Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial chemotaxis in a microfluidic T-maze reveals strong phenotypic heterogeneity in chemotactic sensitivity
Bacterial chemotaxis in a microfluidic T-maze reveals strong phenotypic heterogeneity in chemotactic sensitivity
Chemotaxis is usually considered as a trait of a species or population. Here, the authors use a microfluidics device to reveal that clonal E. coli show individual variation in a key aspect of chemotactic behavior.
- M. Mehdi Salek
- , Francesco Carrara
- & Roman Stocker
-
Article
| Open Access Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata
Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata
Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea are major producers of the gases nitrous oxide and nitric oxide. Here, Kits et al. show that a complete ammonia-oxidizing (comammox) bacterium emits nitrous oxide at levels that are comparable to those produced by ammonia-oxidizing archaea.
- K. Dimitri Kits
- , Man-Young Jung
- & Holger Daims
-
Article
| Open Access Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Gouldian finches have a head colour polymorphism that is also associated with physiological and behavioural differentiation. Here, the authors map this colour polymorphism to a putative regulatory region for follistatin on the Z chromosome and suggest it is maintained by balancing selection.
- Kang-Wook Kim
- , Benjamin C. Jackson
- & Terry Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic potential of uncultured bacteria and archaea associated with petroleum seepage in deep-sea sediments
Metabolic potential of uncultured bacteria and archaea associated with petroleum seepage in deep-sea sediments
Little is known about the microbial ecology of the deep seabed. Here, Dong et al. predict metabolic capabilities and microbial interactions in deep seabed petroleum seeps using shotgun metagenomics, sediment geochemistry, metabolomics, and thermodynamic modelling.
- Xiyang Dong
- , Chris Greening
- & Casey R. J. Hubert
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Conservation decisions to protect land used by migratory birds rely on understanding species’ dynamic habitat associations. Here the authors identify conservation scenarios needed to maintain >30% of the abundances of 117 migratory birds across the Americas, considering spatial and temporal patterns of species abundance.
- Richard Schuster
- , Scott Wilson
- & Joseph. R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China
Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China
Whether or not China can be rice self-sufficient in the future is in question. Here the authors provide a spatially explicit yield-gap analysis of Chinese rice production under future scenarios, identifying priority areas for improving yields to meet demands by 2030.
- Nanyan Deng
- , Patricio Grassini
- & Shaobing Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Diel population and functional synchrony of microbial communities on coral reefs
Diel population and functional synchrony of microbial communities on coral reefs
Microbes structure biogeochemical cycles and food webs in the marine environment. Here, the authors sample coral reef-associated microbes across a 24-hour period, showing clear day–night patterns of microbial populations and thus calling for more studies to consider temporal variation in microbiomes at this scale.
- Linda Wegley Kelly
- , Craig E. Nelson
- & Forest Rohwer
-
Article
| Open Access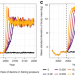 Early warning signals of recovery in complex systems
Early warning signals of recovery in complex systems
While several studies have documented early warning signals of population collapse, the use of such signals as indicators of population recovery has not been investigated. Here the authors use models and empirical fisheries data to show that there are statistical indicators preceding recovery of cod populations.
- Christopher F. Clements
- , Michael A. McCarthy
- & Julia L. Blanchard
-
Article
| Open Access The sponge microbiome within the greater coral reef microbial metacommunity
The sponge microbiome within the greater coral reef microbial metacommunity
Here the authors holistically examine prokaryote communities associated with diverse coral reef hosts, including sponges, nudibranchs, sea cucumbers, and corals. The results show that sponges have a relatively low diversity of prokaryotes, most of which are shared across a wide range of host taxa rather than being sponge-specific.
- Daniel F. R. Cleary
- , Thomas Swierts
- & Nicole J. de Voogd
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive individual variation in phenological responses to perceived predation levels
Adaptive individual variation in phenological responses to perceived predation levels
For phenotypic plasticity to evolve to a changing world, there must be variation in plasticity. Here, the authors show that whether great tits advance or delay breeding in response to perceived predation risk depends on their personality, linking variation in plasticity with that in personality.
- Robin N. Abbey-Lee
- & Niels J. Dingemanse
-
Article
| Open Access More frequent extreme climate events stabilize reindeer population dynamics
More frequent extreme climate events stabilize reindeer population dynamics
Extreme climate events can cause population crashes and may threaten population persistence. Here, the authors model reindeer population dynamics and find that more frequent extremely icy winters can actually reduce extinction risk due to density dependence and a demographic shift to resilient ages.
