Perspective
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access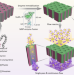 An enzymatic continuous-flow reactor based on a pore-size matching nano- and isoporous block copolymer membrane
An enzymatic continuous-flow reactor based on a pore-size matching nano- and isoporous block copolymer membrane
Continuous-flow biocatalysis with immobilized enzymes is a sustainable route for chemical synthesis, but inadequate biocatalytic efficiency caused by non-productive enzyme immobilization or enzyme-carrier mismatches presents a challenge for its application. Here, the authors report an approach for the fabrication of a high-performance enzymatic continuous-flow reactor via integrating scalable isoporous block copolymer membranes as carriers with an oriented one-step enzyme immobilization via a genetically fused material binding peptide.
- Zhenzhen Zhang
- , Liang Gao
- & Volker Abetz
-
Article
| Open Access ATP-free in vitro biotransformation of starch-derived maltodextrin into poly-3-hydroxybutyrate via acetyl-CoA
ATP-free in vitro biotransformation of starch-derived maltodextrin into poly-3-hydroxybutyrate via acetyl-CoA
Several in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystems (ivSEBs) to produce poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) via acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) have been reported, but suffer from complicated operation procedures, low yields, and/or dependence on costly ATP. Here, the authors report the design of an ATP-free ivSEB for one-pot, high-yield PHB biosynthesis via acetyl-CoA utilizing starch-derived maltodextrin as the sole substrate.
- Xinlei Wei
- , Xue Yang
- & Chun You
-
Article
| Open Access A modular and synthetic biosynthesis platform for de novo production of diverse halogenated tryptophan-derived molecules
A modular and synthetic biosynthesis platform for de novo production of diverse halogenated tryptophan-derived molecules
De novo fermentation and synthetic pathway construction for halogen-containing molecules remain relatively underexplored. Here, the authors report a mix-and-match co-culture platform to de novo generate a large array of halogenated tryptophan derivatives in E. coli from glucose.
- Kevin B. Reed
- , Sierra M. Brooks
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemically coupled CH4 and CO2 consumption driven by microbial processes
Electrochemically coupled CH4 and CO2 consumption driven by microbial processes
The microbial valorisation of greenhouse gases could offer promising approaches climate change mitigation. Here, authors demonstrate the coupling of methane oxidation and carbon dioxide reduction by microbial consortia, facilitated by the redox cycling of iron minerals.
- Yue Zheng
- , Huan Wang
- & Feng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access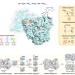 Identifying a key spot for electron mediator-interaction to tailor CO dehydrogenase’s affinity
Identifying a key spot for electron mediator-interaction to tailor CO dehydrogenase’s affinity
Carbon monoxide dehydrogenases (CODH) employ artificial electron mediators like viologens for biocatalysis, but little is known about the interaction between the mediators and the enzyme. Here, the authors discover the critical site for viologen interactions at the D-cluster of Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans CODH2 via alanine mutations and crystallography, and report variants with increased ethyl viologen affinity.
- Suk Min Kim
- , Sung Heuck Kang
- & Yong Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access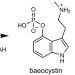 Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
Methyl transfer in psilocybin biosynthesis
The natural hallucinogen psilocybin — produced by so-called magic mushrooms — holds promise for the treatment of depression and other mental health conditions. Here, the authors provide a structural and biochemical analysis of the Psilocybe methyl transferase PsiM that provides mechanistic insight into the last step of psilocybin biosynthesis.
- Jesse Hudspeth
- , Kai Rogge
- & Sebastiaan Werten
-
Article
| Open Access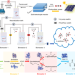 Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven sugar production directly from CO2 via a customizable electrocatalytic–biocatalytic flow system
Solar-driven artificial food synthesis from CO2 provides an approach to overcome the limitations of natural photosynthesis, but it is very challenging. Here, the authors report a hybrid electrocatalytic-biocatalytic flow system, coupling photovoltaics-powered electrocatalysis (CO2 to formate) with a five enzyme cascade platform (formate to sugar), which achieves conversion of CO2 to C6 sugar (L-sorbose) with a solar-to-food energy conversion efficiency of 3.5%.
