Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution of early paclitaxel biosynthetic network
Reconstitution of early paclitaxel biosynthetic network
Paclitaxel is an important anticancer drug whose biosynthetic pathway reconstruction is hindered by the propensity of heterologously expressed pathway cytochromes P450, including taxadiene 5α-hydroxylase (T5αH), to form multiple products. Here, the authors tune the promoter strength for T5αH expression in Nicotiana plants to increase the levels of paclitaxel precursor taxadien-5α-ol by three-fold and reconstitute the six step early biosynthetic pathway of paclitaxel.
- Jack Chun-Ting Liu
- , Ricardo De La Peña
- & Elizabeth S. Sattely
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered regions in proteusin peptides guide post-translational modification by a flavin-dependent RiPP brominase
Disordered regions in proteusin peptides guide post-translational modification by a flavin-dependent RiPP brominase
Here the authors use NMR, SAXS and MD simulations to characterise the structure of proteusin peptides, which are atypically long RiPP substrates. They show a small, unstructured region in the proteusin leader is sufficient for its interaction with a halogenase that brominates the terminal tryptophan residue.
- Nguyet A. Nguyen
- , F. N. U. Vidya
- & Vinayak Agarwal
-
Article
| Open Access Reaction engineering blocks ether cleavage for synthesizing chiral cyclic hemiacetals catalyzed by unspecific peroxygenase
Reaction engineering blocks ether cleavage for synthesizing chiral cyclic hemiacetals catalyzed by unspecific peroxygenase
Hemiacetal compounds are valuable building blocks in synthetic chemistry, but difficult to obtain by enzymatic synthesis. Here, the authors use reaction engineering of an immobilized unspecific peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita for selective C-H bond oxyfunctionalisation of environmentally significant cyclic ethers to chiral cyclic hemiacetals.
- Xiaofeng Han
- , Fuqiang Chen
- & Wuyuan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidation of unusual biosynthesis and DnaN-targeting mode of action of potent anti-tuberculosis antibiotics Mycoplanecins
Elucidation of unusual biosynthesis and DnaN-targeting mode of action of potent anti-tuberculosis antibiotics Mycoplanecins
Mycoplanecins show promising activity against tuberculosis. Here, the authors identify and study mycoplanecins’ biosynthesis, antibacterial effects, and binding mechanism to DnaN, suggesting potential for fighting multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
- Chengzhang Fu
- , Yunkun Liu
- & Rolf Müller
-
Article
| Open Access The polyketide to fatty acid transition in the evolution of animal lipid metabolism
The polyketide to fatty acid transition in the evolution of animal lipid metabolism
Much is still unknown of the evolution of animal metabolic enzymes. This study describes a new enzyme family bridging the production of polyketides and membrane lipids. This expands the known biochemical repertoire of animals for making ecologically and biomedically important natural products.
- Zhenjian Lin
- , Feng Li
- & Eric W. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric α-benzylation of cyclic ketones enabled by concurrent chemical aldol condensation and biocatalytic reduction
Asymmetric α-benzylation of cyclic ketones enabled by concurrent chemical aldol condensation and biocatalytic reduction
Given the importance of the chiral α-benzyl cyclic carbonyl motif in pharmaceutically active compounds, various transformations have been developed to access chiral compounds containing this motif but they often include harsh reaction conditions. Here the authors develop a one-pot concurrent chemoenzymatic cascade reaction and demonstrate the synthesis of α-benzylcyclic ketones with high enantioselectivity.
- Yunting Liu
- , Teng Ma
- & Yanjun Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of type II polyketide synthase-like enzymes for the biosynthesis of cispentacin
Discovery of type II polyketide synthase-like enzymes for the biosynthesis of cispentacin
Type II polyketide synthases (PKSs) normally synthesize polycyclic aromatic compounds, but the potential for the synthesis of further diverse skeletons remains under investigated. Here, the authors report the discovery of the type II PKS machinery for the biosynthesis of a five-membered nonaromatic skeleton contained in the nonproteinogenic amino acid cispentacin and the plant toxin coronatine.
- Genki Hibi
- , Taro Shiraishi
- & Tomohisa Kuzuyama
-
Article
| Open Access Common origin of sterol biosynthesis points to a feeding strategy shift in Neoproterozoic animals
Common origin of sterol biosynthesis points to a feeding strategy shift in Neoproterozoic animals
Sterane molecular fossils are used to compliment evidence from the fossil record. Here, the authors use a molecular clock to explore the origins of the smt gene, tracing the loss of sterol synthesis to dietary shifts in animals at the end-Neoproterozoic.