- Brage B. Hansen
- , Marlène Gamelon
- & Vidar Grøtan
-
Article
| Open Access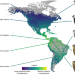 Ecological and geographical overlap drive plumage evolution and mimicry in woodpeckers
Ecological and geographical overlap drive plumage evolution and mimicry in woodpeckers
Many abiotic and biotic factors shape the macroevolution of phenotype, but these factors are rarely disentangled across large radiations. Here, Miller et al. investigate plumage evolution across woodpeckers, finding influences of habitat and climate, but also convergence apparently driven by mimicry
- Eliot T. Miller
- , Gavin M. Leighton
- & Russell A. Ligon
-
Article
| Open Access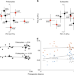 Root traits and belowground herbivores relate to plant–soil feedback variation among congeners
Root traits and belowground herbivores relate to plant–soil feedback variation among congeners
Most studies of plant–soil feedbacks and associated traits look at remotely-related species. Here the authors look at congeners, and show that nematode-driven plant–soil feedbacks depend on root chemical and morphological traits, independent of phylogenetic distance.
- Rutger A. Wilschut
- , Wim H. van der Putten
- & Stefan Geisen
-
Article
| Open Access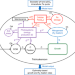 Reduced nitrogenase efficiency dominates response of the globally important nitrogen fixer Trichodesmium to ocean acidification
Reduced nitrogenase efficiency dominates response of the globally important nitrogen fixer Trichodesmium to ocean acidification
Findings regarding the impacts of ocean acidification (OA) on the growth and N2 fixation of Trichodesmium are conflicted. Here, the authors find that Trichodesmium growth rates decrease under OA primarily due to reduced nitrogenase efficiency and OA under RCP 8.5 could reduce the N2 fixation potential of Trichodesmium by 27%.
- Ya-Wei Luo
- , Dalin Shi
- & Futing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Nitrogen-fixing trees could exacerbate climate change under elevated nitrogen deposition
Nitrogen-fixing trees could exacerbate climate change under elevated nitrogen deposition
The balance between CO2 sequestration by forests and soil N2O emissions is poorly constrained. Here, the authors use a theoretical model to demonstrate that symbiotic N2-fixing trees can either mitigate climate change or exacerbate it relative to non-fixing trees.
- Sian Kou-Giesbrecht
- & Duncan Menge
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis reveals that pollinator functional diversity and abundance enhance crop pollination and yield
Meta-analysis reveals that pollinator functional diversity and abundance enhance crop pollination and yield
Pollinator communities could have nuanced effects on crop yield depending on their species and functional trait compositions. Here, the authors use a meta-analysis to show that, in addition to pollinator abundance, functional trait divergence also positively impacts yield of oilseed rape crops.
- B. A. Woodcock
- , M. P. D. Garratt
- & R. F. Pywell
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple plant diversity components drive consumer communities across ecosystems
Multiple plant diversity components drive consumer communities across ecosystems
Here, Schuldt et al. collate data from two long-term grassland and forest biodiversity experiments to ask how plant diversity facets affect the diversity of higher trophic levels. The results show that positive effects of plant diversity on consumer diversity are mediated by plant structural and functional diversity, and vary across ecosystems and trophic levels.
- Andreas Schuldt
- , Anne Ebeling
- & Nico Eisenhauer
-
Article
| Open Access Uncertainty in ensembles of global biodiversity scenarios
Uncertainty in ensembles of global biodiversity scenarios
Attaining global biodiversity projections requires the use of various species distribution and climate modelling and scenario approaches. Here the authors report that model choice can significantly impact results, with particularly uncertainty arising from choice of species distribution model and emission scenario.
- Wilfried Thuiller
- , Maya Guéguen
- & Niklaus E. Zimmermann
-
Article
| Open Access Prominence of the tropics in the recent rise of global nitrogen pollution
Prominence of the tropics in the recent rise of global nitrogen pollution
Nitrogen pollution is influenced by many stressors, and their combined effects are poorly constrained. Here the authors used a global land biosphere model to analyse the past two and a half centuries of land N pollution budgets and fluxes to the ocean and atmosphere and found that land sequesters 11% of global annual reactive N inputs.
- Minjin Lee
- , Elena Shevliakova
- & P. C. D. Milly
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread losses of pollinating insects in Britain
Widespread losses of pollinating insects in Britain
Pollinator loss is a concern but data on their status is lacking. Here Powney et al. use occupancy modelling to estimate the degree of loss in wild bee and hoverfly species across Great Britain, and report a 55% decline in upland species and a 12% increase in dominant crop pollinators.
