Abstract
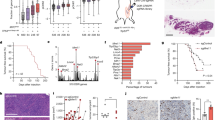
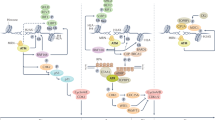
A well-studied RNA-binding protein Hu Antigen-R (HuR), controls post-transcriptional gene regulation and undergoes stress-activated caspase-3 dependent cleavage in cancer cells. The cleavage products of HuR are known to promote cell death; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms facilitating caspase-3 activation and HuR cleavage remains unknown. Here, we show that HuR cleavage associated with active caspase-3 in oral cancer cells treated with ionizing radiation and chemotherapeutic drug, paclitaxel. We determined that oral cancer cells overexpressing cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) limited the cleavage of caspase-3 and HuR, which reduced the rate of cell death in paclitaxel resistant oral cancer cells. Specific inhibition of COX-2 by celecoxib, promoted apoptosis through activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of HuR in paclitaxel-resistant oral cancer cells, both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, oral cancer cells overexpressing cellular HuR increased the half-life of COX-2 mRNA, promoted COX-2 protein expression and exhibited enhanced tumor growth in vivo in comparison with cells expressing a cleavable form of HuR. Finally, our ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation and sequencing (RIP-seq) analyses of HuR in oral cancer cells treated with ionizing radiation (IR), determined that HuR cleavage product-1 (HuR-CP1) bound and promoted the expression of mRNAs encoding proteins involved in apoptosis. Our results indicated that, cellular non-cleavable HuR controls COX-2 mRNA expression and enzymatic activity. In addition, overexpressed COX-2 protein repressed the cleavage of caspase-3 and HuR to promote drug resistance and tumor growth. Altogether, our observations support the use of the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib, in combination with paclitaxel, for the management of paclitaxel resistant oral cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HuR-CP1:
-
Hu Antigen-R cleavage product-1
- HuR-D226A:
-
Non-cleavable isoform of HuR
- RBP:
-
RNA-binding protein
- ARE:
-
AU-rich elements
- 3′ UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- IR:
-
Ionizing radiation
References
Bombard Y, Bach PB, Offit K . Translating genomics in cancer care. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2013; 11: 1343–1353.
Brody JR, Gonye GE . HuR's role in gemcitabine efficacy: an exception or opportunity? Wiley interdisciplinary reviews RNA 2011; 2: 435–444.
Williams TK, Costantino CL, Bildzukewicz NA, Richards NG, Rittenhouse DW, Einstein L et al. pp32 (ANP32A) expression inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and induces gemcitabine resistance by disrupting HuR binding to mRNAs. PloS one 2010; 5: e15455.
Costantino CL, Witkiewicz AK, Kuwano Y, Cozzitorto JA, Kennedy EP, Dasgupta A et al. The role of HuR in gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic cancer: HuR Up-regulates the expression of the gemcitabine metabolizing enzyme deoxycytidine kinase. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 4567–4572.
Filippova N, Yang X, Wang Y, Gillespie GY, Langford C, King PH et al. The RNA-binding protein HuR promotes glioma growth and treatment resistance. Molecular cancer research: MCR 2011; 9: 648–659.
Papadaki O, Milatos S, Grammenoudi S, Mukherjee N, Keene JD, Kontoyiannis DL . Control of thymic T cell maturation, deletion and egress by the RNA-binding protein HuR. Journal of immunology 2009; 182: 6779–6788.
Katsanou V, Milatos S, Yiakouvaki A, Sgantzis N, Kotsoni A, Alexiou M et al. The RNA-binding protein Elavl1/HuR is essential for placental branching morphogenesis and embryonic development. Molecular and cellular biology 2009; 29: 2762–2776.
Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M . Posttranscriptional regulation of cancer traits by HuR. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews RNA 2010; 1: 214–229.
Talwar S, House R, Sundaramurthy S, Balasubramanian S, Yu H, Palanisamy V . Inhibition of caspases protects mice from radiation-induced oral mucositis and abolishes the cleavage of RNA-binding protein HuR. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 3487–3500.