- Guangyu Liu
- , Yuan Zhong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access A concise and scalable chemoenzymatic synthesis of prostaglandins
A concise and scalable chemoenzymatic synthesis of prostaglandins
Prostaglandins are of interest to synthetic chemists due to their biological activities. Here, the authors present a concise chemoenzymatic synthesis method for several representative prostaglandins, achieved in 5 to 7 steps, via the common intermediate bromohydrin, a radical equivalent of Corey lactone.
- Yunpeng Yin
- , Jinxin Wang
- & Jian Li
-
Article
| Open Access The evolutionary origin of naturally occurring intermolecular Diels-Alderases from Morus alba
The evolutionary origin of naturally occurring intermolecular Diels-Alderases from Morus alba
Diels-Alderases (DAs), enzymes catalyzing [4 + 2] cycloaddition reactions, are of high interest, but insights into their evolution are lacking. Here, the authors investigate the evolutionary origins of the intermolecular DAs in the biosynthesis of Moraceae plant-derived Diels-Alder-type secondary metabolites, suggesting they evolved from an ancestor functioning as a flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent oxidocyclase.
- Qi Ding
- , Nianxin Guo
- & Xiaoguang Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Biosynthesis of the highly oxygenated tetracyclic core skeleton of Taxol
Biosynthesis of the highly oxygenated tetracyclic core skeleton of Taxol
Despite intensive investigation, stepwise reactions from diol to Taxol tetracyclic core skeleton remain unclear. Here, authors fill this gap by identifying two P450s and confirming the reaction order.
- Chengshuai Yang
- , Yan Wang
- & Zhihua Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial engineering of single-atom Fe adjacent to Cu-assisted nanozymes for biomimetic O2 activation
Spatial engineering of single-atom Fe adjacent to Cu-assisted nanozymes for biomimetic O2 activation
Integrating heterogeneous single atom nanozyme (SAzyme) configurations and homogeneous enzyme-like mechanism is promising for optimizing SAzymes but elusive. Here the authors address this issue by developing a spatial engineering strategy to fabricate dual-sites SAzymes incorporating single atom Fe active centers (Fe–N4) and Cu atomic sites (Cu–N4) in a vertically stacked Fe–N4 and Cu–N4 geometry.
- Ying Wang
- , Vinod K. Paidi
- & Kwok-Yin Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Biosensor and machine learning-aided engineering of an amaryllidaceae enzyme
Biosensor and machine learning-aided engineering of an amaryllidaceae enzyme
Amaryllidaceae alkaloids, such as the Alzheimer’s medication galantamine, are currently extracted from low-yielding daffodils. Here, authors pair biosensor-assisted screening with machine learning-guided protein design to rapidly engineer an improved Amaryllidaceae enzyme in a microbial host.
- Simon d’Oelsnitz
- , Daniel J. Diaz
- & Andrew D. Ellington
-
Article
| Open Access Topological barrier to Cas12a activation by circular DNA nanostructures facilitates autocatalysis and transforms DNA/RNA sensing
Topological barrier to Cas12a activation by circular DNA nanostructures facilitates autocatalysis and transforms DNA/RNA sensing
The authors find that small circular DNA nanostructures which partially match gRNA sequences only minimally activate Cas12a. They report AutoCAR (Autocatalytic Cas12a Circular DNA Amplification Reaction) which allows a single nucleic acid target to activate multiple ribonucleoproteins, and increases reporter cleavage rates.