- Gary D. Powney
- , Claire Carvell
- & Nick J. B. Isaac
-
Article
| Open Access Hurricane María tripled stem breaks and doubled tree mortality relative to other major storms
Hurricane María tripled stem breaks and doubled tree mortality relative to other major storms
Given the potential for increasingly common and intense tropical storms, it is important to understand their effects on island forest communities. Here, the authors show that Hurricane María’s strength and rainfall had larger effects on tree mortality than other less severe storms, and that large trees and species with low-density wood were most susceptible.
- María Uriarte
- , Jill Thompson
- & Jess K. Zimmerman
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis shows positive effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and respiration
Meta-analysis shows positive effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and respiration
The effect of plant biodiversity on microbial function has been tested in limited studies and is likely to be context-dependent. In this meta-analysis of 106 prior studies comparing plant monocultures to mixtures, the authors find that plant diversity increases microbial biomass and respiration rates, an effect moderated by stand age.
- Chen Chen
- , Han Y. H. Chen
- & Zhiqun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Breeders that receive help age more slowly in a cooperatively breeding bird
Breeders that receive help age more slowly in a cooperatively breeding bird
Sociality explains substantial variation in ageing across species, but less is known about this relationship within species. Here, the authors show that female dominant Seychelles warblers with helpers at the nest have higher late-life survival and lower telomere attrition and the probability of having helpers increases with age.
- Martijn Hammers
- , Sjouke A. Kingma
- & David S. Richardson
-
Article
| Open Access Female genitalia can evolve more rapidly and divergently than male genitalia
Female genitalia can evolve more rapidly and divergently than male genitalia
Although male genital shape is known to evolve rapidly in response to sexual selection, relatively little is known about the evolution of female genital shape. Here, the authors show that across onthophagine dung beetles, female genital shape has diverged much more rapidly than male genital shape.
- Leigh W. Simmons
- & John L. Fitzpatrick
-
Article
| Open Access Dispersal homogenizes communities via immigration even at low rates in a simplified synthetic bacterial metacommunity
Dispersal homogenizes communities via immigration even at low rates in a simplified synthetic bacterial metacommunity
Fodelianakis et al. examine the role of immigration and selection as the means of community homogenisation in a bacterial metacommunity. They confirmed the role of immigration in homogenisation, even when immigration was four times slower than growth.
- Stilianos Fodelianakis
- , Alexander Lorz
- & Daniele Daffonchio
-
Article
| Open Access Stronger influence of anthropogenic disturbance than climate change on century-scale compositional changes in northern forests
Stronger influence of anthropogenic disturbance than climate change on century-scale compositional changes in northern forests
Separating anthropogenic and climatic impacts on forest compositions can be challenging due to a lack of data. Here the authors look at forest compositional changes in eastern Canada since the 19th century and find land use has most strongly shaped communities towards disturbance-adapted species.
- Victor Danneyrolles
- , Sébastien Dupuis
- & Dominique Arseneault
-
Article
| Open Access A global analysis of coral bleaching over the past two decades
A global analysis of coral bleaching over the past two decades
Coral bleaching is generally linked to higher sea temperatures, but there may be geographic variation in this effect. Here, in a synthesis of global coral bleaching data, the authors show that bleaching probability is highest at mid-latitude sites despite equivalent thermal stress at equatorial sites.
- S. Sully
- , D. E. Burkepile
- & R. van Woesik
-
Article
| Open Access Foliar-feeding insects acquire microbiomes from the soil rather than the host plant
Foliar-feeding insects acquire microbiomes from the soil rather than the host plant
Leaf-feeding insect microbiomes could be influenced by the soil, the plant, or a product of the two. Here, the authors conduct a series of experiments to show that an herbivorous insect predominantly acquires its microbiome from the soil rather than the plant, and that these insect microbiomes reflect soil legacies of earlier growing plants.
- S. Emilia Hannula
- , Feng Zhu
- & T. Martijn Bezemer
-
Article
| Open Access Patterns of satellite tagged hen harrier disappearances suggest widespread illegal killing on British grouse moors
Patterns of satellite tagged hen harrier disappearances suggest widespread illegal killing on British grouse moors
Tackling wildlife crimes requires determining their occurrence and distribution, but they are often difficult to detect. Here, the authors use hen harrier tracking data to show patterns of unexpected tag failure that suggest widespread illegal killing on moors managed for recreational shooting of red grouse.
- Megan Murgatroyd
- , Stephen M. Redpath
- & Arjun Amar
-
Article
| Open Access Plant diversity alters the representation of motifs in food webs
Plant diversity alters the representation of motifs in food webs
Plant diversity affects ecosystem function in myriad ways, but the effect on food webs has received less investigation. Here, the authors use high-resolution food web data from a grassland diversity experiment to show that apparent and exploitative competition motifs increase with plant diversity.
