is promising for next generation memory devices but limited by the low efficiency and functioning temperature. Here the authors achieved 20% tunneling anisotropic magnetoresistance at room temperature in magnetic tunnel junctions with one α′-FeRh magnetic electrode.
- X. Z. Chen
- , J. F. Feng
- & F. Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Above-threshold scattering about a Feshbach resonance for ultracold atoms in an optical collider
Above-threshold scattering about a Feshbach resonance for ultracold atoms in an optical collider
Studies on energy-dependent scattering of ultracold atoms were previously carried out near zero collision energies. Here, the authors observe a magnetic Feshbach resonance in ultracold Rb collisions for above-threshold energies and their method can also be used to detect higher partial wave resonances.
- Milena S. J. Horvath
- , Ryan Thomas
- & Niels Kjærgaard
-
Article
| Open Access Alkaline earth metal vanadates as sodium-ion battery anodes
Alkaline earth metal vanadates as sodium-ion battery anodes
The development of suitable anode materials is essential to advance sodium-ion battery technologies. Here the authors report that alkaline earth metal vanadates are promising candidates due to the favorable electrochemical properties and interesting sodium-storage mechanism.
- Xiaoming Xu
- , Chaojiang Niu
- & Liqiang Mai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast isomerization in acetylene dication after carbon K-shell ionization
Ultrafast isomerization in acetylene dication after carbon K-shell ionization
The timescale of isomerization in molecules involving ultrafast migration of constituent atoms is difficult to measure. Here the authors report that sub-100 fs isomerization time on acetylene dication in lower electronic states is not possible and point to misinterpretation of recent experimental results.
- Zheng Li
- , Ludger Inhester
- & Todd J. Martinez
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen bond based smart polymer for highly selective and tunable capture of multiply phosphorylated peptides
Hydrogen bond based smart polymer for highly selective and tunable capture of multiply phosphorylated peptides
Capture of low-abundance multiply phosphorylated peptides (MPPs) is difficult due to limitation of enrichment materials and their interactions with phosphates. Here the authors show, a smart polymer driven by specific but tunable hydrogen bonding interactions can differentially complex with MPPs, singly phosphorylated and non-modified peptides.
- Guangyan Qing
- , Qi Lu
- & Taolei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon quantum processor with robust long-distance qubit couplings
Silicon quantum processor with robust long-distance qubit couplings
Quantum computers will require a large network of coherent qubits, connected in a noise-resilient way. Tosi et al. present a design for a quantum processor based on electron-nuclear spins in silicon, with electrical control and coupling schemes that simplify qubit fabrication and operation.
- Guilherme Tosi
- , Fahd A. Mohiyaddin
- & Andrea Morello
-
Article
| Open Access Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Lithium polysulfide batteries suffer from the precipitation of insoluble and irreversible sulfide species on the surface of carbon and lithium. Here the authors show a reactivation strategy by a reaction with cheap sulfur powder under stirring and heating to recover the cell capacity.
- Yang Jin
- , Guangmin Zhou
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Towards designer organelles by subverting the peroxisomal import pathway
Designer organelles could allow the isolation of synthetic biological pathways from endogenous components of the host cell. Here the authors engineer a peroxisomal protein import pathway orthogonal to the naturally occurring system.
- Laura L. Cross
- , Rupesh Paudyal
- & Stuart L. Warriner
-
Article
| Open Access Electron paramagnetic resonance microscopy using spins in diamond under ambient conditions
Electron paramagnetic resonance microscopy using spins in diamond under ambient conditions
Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy has important scientific and medical uses but improving the resolution of conventional methods requires cryogenic, vacuum environments. Simpson et al. show nitrogen vacancy centres can be used for sub-micronmetre imaging with improved sensitivity in ambient conditions.
- David A. Simpson
- , Robert G. Ryan
- & Lloyd C. L. Hollenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Exact broadband excitation of two-level systems by mapping spins to springs
Exact broadband excitation of two-level systems by mapping spins to springs
Coherent control of two-level systems is crucial for achieving fidelity in spectroscopy and quantum computing, but inherent nonlinearities and parameter variation have, to date, required an approximate, numerical approach. Here, Li et al. show how to map a spin ensemble to a spring model so analytic pulses can be designed using linear methods.
- Jr-Shin Li
- , Justin Ruths
- & Steffen J. Glaser
-
Article
| Open Access Observing the oxidation of platinum
Observing the oxidation of platinum
Improving platinum as an oxidation catalyst requires understanding its structure under catalytic conditions. Here, the authors discover that catalytically important surface oxides form only when Pt is exposed to high pressure and temperature, highlighting the need to study catalysts in realistic environments.
- Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- , Joost W. M. Frenken
- & Irene M. N. Groot
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of native peptide sequences in prebiotic replication networks
Emergence of native peptide sequences in prebiotic replication networks
The synthesis of biopolymers in living cells is perfected by complex machinery, however this was not the case on early Earth. Here the authors show the role of non-enzymatic replication in the enrichment of certain products within prebiotically relevant mixtures.
- Jayanta Nanda
- , Boris Rubinov
- & Gonen Ashkenasy
-
Article
| Open Access Unpredictability of escape trajectory explains predator evasion ability and microhabitat preference of desert rodents
Unpredictability of escape trajectory explains predator evasion ability and microhabitat preference of desert rodents
Biomechanical understanding of animal gait and maneuverability has primarily been limited to species with more predictable, steady-state movement patterns. Here, the authors develop a method to quantify movement predictability, and apply the method to study escape-related movement in several species of desert rodents.
- Talia Y. Moore
- , Kimberly L. Cooper
- & Ramanarayan Vasudevan
-
Article
| Open Access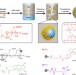 Higher-order assembly of crystalline cylindrical micelles into membrane-extendable colloidosomes
Higher-order assembly of crystalline cylindrical micelles into membrane-extendable colloidosomes
Functional nanoscale objects can be prepared via crystallization-driven self-assembly of diblock copolymers. Here the authors show the self-assembly of crystalline block copolymers into size-specific cylindrical micelles for the hierarchical construction of mechanically robust colloidosomes with a range of membrane textures.
- Hongjing Dou
- , Mei Li
- & Ian Manners
-
Article
| Open Access White light emission from a single organic molecule with dual phosphorescence at room temperature
White light emission from a single organic molecule with dual phosphorescence at room temperature
The development of single molecule white light-emitters is extremely challenging for pure phosphorescent metal-free systems at room temperature. Here the authors show a single pure organic room temperature phosphor, 4-chlorobenzoyldibenzothiophene, utilizing the emission from both T1 and T2 states.
- Zikai He
- , Weijun Zhao
- & Ben Zhong Tang

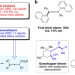 Organocatalytic synthesis of chiral tetrasubstituted allenes from racemic propargylic alcohols
Organocatalytic synthesis of chiral tetrasubstituted allenes from racemic propargylic alcohols