- T. Brunoir
- , C. Mulligan
- & D. A. Gold
-
Article
| Open Access Resurrecting ancestral antibiotics: unveiling the origins of modern lipid II targeting glycopeptides
Resurrecting ancestral antibiotics: unveiling the origins of modern lipid II targeting glycopeptides
Glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) are microbial natural products synthesized by multiple enzymes, including a nonribosomal peptide synthetase for assembly of the peptide core. Here, the authors use computational techniques to infer a gene set for biosynthesis of an ancestral GPA, produce the peptide in a microbial host, and provide insights into the evolution of key enzymatic domains.
- Mathias H. Hansen
- , Martina Adamek
- & Nadine Ziemert
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the missing apiosylation step in flavonoid apiosides biosynthesis of Leguminosae plants
Insights into the missing apiosylation step in flavonoid apiosides biosynthesis of Leguminosae plants
Apiosides are plant bioactive natural products containing apiose, but the details of the key apiosylation reaction in their biosynthesis are missing. Here, the authors identify the apiosyltransferase GuApiGT that could efficiently catalyze 2″-O-apiosylation of flavonoid glycosides, solve its crystal structure and obtain mutants with altered sugar selectivity.
- Hao-Tian Wang
- , Zi-Long Wang
- & Min Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis and engineering of the nonribosomal peptides with a C-terminal putrescine
Biosynthesis and engineering of the nonribosomal peptides with a C-terminal putrescine
Nonribosomal peptides have diverse bioactivities and can possess unusual moieties at their C-terminus, such as polyamines. In this study, the authors identify a class of dodecapeptides glidonins that feature diverse N-terminal modifications and a uniform putrescine moiety at the C-terminus, elucidate their biosynthesis, and introduce the putrescine into the C-terminus of other nonribosomal peptides.
- Hanna Chen
- , Lin Zhong
- & Xiaoying Bian
-
Article
| Open Access O-methyltransferase-like enzyme catalyzed diazo installation in polyketide biosynthesis
O-methyltransferase-like enzyme catalyzed diazo installation in polyketide biosynthesis
Diazo compounds, such as kinamycin, are rare bioactive natural products whose assembly has been extensively studied, but the formation of the diazo group is elusive. Here, the authors report O-methyltransferase-like protein, AlpH, which is responsible for the l-glutamylhydrazine incorporation in kinamycin biosynthesis.
- Yuchun Zhao
- , Xiangyang Liu
- & Ming Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocompartment-confined polymerization in living systems
Nanocompartment-confined polymerization in living systems
Polymerizations in living systems can effectively regulate cell functions and behaviors, but their uses have been hindered by the existence of complicated intracorporal interferences, the needs of high concentration of monomers and extra stimulates. Here, the authors address these issues by developing a nanocompartment-confined strategy to achieve broad-spectrum polymerizations in living systems.
- Yun Chen
- , Mengxuan Zuo
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Engineering polyketide synthases can be challenging due to the absence of efficient high-throughput methods. Here, the authors used a solubility biosensor to identify stable variants from libraries of modified polyketide synthases.
- Elias Englund
- , Matthias Schmidt
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of lasso peptide epimerase MslH reveals metal-dependent acid/base catalytic mechanism
Structure of lasso peptide epimerase MslH reveals metal-dependent acid/base catalytic mechanism
MslH, encoded in the MS-271 biosynthetic gene cluster, catalyzes the epimerization at the Cα center of the MslA C-terminal Trp21, however, the detailed catalytic process was unknown. Here, the authors report MslH is a metallo-dependent peptide epimerase with a calcineurin-like fold.
- Yu Nakashima
- , Atsushi Kawakami
- & Hiroyuki Morita
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into the catalytic promiscuity of a bacterial diterpene synthase
Molecular insights into the catalytic promiscuity of a bacterial diterpene synthase
Diterpene synthase VenA catalyses the synthesis of venezuelaene A with a unique 5-5-6-7 tetracyclic skeleton from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Here, the authors report crystal structures of apo- and holo-VenA, provide mechanistic insights into its substrate selectivity and promiscuity, and engineer VenA into a sesterterpene synthase.