- Fei Deng
- , Yi Li
- & Ewa M. Goldys
-
Article
| Open Access A non-canonical nucleophile unlocks a new mechanistic pathway in a designed enzyme
A non-canonical nucleophile unlocks a new mechanistic pathway in a designed enzyme
The authors previously showed that a histidine nucleophile and a flexible arginine can work in synergy to accelerate the Morita Baylis-Hillman (MBH) reaction. Here, they report another efficient MBHase that employs a non-canonical Nδ-methylhistidine nucleophile paired with a catalytic glutamate, providing an alternative mechanistic solution for MBH catalysis.
- Amy E. Hutton
- , Jake Foster
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding activity-stability tradeoffs in biocatalysts by enzyme proximity sequencing
Understanding activity-stability tradeoffs in biocatalysts by enzyme proximity sequencing
Understanding the complex relationships between enzyme sequence, folding stability and catalytic activity is essential for applications, but current technologies cannot simultaneously resolve both stability and activity phenotypes and couple these to gene sequences at large scale. Here, the authors report Enzyme Proximity Sequencing (EP-Seq), a deep mutational scanning method to assay both expression level and catalytic activity of thousands of oxidoreductase variants from a cellular pool in a single experiment.
- Rosario Vanella
- , Christoph Küng
- & Michael A. Nash
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstitution of early paclitaxel biosynthetic network
Reconstitution of early paclitaxel biosynthetic network
Paclitaxel is an important anticancer drug whose biosynthetic pathway reconstruction is hindered by the propensity of heterologously expressed pathway cytochromes P450, including taxadiene 5α-hydroxylase (T5αH), to form multiple products. Here, the authors tune the promoter strength for T5αH expression in Nicotiana plants to increase the levels of paclitaxel precursor taxadien-5α-ol by three-fold and reconstitute the six step early biosynthetic pathway of paclitaxel.
- Jack Chun-Ting Liu
- , Ricardo De La Peña
- & Elizabeth S. Sattely
-
Article
| Open Access Computational redesign of a hydrolase for nearly complete PET depolymerization at industrially relevant high-solids loading
Computational redesign of a hydrolase for nearly complete PET depolymerization at industrially relevant high-solids loading
The application of the LCC variant of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) hydrolase for industrial degradation of PET has been hindered by the 10% of nonbiodegradable PET. Here, the authors use a computational strategy to engineer TurboPETase which outperforms other PETase variants and achieves nearly complete depolymerization of the postconsumer PET bottles at a high, industrially relevant, level of solids loading.
- Yinglu Cui
- , Yanchun Chen
- & Bian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Reaction engineering blocks ether cleavage for synthesizing chiral cyclic hemiacetals catalyzed by unspecific peroxygenase
Reaction engineering blocks ether cleavage for synthesizing chiral cyclic hemiacetals catalyzed by unspecific peroxygenase
Hemiacetal compounds are valuable building blocks in synthetic chemistry, but difficult to obtain by enzymatic synthesis. Here, the authors use reaction engineering of an immobilized unspecific peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita for selective C-H bond oxyfunctionalisation of environmentally significant cyclic ethers to chiral cyclic hemiacetals.
- Xiaofeng Han
- , Fuqiang Chen
- & Wuyuan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Natural diversity screening, assay development, and characterization of nylon-6 enzymatic depolymerization
Natural diversity screening, assay development, and characterization of nylon-6 enzymatic depolymerization
Polyamides (PAs) or nylons are types of plastics with wide applications, but due to their accumulation in the environment, strategies for their deconstruction are of interest. Here, the authors screen 40 potential nylon-hydrolyzing enzymes (nylonases) using a mass spectrometry-based approach and identify a thermostabilized N-terminal nucleophile hydrolase as the most promising for further development, as well as crucial targets for progressing PA6 enzymatic depolymerization.
- Elizabeth L. Bell
- , Gloria Rosetto
- & Gregg T. Beckham
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning oxidant and antioxidant activities of ceria by anchoring copper single-site for antibacterial application
Tuning oxidant and antioxidant activities of ceria by anchoring copper single-site for antibacterial application
Nanozymes used for antibacterial therapy conventionally have complex catalytic activities that cause multiple pathways in parallel and unwanted outcome. Here, the authors report a Cu-CeO2 single site nanozyme in which Cu single site modification can enhance the peroxidase-like activity and inhibit the hydroxyl radical antioxidant capacity of CeO2 to optimise the antibacterial effects.