Talwar S, Jin J, Carroll B, Liu A, Gillespie MB, Palanisamy V . Caspase-mediated cleavage of RNA-binding protein HuR regulates c-Myc protein expression after hypoxic stress. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 32333–32343.
von Roretz C, Lian XJ, Macri AM, Punjani N, Clair E, Drouin O et al. Apoptotic-induced cleavage shifts HuR from being a promoter of survival to an activator of caspase-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2013; 20: 154–168.
Fulda S, Debatin KM . Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4798–4811.
Nagata S . Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 1999; 33: 29–55.
McIlwain DR, Berger T, Mak TW . Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013; 5: a008656.
Wang D, Dubois RN . Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 181–193.
Ristimaki A, Honkanen N, Jankala H, Sipponen P, Harkonen M . Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 1276–1280.
Hida T, Yatabe Y, Achiwa H, Muramatsu H, Kozaki K, Nakamura S et al. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase 2 occurs frequently in human lung cancers, specifically in adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 3761–3764.
Zimmermann KC, Sarbia M, Weber AA, Borchard F, Gabbert HE, Schror K . Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 198–204.
Itoh S, Matsui K, Furuta I, Takano Y . Immunohistochemical study on overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: its importance as a prognostic predictor. Oral Oncol 2003; 39: 829–835.
Sakurai K, Urade M, Noguchi K, Hashitani S, Takaoka K, Segawa E et al. Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 and DNA topoisomerase IIalpha expression in oral carcinoma. Head Neck 2007; 29: 1002–1009.
Renkonen J, Wolff H, Paavonen T . Expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 in human tongue carcinoma and its precursor lesions. Virchows Arch 2002; 440: 594–597.
Sudbo J, Ristimaki A, Sondresen JE, Kildal W, Boysen M, Koppang HS et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in high-risk premalignant oral lesions. Oral Oncol 2003; 39: 497–505.
Dandekar DS, Lopez M, Carey RI, Lokeshwar BL . Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib augments chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis by enhancing activation of caspase-3 and -9 in prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2005; 115: 484–492.
Barbisan F, Mazzucchelli R, Santinelli A, Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L, Scarpelli M et al. Overexpression of ELAV-like protein HuR is associated with increased COX-2 expression in atrophy, high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and incidental prostate cancer in cystoprostatectomies. Eur Urol 2009; 56: 105–112.
Do SI, Araujo ES, Kalil RK, Bacchini P, Bertoni F, Unni KK et al. Expression of embryonic lethal abnormal vision (ELAV)-like protein HuR and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Ewing sarcoma. Tumori 2008; 94: 347–350.
Mohammad S, Ram H, Gupta PN, Husain N, Bhatt ML . Overexpression of COX-2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing chemoradiotherapy. Natl J Maxillofac Surg 2011; 2: 17–21.
Niesporek S, Kristiansen G, Thoma A, Weichert W, Noske A, Buckendahl AC et al. Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR in human prostate carcinoma is an indicator of disease relapse and linked to COX-2 expression. Int J Oncol 2008; 32: 341–347.
Mazroui R, Di Marco S, Clair E, von Roretz C, Tenenbaum SA, Keene JD et al. Caspase-mediated cleavage of HuR in the cytoplasm contributes to pp32/PHAP-I regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 2008; 180: 113–127.
Ferrandina G, Ranelletti FO, Martinelli E, Paglia A, Zannoni GF, Scambia G . Cyclo-oxygenase-2 (Cox-2) expression and resistance to platinum versus platinum/paclitaxel containing chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2006; 6: 182.
Kulmacz RJ, Lands WE . Requirements for hydroperoxide by the cyclooxygenase and peroxidase activities of prostaglandin H synthase. Prostaglandins 1983; 25: 531–540.
Mukherjee N, Corcoran DL, Nusbaum JD, Reid DW, Georgiev S, Hafner M et al. Integrative regulatory mapping indicates that the RNA-binding protein HuR couples pre-mRNA processing and mRNA stability. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 327–339.
Young LE, Dixon DA . Posttranscriptional Regulation of Cyclooxygenase 2 Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 2010; 6: 60–67.
Kargman SL, O'Neill GP, Vickers PJ, Evans JF, Mancini JA, Jothy S . Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase-1 and -2 protein in human colon cancer. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 2556–2559.