- Zhong Li
- , Lilan Zhang
- & Shengying Li
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of extended product structural space of the fungal dioxygenase AsqJ
Discovery of extended product structural space of the fungal dioxygenase AsqJ
The fungal dioxygenase AsqJ catalyses the conversion of benzo[1,4]diazepine-2,5-diones into quinolone antibiotics, and can also catalyse the production of quinazolinones. Here, the authors perform comprehensive substrate promiscuity mapping of AsqJ revealing its large tolerance towards various substrates, giving biocatalytic access to a plethora of biomedically valuable heterocyclic frameworks.
- Manuel Einsiedler
- & Tobias A. M. Gulder
-
Article
| Open Access Tyrosine residues initiated photopolymerization in living organisms
Tyrosine residues initiated photopolymerization in living organisms
Developing a biocompatible polymerization system applicable for the synthesis of intrinsically non-natural polymers is a key step towards intracellular engineering of living organism. Here the authors report tyrosine residues-mediated radical photopolymerizations for intracellular synthesis of non-natural macromolecules
- Mei Zhu
- , Shengliang Wang
- & Xin Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
Natural proteins exhibit rich structural diversity based on the folds of an invariably linear chain. Here the authors design a single-domain GFP catenane as the counterpart of conventional linear GFP with enhanced thermal resilience and to provide a robust scaffold for making fusion protein catenanes.
- Zhiyu Qu
- , Jing Fang
- & Wen-Bin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A flavin-monooxygenase catalyzing oxepinone formation and the complete biosynthesis of vibralactone
A flavin-monooxygenase catalyzing oxepinone formation and the complete biosynthesis of vibralactone
Vibralactone is a strong lipase inhibitor and a bicyclic β-lactone containing an oxepinone ring, whose biosynthetic construction was unknown. Here the authors identify an oxepinone-building flavin monooxygenase VibO that is involved in the biosynthesis of vibralactone, and determine its X-ray crystal structure.
- Ke-Na Feng
- , Yue Zhang
- & Ying Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and biosynthesis of tricyclic copper-binding ribosomal peptides containing histidine-to-butyrine crosslinks
Discovery and biosynthesis of tricyclic copper-binding ribosomal peptides containing histidine-to-butyrine crosslinks
Cyclic peptides are important bioactive compounds and drugs, synthesised by enzymatic side-chain macrocyclization of ribosomal peptides, which rarely involves histidine residues. Here, the authors report the discovery and biosynthesis of tricyclic lanthipeptide noursin, constrained by a tri amino acid labionin crosslink and histidine-to-butyrine crosslink, which is important for copper binding of noursin.
- Yuqing Li
- , Yeying Ma
- & Huan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial synthesis of Prussian blue for potentiating checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
Microbial synthesis of Prussian blue for potentiating checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
Prussian blue has been used as a photothermal agent for cancer therapy. Here the authors describe the production of Prussian blue nanoparticles from S. oneidensis MR-1 bacteria and show that a Prussian blue-based mitochondria-targeting nanoplatform potentiates response to immune checkpoint blockade.
- Dongdong Wang
- , Jiawei Liu
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access De novo cholesterol biosynthesis in bacteria
De novo cholesterol biosynthesis in bacteria
Production of highly modified sterols, such as cholesterol, is essential to eukaryotic physiology but has not been yet reported for bacteria. Here, Lee et al. show that a marine myxobacterium produces cholesterol, and provide evidence for further downstream modifications in this and other bacterial species.
- Alysha K. Lee
- , Jeremy H. Wei
- & Paula V. Welander
-
Article
| Open Access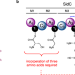 Elucidating the molecular programming of a nonlinear non-ribosomal peptide synthetase responsible for fungal siderophore biosynthesis
Elucidating the molecular programming of a nonlinear non-ribosomal peptide synthetase responsible for fungal siderophore biosynthesis
Fungal siderophores are biosynthesised by nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) with highly unusual domain architectures. Here, the authors characterise cryptic programming events occurring within SidC NRPS, responsible for ferricrocin biosynthesis in Aspergillus nidulans.