- Darren P. Giling
- , Anne Ebeling
- & Jes Hines
-
Article
| Open Access Life habits and evolutionary biology of new two-winged long-proboscid scorpionflies from mid-Cretaceous Myanmar amber
Life habits and evolutionary biology of new two-winged long-proboscid scorpionflies from mid-Cretaceous Myanmar amber
Long-proboscid scorpionflies were associated with mid-Mesozoic gymnosperm pollination. Here, Lin et al. establish a new family of long-proboscid scorpionflies from Myanmar amber, elucidate evolutionary mechanisms of hind-wing reduction, and detail feeding and reproductive habits of these insects.
- Xiaodan Lin
- , Conrad C. Labandeira
- & Dong Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic marine viral infections and major contribution to photosynthetic processes shown by spatiotemporal picoplankton metatranscriptomes
Dynamic marine viral infections and major contribution to photosynthetic processes shown by spatiotemporal picoplankton metatranscriptomes
Here, Sieradzki et al. use metatranscriptomics to study active community-wide viral infections at three coastal California sites throughout a year, identify potential viral hosts, and show that viruses can contribute a substantial amount to photosystem-II psbA expression.
- Ella T. Sieradzki
- , J. Cesar Ignacio-Espinoza
- & Jed A. Fuhrman
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse resource allocation between vision and olfaction across the genus Drosophila
Inverse resource allocation between vision and olfaction across the genus Drosophila
Neural architecture may be shaped by selection, but is likely also constrained by development. Here, Keesey and colleagues find an inverse relationship between allocation towards visual and olfactory sensory systems across the genus Drosophila, which may reflect a developmental trade-off.
- Ian W. Keesey
- , Veit Grabe
- & Bill S. Hansson
-
Article
| Open Access Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage
Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage
Obtaining data on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) from healthy human populations is difficult. Here, Hendriksen et al. use metagenomic analysis to obtain AMR data from untreated sewage from 79 sites in 60 countries, finding correlations with socio-economic, health and environmental factors.
- Rene S. Hendriksen
- , Patrick Munk
- & Frank M. Aarestrup
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent national-scale trends of microbial and animal biodiversity revealed across diverse temperate soil ecosystems
Divergent national-scale trends of microbial and animal biodiversity revealed across diverse temperate soil ecosystems
It is unclear whether microbes and animals residing in soils follow similar distribution patterns. Here, the authors report richness and diversity of soil microbes and invertebrates across soil, vegetation, and land use gradients in Wales, showing that land use affects animals while soil traits affect microbes.
- Paul B. L. George
- , Delphine Lallias
- & Davey L. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Ecological niche modelling does not support climatically-driven dinosaur diversity decline before the Cretaceous/Paleogene mass extinction
Ecological niche modelling does not support climatically-driven dinosaur diversity decline before the Cretaceous/Paleogene mass extinction
The fossil record shows a decline in dinosaur diversity preceding their mass extinction. Here, the authors apply ecological niche modelling to show that suitable dinosaur habitat was declining in areas with present-day rock-outcrop, but not across North America as a whole, possibly generating sampling bias in the fossil record.
- Alfio Alessandro Chiarenza
- , Philip D. Mannion
- & Peter A. Allison
-
Article
| Open Access Modularity and predicted functions of the global sponge-microbiome network
Modularity and predicted functions of the global sponge-microbiome network
Lurgi et al. analyse the distribution of microbial symbionts across many sponge species and reveal modules of non-random associations which are primarily driven by host features and microbial phylogenies, and less by the environment. Results also show that metabolic functions are distinct across modules.
- Miguel Lurgi
- , Torsten Thomas
- & Jose M. Montoya
-
Article
| Open Access A snapshot of biodiversity protection in Antarctica
A snapshot of biodiversity protection in Antarctica
Antarctic biodiversity is increasingly under threat. Here, Wauchope et al. provide a continent-wide assessment of its terrestrial biodiversity, and find biodiversity protection is regionally uneven and biased towards easily detectable and charismatic species.
- Hannah S. Wauchope
- , Justine D. Shaw
- & Aleks Terauds
-
Article
| Open Access On the predictability of infectious disease outbreaks
On the predictability of infectious disease outbreaks
Forecasting of infectious disease outbreaks can inform appropriate intervention measures, but whether fundamental limits to accurate prediction exist is unclear. Here, the authors use permutation entropy as a model independent measure of predictability to study limitations across a broad set of infectious diseases.