Shirahama T . Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is up-regulated in transitional cell carcinoma and its preneoplastic lesions in the human urinary bladder. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2424–2430.
Yoshimura R, Sano H, Masuda C, Kawamura M, Tsubouchi Y, Chargui J et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2000; 89: 589–596.
Subbaramaiah K, Marmo TP, Dixon DA, Dannenberg AJ . Regulation of cyclooxgenase-2 mRNA stability by taxanes: evidence for involvement of p38, MAPKAPK-2, and HuR. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 37637–37647.
Devarajan E, Sahin AA, Chen JS, Krishnamurthy RR, Aggarwal N, Brun AM et al. Down-regulation of caspase 3 in breast cancer: a possible mechanism for chemoresistance. Oncogene 2002; 21: 8843–8851.
Olsson M, Zhivotovsky B . Caspases and cancer. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1441–1449.
Hague A, Eveson JW, MacFarlane M, Huntley S, Janghra N, Thavaraj S . Caspase-3 expression is reduced, in the absence of cleavage, in terminally differentiated normal oral epithelium but is increased in oral squamous cell carcinomas and correlates with tumour stage. J Pathol 2004; 204: 175–182.
Beauchamp P, Nassif C, Hillock S, van der Giessen K, von Roretz C, Jasmin BJ et al. The cleavage of HuR interferes with its transportin-2-mediated nuclear import and promotes muscle fiber formation. Cell Death Differ 2010.
von Roretz C, Gallouzi IE . Protein kinase RNA/FADD/caspase-8 pathway mediates the proapoptotic activity of the RNA-binding protein human antigen R (HuR). J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 16806–16813.
Li M, Zhu Y, Zhang H, Li L, He P, Xia H et al. Delivery of inhibitor of growth 4 (ING4) gene significantly inhibits proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells. Sci Rep 2014; 4: 7380.
Chen D, Li X, Zhai Z, Shu HB . A novel zinc finger protein interacts with receptor-interacting protein (RIP) and inhibits tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- and IL1-induced NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 15985–15991.
Lahti JM, Xiang J, Heath LS, Campana D, Kidd VJ . PITSLRE protein kinase activity is associated with apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 1–11.
Brenner JC, Graham MP, Kumar B, Saunders LM, Kupfer R, Lyons RH et al. Genotyping of 73 UM-SCC head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Head Neck 2010; 32: 417–426.
Lopez de Silanes I, Zhan M, Lal A, Yang X, Gorospe M . Identification of a target RNA motif for RNA-binding protein HuR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101: 2987–2992.
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012; 7: 562–578.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S . Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014; 15: 550.
Kozak I, Sasik R, Freeman WR, Sprague LJ, Gomez ML, Cheng L et al. A degenerative retinal process in HIV-associated non-infectious retinopathy. PLoS One 2013; 8: e74712.
Paolini P, Pick D, Lapira J, Sannino G, Pasqualini L, Ludka C et al. Developmental and extracellular matrix-remodeling processes in rosiglitazone-exposed neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Pharmacogenomics 2014; 15: 759–774.
Hulsen T, de Vlieg J, Alkema W . BioVenn - a web application for the comparison and visualization of biological lists using area-proportional Venn diagrams. BMC Genomics 2008; 9: 488.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the funding source from the National Institutes of Health R01DE022776 and R01DE022776S1 to VP. We acknowledge the Center for Oral Health Research (L-COHR) which is supported by the NIH grant P30 GM103331.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janakiraman, H., House, R., Talwar, S. et al. Repression of caspase-3 and RNA-binding protein HuR cleavage by cyclooxygenase-2 promotes drug resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 36, 3137–3148 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.451
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.451
This article is cited by
-
Relationship between HuR and tumor drug resistance
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 exerts anti-oncogenic effects on bladder cancer via restoration of RARB as a sponge of microRNA-146
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
A novel multi-functionalized multicellular nanodelivery system for non-small cell lung cancer photochemotherapy
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2021)
-
Downregulation of SRSF3 by antisense oligonucleotides sensitizes oral squamous cell carcinoma and breast cancer cells to paclitaxel treatment
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2019)
-
Multiple functions of HuR in urinary tumors
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2019)