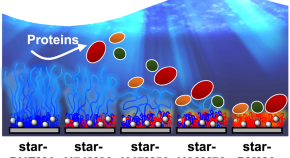
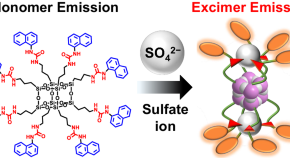
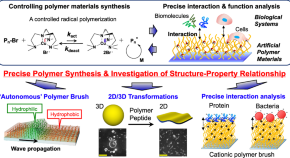
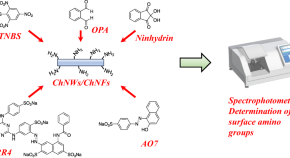
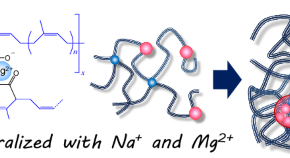
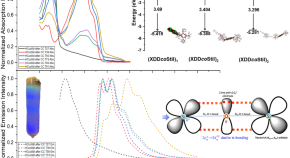
Improving the marine biodegradability of poly(alkylene succinate)-based copolymers
The marine biodegradability of novel poly(ethylene succinate)(PES)-based copolymers is improved by incorporating long-chain dicarboxylic acid units. These PES-based copolymers are easily biodegradable