- Matthew Jenner
- , Yang Hai
- & Yi Tang
-
Article
| Open Access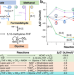 Turn air-captured CO2 with methanol into amino acid and pyruvate in an ATP/NAD(P)H-free chemoenzymatic system
Turn air-captured CO2 with methanol into amino acid and pyruvate in an ATP/NAD(P)H-free chemoenzymatic system
The use of gaseous and air-captured CO2 for technical biosynthesis is highly desired but challenging due to high energy demands. Here, the authors present an ATP and NAD(P)H-free chemoenzymatic system for glycine, serine, and pyruvate biosynthesis by coupling methanol with gaseous and air-captured CO2.
- Jianming Liu
- , Han Zhang
- & An-Ping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered repeat proteins as scaffolds to assemble multi-enzyme systems for efficient cell-free biosynthesis
Engineered repeat proteins as scaffolds to assemble multi-enzyme systems for efficient cell-free biosynthesis
Multi-enzymatic cascades benefit from precise nanometric organization but achieving this using available scaffolds is challenging. Here the authors present strategy for organizing multienzymatic systems using a protein scaffold based on TRAP domains, and demonstrate improved catalytic output.
- Alba Ledesma-Fernandez
- , Susana Velasco-Lozano
- & Aitziber L. Cortajarena
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling an indole alkaloid diketopiperazine biosynthetic pathway that features a unique stereoisomerase and multifunctional methyltransferase
Unveiling an indole alkaloid diketopiperazine biosynthetic pathway that features a unique stereoisomerase and multifunctional methyltransferase
Diketopiperazine (DKP) natural products have diverse structures and biological functions. Here, the authors elucidate the biosynthetic pathway for indole alkaloid DKP nocardioazine B which includes DKP stereoisomerization by an unusual aspartate/glutamate racemase homolog and N- and C-methylation by a dual function methyltransferase.
- Garrett Deletti
- , Sajan D. Green
- & Amy L. Lane
-
Article
| Open Access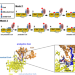 Allosteric role of the citrate synthase homology domain of ATP citrate lyase
Allosteric role of the citrate synthase homology domain of ATP citrate lyase
ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) is the main nucleocytosolic source of acetyl-CoA and the enzyme contains citrate synthase homology (CSH) and acyl-CoA synthetase homology (ASH) domains. Here, the authors report data on an ACLY mutant that supports an allosteric role for the CSH domain in ACLY catalysis.
- Xuepeng Wei
- , Kollin Schultz
- & Ronen Marmorstein
-
Review Article
| Open Access Trimming the genomic fat: minimising and re-functionalising genomes using synthetic biology
Trimming the genomic fat: minimising and re-functionalising genomes using synthetic biology
Naturally evolved genomes tend to be unnecessarily large and redundant, and are not optimised for biotechnological or research applications. In this review, the authors explore genome minimization and re-functionalisation approaches, and discuss their potential for industrial applications.
- Xin Xu
- , Felix Meier
- & Thomas C. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access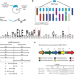 Genome mining unveils a class of ribosomal peptides with two amino termini
Genome mining unveils a class of ribosomal peptides with two amino termini
RiPP discovery has expanded the scope of post-translational modification chemistry, but genome mining of RiPP classes remains an unsolved challenge. Here, the authors employed bioinformatics and synthetic biology approaches to discover and characterize an unknown class of RiPPs, defined by an unusual amino-modified C-terminus.
- Hengqian Ren
- , Shravan R. Dommaraju
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Decrypting the programming of β-methylation in virginiamycin M biosynthesis
Decrypting the programming of β-methylation in virginiamycin M biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of complex polyketides by polyketide synthases often relies on trans-acting enzymes to modify the intermediates. Here, the authors elucidate how β-methylation enzymes identify their substrates. The recognition is imperfect, resulting in a doubly β-methylated virginiamycin derivative.
- Sabrina Collin
- , Russell J. Cox
- & Arnaud Gruez
-
Article
| Open Access Structural consequences of turnover-induced homocitrate loss in nitrogenase
Structural consequences of turnover-induced homocitrate loss in nitrogenase
Biological nitrogen fixation is achieved by nitrogenase, but the mechanism remains enigmatic. Here, the authors report high resolution single particle cryoEM structures of homocitrate-compromised MoFe-proteins and unveil a new binding partner.