- Peng Jiang
- , Ludan Zhang
- & Yuguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access De novo biosynthesis of antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline
De novo biosynthesis of antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline
Ajmaline is an antiarrhythmic monoterpenoid indole alkaloid produced by the root of Rauwolfia serpentina. Here, the authors complete the ajmaline biosynthetic pathway by identifying two reductases and two esterases, and achieve the de novo ajmaline biosynthesis by engineering Baker’s yeast.
- Jun Guo
- , Di Gao
- & Yang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible modulation of interlayer stacking in 2D copper-organic frameworks for tailoring porosity and photocatalytic activity
Reversible modulation of interlayer stacking in 2D copper-organic frameworks for tailoring porosity and photocatalytic activity
The precise control of interlayer stacking mode of 2D materials is a long-standing pursuit. Here, the authors report two 2D copper-organic frameworks that can undergo the reversible interlayer sliding through environmental stimulation.
- Pei-Ye You
- , Kai-Ming Mo
- & Dan Li
-
Article
| Open Access A natural biogenic nanozyme for scavenging superoxide radicals
A natural biogenic nanozyme for scavenging superoxide radicals
The inorganic minerals are believed to exert a critical catalytic role in the prebiotic time, but biominerals (e.g., bones) in modern living organisms are known mainly for their physical property-related functions. Here the authors identify natural ferritin iron core as a superoxide dismutase-like nanozyme exhibiting species-related activity and elucidate its specific catalytic mechanism.
- Long Ma
- , Jia-Jia Zheng
- & Kelong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Modular assembly of an artificially concise biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids
Modular assembly of an artificially concise biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids
Plant alkaloids – an important class of pharmaceuticals - are still largely acquired through phytoextraction. Here, the authors develop an artificial and concise four-enzyme biocatalytic cascade for synthesizing various phenethylisoquinoline alkaloids from readily available starting materials.
- Yue Gao
- , Fei Li
- & Yijian Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming biocatalytic futile cycles through computational engineering of stereochemical promiscuity to create an amine racemase
Reprogramming biocatalytic futile cycles through computational engineering of stereochemical promiscuity to create an amine racemase
Racemization of chiral amines poses a challenge, making dynamic kinetic resolution inaccessible for industrial applications. Here, the authors demonstrate in silico engineering of an amine transaminase to create a new-to-nature amine racemase.
- Sang-Woo Han
- , Youngho Jang
- & Jong-Shik Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric α-benzylation of cyclic ketones enabled by concurrent chemical aldol condensation and biocatalytic reduction
Asymmetric α-benzylation of cyclic ketones enabled by concurrent chemical aldol condensation and biocatalytic reduction
Given the importance of the chiral α-benzyl cyclic carbonyl motif in pharmaceutically active compounds, various transformations have been developed to access chiral compounds containing this motif but they often include harsh reaction conditions. Here the authors develop a one-pot concurrent chemoenzymatic cascade reaction and demonstrate the synthesis of α-benzylcyclic ketones with high enantioselectivity.
- Yunting Liu
- , Teng Ma
- & Yanjun Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Staphylococcus aureus functional amyloids catalyze degradation of β-lactam antibiotics
Staphylococcus aureus functional amyloids catalyze degradation of β-lactam antibiotics
A number of mechanisms are known to mediate bacterial antibiotic resistance. Here, Arad et al show that amyloid fibrils produced by Staphylococcus aureus rapidly degrade common antibiotic molecules.