- Samuel V. Scarpino
- & Giovanni Petri
-
Article
| Open Access Ediacaran biozones identified with network analysis provide evidence for pulsed extinctions of early complex life
Ediacaran biozones identified with network analysis provide evidence for pulsed extinctions of early complex life
The Ediacara biota—the first large, complex organisms to evolve on Earth—disappeared prior to the radiation of animals during the Cambrian Period. Here, Muscente et al. perform network analysis of Ediacaran fossils and show that there were two global extinction events before the Cambrian radiation.
- A. D. Muscente
- , Natalia Bykova
- & Andrew H. Knoll
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: “Global conservation of phylogenetic diversity captures more than just functional diversity”
- Florent Mazel
- , Matthew W. Pennell
- & William D. Pearse
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Global conservation of phylogenetic diversity captures more than just functional diversity
Global conservation of phylogenetic diversity captures more than just functional diversity
- Nisha R. Owen
- , Rikki Gumbs
- & Daniel P. Faith
-
Article
| Open Access Decadal biomass increment in early secondary succession woody ecosystems is increased by CO2 enrichment
Decadal biomass increment in early secondary succession woody ecosystems is increased by CO2 enrichment
It is unclear whether CO2-stimulation of photosynthesis can propagate through slower ecosystem processes and lead to long-term increases in terrestrial carbon. Here the authors show that CO2-stimulation of photosynthesis leads to a 30% increase in forest regrowth over a decade of CO2 enrichment.
- Anthony P. Walker
- , Martin G. De Kauwe
- & Richard J. Norby
-
Article
| Open Access Numerous cultivated and uncultivated viruses encode ribosomal proteins
Numerous cultivated and uncultivated viruses encode ribosomal proteins
Viruses can encode genes that regulate the host's translational machinery to their advantage. Here, the authors show that viruses encode ribosomal proteins that can be incorporated into the host’s ribosome and may affect translation.
- Carolina M. Mizuno
- , Charlotte Guyomar
- & Mart Krupovic
-
Article
| Open Access Soil carbon sequestration accelerated by restoration of grassland biodiversity
Soil carbon sequestration accelerated by restoration of grassland biodiversity
Abandoned and degraded agricultural lands undergo ecological succession that sequesters atmospheric CO2 as soil carbon, but at low rates. Here the authors show that restoration of high plant diversity provides a greenhouse gas benefit by greatly increasing the rate of soil carbon sequestration on such lands.
- Yi Yang
- , David Tilman
- & Clarence Lehman
-
Article
| Open Access Clothianidin seed-treatment has no detectable negative impact on honeybee colonies and their pathogens
Clothianidin seed-treatment has no detectable negative impact on honeybee colonies and their pathogens
There has been a lack of multi-year landscape-scale studies on the effect of neonicotinoids on honeybee health. Here, Osterman et al. show that clothianidin exposure via seed-treated rapeseed has no negative impact on honeybee colony development, microbial pathogens/symbionts or immune gene expression.
- Julia Osterman
- , Dimitry Wintermantel
- & Joachim R. de Miranda
-
Article
| Open Access Ecosystem structural changes controlled by altered rainfall climatology in tropical savannas
Ecosystem structural changes controlled by altered rainfall climatology in tropical savannas
Changing rainfall patterns may drive changes in the structure of tropical savanna. Here Zhang et al. use satellite data from global tropical savannas, and find evidence to suggest that altered rainfall may be favouring woody plants over herbaceous plants in these ecosystems.
- Wenmin Zhang
- , Martin Brandt
- & Rasmus Fensholt
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary highways to persistent bacterial infection
Evolutionary highways to persistent bacterial infection
The pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa undergoes complex trait adaptation within cystic fibrosis patients. Here, Bartell, Sommer, and colleagues use statistical modeling of longitudinal isolates to characterize the joint genetic and phenotypic evolutionary trajectories of P. aeruginosa within hosts.
- Jennifer A. Bartell
- , Lea M. Sommer
- & Helle Krogh Johansen
-
Article
| Open Access The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
The coevolution of lifespan and reversible plasticity
Reversible phenotypic plasticity is expected to be favoured by long lifespan, as this increases the environmental variation individuals experience. Here, the authors develop a model showing how phenotypic plasticity can drive selection on lifespan, leading to coevolution of these traits.
- Irja I. Ratikainen
- & Hanna Kokko
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

 Water quality improvements offset the climatic debt for stream macroinvertebrates over twenty years
Water quality improvements offset the climatic debt for stream macroinvertebrates over twenty years