- Rebeccah A. Warmack
- , Ailiena O. Maggiolo
- & Douglas C. Rees
-
Article
| Open Access The natural pyrazolotriazine pseudoiodinine from Pseudomonas mosselii 923 inhibits plant bacterial and fungal pathogens
The natural pyrazolotriazine pseudoiodinine from Pseudomonas mosselii 923 inhibits plant bacterial and fungal pathogens
Natural antimicrobial metabolites produced by soil microorganisms can be used as green pesticides. Here, the authors isolated a Pseudomonas mosselii strain 923 from rice rhizosphere soils and identify the compound pyrazolotriazine pseudoiodinine inhibits the growth of plant bacterial and fungal pathogens.
- Ruihuan Yang
- , Qing Shi
- & Gongyou Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into azalomycin F assembly-line contribute to evolution-guided polyketide synthase engineering and identification of intermodular recognition
Insights into azalomycin F assembly-line contribute to evolution-guided polyketide synthase engineering and identification of intermodular recognition
Intermodular recognition in polyketide synthase (PKS) is a key prerequisite for catalysis and assembly-line engineering. Here, the authors present a specific domain interaction between modules and an evolution-oriented strategy for PKS engineering derived from the enoylreduction module of azalomycin F.
- Guifa Zhai
- , Yan Zhu
- & Yuhui Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and biosynthesis of karnamicins as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Discovery and biosynthesis of karnamicins as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Treatment of hypertension entails use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Here, the authors show a series of karnamicins with significant inhibitory activity and identify two unusual flavoprotein hydroxylases involved in the assembly of the fully-substituted hydroxypyridine core of karnamicins.
- Zhiyin Yu
- , Jian-Ping Huang
- & Sheng-Xiong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Merging enzymatic and synthetic chemistry with computational synthesis planning
Merging enzymatic and synthetic chemistry with computational synthesis planning
The identification of synthetic routes combining enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions has been challenging and requiring expert knowledge. Here, the authors describe a computational retrosynthetic approach relying on neural network models for planning synthetic routes using both strategies.
- Itai Levin
- , Mengjie Liu
- & Connor W. Coley
-
Article
| Open Access A growth selection system for the directed evolution of amine-forming or converting enzymes
A growth selection system for the directed evolution of amine-forming or converting enzymes
Fast screening of enzymes is key for directed evolution of industrial biocatalysts. Here, the authors report a simple, high-throughput, and low-equipment-dependent growth selection system for engineering three enzymes for synthesis of chiral amines.
- Shuke Wu
- , Chao Xiang
- & Uwe T. Bornscheuer
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected assembly machinery for 4(3H)-quinazolinone scaffold synthesis
Unexpected assembly machinery for 4(3H)-quinazolinone scaffold synthesis
4(3H)-quinazolinone is the core scaffold in more than 200 natural alkaloids and numerous drugs. Here, the authors show an alternative assembly machinery for 4(3H)-quinazolinone mainly includes a two-module NRPS catalysing tripeptide formation, unusual N-3 original sources and an α-KGD catalysing the C-N bond oxidative cleavage of a tripeptide to form a dipeptide.
- Xi-Wei Chen
- , Li Rao
- & Yi Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Ribosome-mediated biosynthesis of pyridazinone oligomers in vitro
Ribosome-mediated biosynthesis of pyridazinone oligomers in vitro
Ribosomes have evolved to polymerize L-α-amino acids into proteins comprising a peptide backbone. Here, a pyridazinone backbone is formed using ribosomes in vitro, producing a variety of sequence-defined alternating block-copolymers.
- Joongoo Lee
- , Jaime N. Coronado
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access Biochemical and structural insights of multifunctional flavin-dependent monooxygenase FlsO1-catalyzed unexpected xanthone formation
Biochemical and structural insights of multifunctional flavin-dependent monooxygenase FlsO1-catalyzed unexpected xanthone formation
The biosynthesis of xanthones has not been well documented. Here, the authors report that monooxygenase FlsO1 catalyzes three successive oxidations – hydroxylation, epoxidation and Baeyer–Villiger oxidation—to form the xanthone scaffold in actinomycetes.
- Chunfang Yang
- , Liping Zhang
- & Changsheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding the terpene biosynthetic code with non-canonical 16 carbon atom building blocks
Expanding the terpene biosynthetic code with non-canonical 16 carbon atom building blocks
Establishing methods to access the chemical space that lies beyond canonical terpenoid biosynthesis will increase the applications of isoprenoids. Here, the authors reconstruct the modular structure of terpene biosynthesis on 16-carbon backbones by engineered yeast and synthesize 28 different unique terpenes.