- Elad Arad
- , Kasper B. Pedersen
- & Raz Jelinek
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral metal-organic frameworks incorporating nanozymes as neuroinflammation inhibitors for managing Parkinson’s disease
Chiral metal-organic frameworks incorporating nanozymes as neuroinflammation inhibitors for managing Parkinson’s disease
The treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is hampered by the lack of effective blood–brain barrier (BBB) traversing drugs. Here, the authors report nanozyme-integrated metal-organic frameworks with antioxidant activity and chiral-dependent BBB transendocytosis as anti-neuroinflammatory agents for PD treatment.
- Wei Jiang
- , Qing Li
- & Kelong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic manifold in a hemoprotein-catalyzed cyclopropanation reaction with diazoketone
Mechanistic manifold in a hemoprotein-catalyzed cyclopropanation reaction with diazoketone
Hemoproteins have recently emerged as promising biocatalysts for carbene transfer reactions but mechanistic understanding of the interplay between productive and unproductive pathways in these processes is limited. Here, the authors use a combination of spectroscopic, crystallographic, and computational tools to elucidate the mechanism of a recently reported myoglobin-catalyzed cyclopropanation reaction with diazoketones.
- Donggeon Nam
- , John-Paul Bacik
- & Rudi Fasan
-
Article
| Open Access Illuminating the mechanism and allosteric behavior of NanoLuc luciferase
Illuminating the mechanism and allosteric behavior of NanoLuc luciferase
NanoLuc luciferase is a popular bioluminescent enzyme, but the molecular details of its mechanism of action on luciferins such as coelenterazine remained elusive. Here the authors use, protein crystal structures and biochemical analyses to provide an atomistic description of its catalytic mechanism and allosteric behaviour.
- Michal Nemergut
- , Daniel Pluskal
- & Martin Marek
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of a non-canonical prototype long-chain monoacylglycerol lipase through a structure-based endogenous reaction intermediate complex
Discovery of a non-canonical prototype long-chain monoacylglycerol lipase through a structure-based endogenous reaction intermediate complex
Here, the authors present the structure of an orphan lipase in complex with an endogenous C18 monoacylglycerol ester reaction intermediate derived from the expression host, which along with enzymatic assays enabled functional assignment as a prototypical long-chain monoacylglycerol lipase.
- Nikos Pinotsis
- , Anna Krüger
- & Matthias Wilmanns
-
Article
| Open Access The structural and functional investigation into an unusual nitrile synthase
The structural and functional investigation into an unusual nitrile synthase
The nitrile synthase AetD is a crucial component in the biosynthetic pathway of neurotoxin aetokthonotoxin (AETX). Here, the authors solved crystal structures of AetD in complex with different substrates, revealing that AetD represents a new type of HO-like diiron enzyme and the possibility of expanding its substrate spectrum.
- Hao Li
- , Jian-Wen Huang
- & Chun-Chi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering sulfonate group donor regeneration systems to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds
Engineering sulfonate group donor regeneration systems to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds
Sufficient supply of sulfonate group donor is critical to biomanufacturing of the sulfate containing compounds. Here, the authors engineer two sulfonate group donor regeneration systems, including 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate and the newly discovered 5'-phosphosulfate, to boost biosynthesis of sulfated compounds.
- Ruirui Xu
- , Weijao Zhang
- & Zhen Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of peptide secretion for Quorum sensing by ComA
Structural basis of peptide secretion for Quorum sensing by ComA
Quorum sensing is a regulatory mechanism controlling bacterial signaling and ComA, a conserved efflux pump, is responsible for the maturation and secretion of peptide signals. Here, authors determine the 3D structure and demonstrate its function as an ABC transporter.
- Lin Yu
- , Xin Xu
- & Min Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic β-elimination in natural product O- and C-glycoside deglycosylation
Enzymatic β-elimination in natural product O- and C-glycoside deglycosylation
Biological degradation of glycosides involves, alongside hydrolysis, β-elimination for glycosidic bond cleavage. Here, the authors report an O-glycoside β-eliminase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens that converts the C3-oxidized O-β-d-glucoside of phloretin into the aglycone and the 2-hydroxy-3-keto-d-glycal elimination product, and suggest convergent evolution of β-eliminase active sites for the cleavage of natural product 3-keto-O-glycosides.