- Codruta Ignea
- , Morten H. Raadam
- & Sotirios C. Kampranis
-
Article
| Open Access A ribosomally synthesised and post-translationally modified peptide containing a β-enamino acid and a macrocyclic motif
A ribosomally synthesised and post-translationally modified peptide containing a β-enamino acid and a macrocyclic motif
The chemical diversity of peptides from ribosomal origin is a growing field of research. Here, the authors report the discovery, genomic and biosynthetic investigations of kintamdin, a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides featuring a beta-enamino acid and a bis-thioether macrocyclic motif.
- Shan Wang
- , Sixing Lin
- & Hai Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic innovation underlies independent recruitment of polyketide synthases in cocaine and hyoscyamine biosynthesis
Catalytic innovation underlies independent recruitment of polyketide synthases in cocaine and hyoscyamine biosynthesis
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid produced by Erythroxylum novogranatense. Here the authors identify two polyketide synthases involved in cocaine biosynthesis and provide insight into the parallel evolution of these enzymes in tropane alkaloids-producing plants.
- Tian Tian
- , Yong-Jiang Wang
- & Sheng-Xiong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Flavin-enabled reductive and oxidative epoxide ring opening reactions
Flavin-enabled reductive and oxidative epoxide ring opening reactions
Epoxide ring opening reactions are important in both biological processes and synthetic applications. Here, the authors show that flavin cofactors can catalyze reductive and oxidative epoxide ring opening reactions and propose the underlying mechanisms.
- Bidhan Chandra De
- , Wenjun Zhang
- & Changsheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Copper starvation induces antimicrobial isocyanide integrated into two distinct biosynthetic pathways in fungi
Copper starvation induces antimicrobial isocyanide integrated into two distinct biosynthetic pathways in fungi
The genomes of filamentous fungi, such as Aspergillus, include many biosynthetic gene clusters of unknown function. Here, the authors show that copper starvation induces expression of an enzyme that generates a valine-derived isocyanide participating in two different pathways, for biosynthesis of acylated sugar alcohols and modified ergot alkaloids.
- Tae Hyung Won
- , Jin Woo Bok
- & Frank C. Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access AvmM catalyses macrocyclization through dehydration/Michael-type addition in alchivemycin A biosynthesis
AvmM catalyses macrocyclization through dehydration/Michael-type addition in alchivemycin A biosynthesis
Macrocyclization is an important process in bioactive natural product synthesis. Here, the authors report on the study of a macrocyclic ring constructing enzyme in the biosynthesis of alchivemycin A and using gene deletion, biochemical assays and isotope labelling show the enzyme catalyses tandem dehydration and Michael-type addition.
- Hong Jie Zhu
- , Bo Zhang
- & Hui Ming Ge
-
Article
| Open Access A cryptic third active site in cyanophycin synthetase creates primers for polymerization
A cryptic third active site in cyanophycin synthetase creates primers for polymerization
Cyanophycin synthetase CphA1 polymerizes Asp and Arg into the nitrogen reserve polymer cyanophycin using two active sites. Sharon et al. show CphA1 has a cryptic 3rd active site that cleaves cyanophycin into primers for self-sufficient biosynthesis.
- Itai Sharon
- , Sharon Pinus
- & T. Martin Schmeing
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Haloacid dehalogenase-like phosphatases are widespread across all domains of life and play a crucial role in the regulation of levels of sugar phosphate metabolites in cells. The authors report on the structure-guided engineering of phosphatases for dedicated substrate specificity for the conversion of sucrose and starch into fructose and mannose.
- Chaoyu Tian
- , Jiangang Yang
- & Yanhe Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Bifurcation drives the evolution of assembly-line biosynthesis
Bifurcation drives the evolution of assembly-line biosynthesis
Reprogramming biosynthetic assembly-lines is a topic of interest for antibiotics. Here, the authors explore the evolutionary biosynthesis of anti-tubercular wollamides, show gene duplication and neo-functionalisation results in bifurcation allowing for testing of new structures with the ability to recover old structures by gene loss.
- Thomas J. Booth
- , Kenan A. J. Bozhüyük
- & Barrie Wilkinson

 The evolutionary origin of naturally occurring intermolecular Diels-Alderases from Morus alba
The evolutionary origin of naturally occurring intermolecular Diels-Alderases from Morus alba