- Johannes Bitter
- , Martin Pfeiffer
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Tandem-biocatalysis reactors constructed by topological evolution of CaCO3 particles into hollow metal hydroxide spheres
Tandem-biocatalysis reactors constructed by topological evolution of CaCO3 particles into hollow metal hydroxide spheres
Hollow inorganic spheres (HISs) hold potential in various technological areas including biocatalysis and biomedicine, but the harsh synthetic conditions have precluded the use of HISs in biological fields. Here, the authors report a biocompatible strategy for synthesizing metal hydroxide HISs that can function as tandem-biocatalytic reactors.
- Sang Yeong Han
- , Nayoung Kim
- & Insung S. Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
The design of programmable artificial photosynthetic cells is hindered by the requirement for cofactor generation for the biocatalytic module. Here, the authors report on the design of artificial photosynthetic cells using biotic–abiotic thylakoid–CdTe as hybrid energy modules, which enhance the regeneration of NADPH, NADH and ATP cofactors without external supplements by promoting proton-coupled electron transfer.
- Feng Gao
- , Guangyu Liu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Repurposing conformational changes in ANL superfamily enzymes to rapidly generate biosensors for organic and amino acids
Repurposing conformational changes in ANL superfamily enzymes to rapidly generate biosensors for organic and amino acids
Biosensors have a wide number of potential applications, but rapidly constructing genetically encoded biosensors remains challenging. Here, authors report a method for rapidly converting ANL superfamily enzymes into biosensors for organic acids, based on their conformational changes upon binding.
- Jin Wang
- , Ning Xue
- & Meng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the missing apiosylation step in flavonoid apiosides biosynthesis of Leguminosae plants
Insights into the missing apiosylation step in flavonoid apiosides biosynthesis of Leguminosae plants
Apiosides are plant bioactive natural products containing apiose, but the details of the key apiosylation reaction in their biosynthesis are missing. Here, the authors identify the apiosyltransferase GuApiGT that could efficiently catalyze 2″-O-apiosylation of flavonoid glycosides, solve its crystal structure and obtain mutants with altered sugar selectivity.
- Hao-Tian Wang
- , Zi-Long Wang
- & Min Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic single Al-OH site with high acetylcholinesterase-like activity and self-defense ability for neuroprotection
Biomimetic single Al-OH site with high acetylcholinesterase-like activity and self-defense ability for neuroprotection
The neurotoxicity of organophosphate compounds damages nerve system by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (AChE) expression, but it is difficult to overcome the deactivation of AChE. Here, the authors report the design of Lewis acid sites in metal-organic frameworks as AChE mimics for effective neuroprotection.
- Weiqing Xu
- , Xiaoli Cai
- & Chengzhou Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Dual enzyme-powered chemotactic cross β amyloid based functional nanomotors
Dual enzyme-powered chemotactic cross β amyloid based functional nanomotors
Nanomotor chassis constructed from biological precursors and powered by biocatalytic transformations can offer important applications in the future. Here, the authors prepare short-peptide-based cross β amyloid nanomotors which can host dedicated enzymes with orthogonal substrates for motility and navigation.
- Chandranath Ghosh
- , Souvik Ghosh
- & Dibyendu Das
-
Article
| Open Access Custom tuning of Rieske oxygenase reactivity
Custom tuning of Rieske oxygenase reactivity
Rieske oxygenase chemistry is important for biochemical pathways, but it remains elusive how a common protein scaffold can be predictively tuned to catalyze divergent reactions. Here, the authors report a strategy that can rationally tune TsaM, a Rieske monooxygenase to catalyze dioxygenation and sequential monooxygenation reactions, and customize the reactivity of other Rieske oxygenases.
- Jiayi Tian
- , Jianxin Liu
- & Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
-
Article
| Open Access Histidine modulates amyloid-like assembly of peptide nanomaterials and confers enzyme-like activity
Histidine modulates amyloid-like assembly of peptide nanomaterials and confers enzyme-like activity
In this work, the authors report that Histidine residues play a critical role in modulating amyloid-like assembly and building active sites for Fmoc–F–F and Aβ aggregates. Aβ1-42 filaments were found to perform peroxidase-like activity to enhance oxidative stress, which might also be ascribed to the interaction mode of His and F-F.
- Ye Yuan
- , Lei Chen
- & Lizeng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access A biocatalytic platform for asymmetric alkylation of α-keto acids by mining and engineering of methyltransferases
A biocatalytic platform for asymmetric alkylation of α-keto acids by mining and engineering of methyltransferases
Catalytic asymmetric a-alkylation of carbonyl compounds represents a longstanding challenge in synthetic organic chemistry but general methods for the catalytic symmetric alkylation of carbonyl compounds remain elusive. Here, the authors mine and engineer methyltransferases as synthetically useful biocatalysts for the catalytic asymmetric alkylation reactions of carbonyl compounds.
- Shuyun Ju
- , Kaylee P. Kuzelka
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailored photoenzymatic systems for selective reduction of aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds fueled by light
Tailored photoenzymatic systems for selective reduction of aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds fueled by light
The selective enzymatic reduction of nitroaliphatic and nitroaromatic compounds is challenging. Here, the authors report selective (sun)light-driven photoenzymatic reduction of a wide variety of nitro compounds to aliphatic amines and amino-, azoxy- and azo-aromatics using flavin-dependent nitroreductases and chlorophyll as photocatalyst
- Alejandro Prats Luján
- , Mohammad Faizan Bhat
- & Gerrit J. Poelarends
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-inspired design of cascade catalysis system by 3D spatially separated active sites
Cell-inspired design of cascade catalysis system by 3D spatially separated active sites
Cells contain isolated compartments that spatially confine different enzymes, enabling high-efficiency enzymatic cascade reactions. Herein, the authors report a cell-inspired design of biomimetic cascade catalysis system by immobilizing Fe single atoms and Au nanoparticles on the inner and outer layers of three-dimensional nanocapsules, respectively, to enable highly selective colorimetric glucose detection.
- Qiuping Wang
- , Kui Chen
- & Yuen Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic principle to enhance enzymatic activity using the substrate affinity
Thermodynamic principle to enhance enzymatic activity using the substrate affinity
Currently, there is no well-defined strategy to increase the activity of enzymes. Here, the authors provide mathematical evidence that adjusting the Michaelis-Menten constant to the substrate concentration maximizes enzymatic activity.
- Hideshi Ooka
- , Yoko Chiba
- & Ryuhei Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic cell-free 36-enzyme reaction system for vitamin B12 production
A synthetic cell-free 36-enzyme reaction system for vitamin B12 production
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) is an essential vitamin whose production is limited to bacterial fermentation. Here, the authors report an alternative method for the synthesis of AdoCbl based on a cell-free reaction system integrating more than 30 biocatalytic reactions to produce AdoCbl from 5-aminolevulinic acid.
- Qian Kang
- , Huan Fang
- & Dawei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mimicking reductive dehalogenases for efficient electrocatalytic water dechlorination
Mimicking reductive dehalogenases for efficient electrocatalytic water dechlorination
Designing electrocatalysts for water treatment with high activity/selectivity as elaborately as natural enzymes remains a challenge. This work presents the design of electrocatalysts by mimicking the binding pocket configuration and active center of dehalogenases, achieving efficient water dechlorination.
- Yuan Min
- , Shu-Chuan Mei
- & Yujie Xiong

 Automated in vivo enzyme engineering accelerates biocatalyst optimization
Automated in vivo enzyme engineering accelerates biocatalyst optimization