Abstract
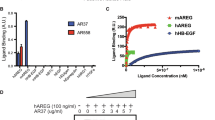
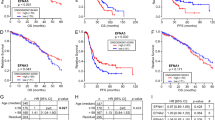
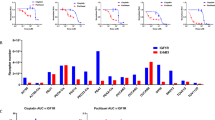
Growth factors of the epidermal growth factor (EGF)/neuregulin family are involved in tumor progression and, accordingly, antibodies that intercept a cognate receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/ERBB1, or a co-receptor, HER2, have been approved for cancer therapy. Although they might improve safety and delay onset of chemoresistance, no anti-ligand antibodies have been clinically approved. To identify suitable ligands, we surveyed fluids from ovarian and lung cancer patients and found that amphiregulin (AREG) is the most abundant and generalized ligand secreted by advanced tumors. AREG is a low affinity EGFR ligand, which is upregulated following treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. Because AREG depletion retarded growth of xenografted ovarian tumors in mice, we generated a neutralizing monoclonal anti-AREG antibody. The antibody inhibited growth of ovarian cancer xenografts and strongly enhanced chemotherapy efficacy. Taken together, these results raise the possibility that AREG and other low- or high-affinity binders of EGFR might serve as potential targets for cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Witsch E, Sela M, Yarden Y . Roles for growth factors in cancer progression. Physiology (Bethesda) 2010; 25: 85–101.
Burgess AW . EGFR family: structure physiology signalling and therapeutic targets. Growth Factors 2008; 26: 263–274.
Hynes NE, MacDonald G . ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21: 177–184.
Jones JT, Akita RW, Sliwkowski MX . Binding specificities and affinities of egf domains for ErbB receptors. FEBS Lett 1999; 447: 227–231.
Kochupurakkal BS, Harari D, Di-Segni A, Maik-Rachline G, Lyass L, Gur G et al. Epigen, the last ligand of ErbB receptors, reveals intricate relationships between affinity and mitogenicity. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 8503–8512.
Amit I, Citri A, Shay T, Lu Y, Katz M, Zhang F et al. A module of negative feedback regulators defines growth factor signaling. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 503–512.
Lazzara MJ, Lauffenburger DA . Quantitative modeling perspectives on the ErbB system of cell regulatory processes. Exp Cell Res 2009; 315: 717–725.
Reddy CC, Niyogi SK, Wells A, Wiley HS, Lauffenburger DA . Engineering epidermal growth factor for enhanced mitogenic potency. Nat Biotechnol 1996; 14: 1696–1699.
Tzahar E, Moyer JD, Waterman H, Barbacci EG, Bao J, Levkowitz G et al. Pathogenic poxviruses reveal viral strategies to exploit the ErbB signaling network. EMBO J 1998; 17: 5948–5963.
Wilson KJ, Mill C, Lambert S, Buchman J, Wilson TR, Hernandez-Gordillo V et al. EGFR ligands exhibit functional differences in models of paracrine and autocrine signaling. Growth factors (Chur, Switzerland) 2012; 30: 107–116.
Berasain C, Avila MA . Amphiregulin. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2014; 28C: 31–41.
Willmarth NE, Ethier SP . Autocrine and juxtacrine effects of amphiregulin on the proliferative, invasive, and migratory properties of normal and neoplastic human mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 37728–37737.
Higginbotham JN, Demory Beckler M, Gephart JD, Franklin JL, Bogatcheva G, Kremers GJ et al. Amphiregulin exosomes increase cancer cell invasion. Curr Biol 2011; 21: 779–786.
Sternlicht MD, Sunnarborg SW, Kouros-Mehr H, Yu Y, Lee DC, Werb Z . Mammary ductal morphogenesis requires paracrine activation of stromal EGFR via ADAM17-dependent shedding of epithelial amphiregulin. Development 2005; 132: 3923–3933.
Shoyab M, Plowman GD, McDonald VL, Bradley JG, Todaro GJ . Structure and function of human amphiregulin: a member of the epidermal growth factor family. Science 1989; 243: 1074–1076.
DeWitt A, Iida T, Lam HY, Hill V, Wiley HS, Lauffenburger DA . Affinity regulates spatial range of EGF receptor autocrine ligand binding. Dev Biol 2002; 250: 305–316.
Ebner R, Derynck R . Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha: differential intracellular routing and processing of ligand-receptor complexes. Cell Regul 1991; 2: 599–612.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Zamir E, Kam Z, Oved S, Langdon WY et al. c-Cbl/Sli-1 regulates endocytic sorting and ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 3663–3674.
Stern KA, Place TL, Lill NL . EGF and amphiregulin differentially regulate Cbl recruitment to endosomes and EGF receptor fate. Biochem J 2008; 410: 585–594.
Baldys A, Gooz M, Morinelli TA, Lee MH, Raymond JR Jr, Luttrell LM et al. Essential role of c-Cbl in amphiregulin-induced recycling and signaling of the endogenous epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry 2009; 48: 1462–1473.
Roepstorff K, Grandal MV, Henriksen L, Knudsen SL, Lerdrup M, Grovdal L et al. Differential effects of EGFR ligands on endocytic sorting of the receptor. Traffic 2009; 10: 1115–1127.
Zwang Y, Yarden Y . Systems biology of growth factor-induced receptor endocytosis. Traffic 2009; 10: 349–363.
Frosi Y, Anastasi S, Ballaro C, Varsano G, Castellani L, Maspero E et al. A two-tiered mechanism of EGFR inhibition by RALT/MIG6 via kinase suppression and receptor degradation. J Cell Biol 2010; 189: 557–571.
Keyse SM . Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2008; 27: 253–261.
Lopez J, Banerjee S, Kaye SB . New developments in the treatment of ovarian cancer—future perspectives. Ann Oncol 2013; 24: x69–x76.
Eckstein N, Servan K, Girard L, Cai D, von Jonquieres G, Jaehde U et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway analysis identifies amphiregulin as a key factor for cisplatin resistance of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 739–750.
Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK, Perez EA, Puglisi F, Gianni L . Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2012; 9: 16–32.
Yarden Y, Pines G . The ERBB network: at last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 553–563.
Sheng Q, Liu X, Fleming E, Yuan K, Piao H, Chen J et al. An activated ErbB3/NRG1 autocrine loop supports in vivo proliferation in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 298–310.
Gui T, Shen K . The epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 2012; 36: 490–496.
Siwak DR, Carey M, Hennessy BT, Nguyen CT, McGahren Murray MJ, Nolden L et al. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in epithelial ovarian cancer: current knowledge and future challenges. J Oncol 2010; 2010: 568938.
Murphy M, Stordal B . Erlotinib or gefitinib for the treatment of relapsed platinum pretreated non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer: a systematic review. Drug Resist Updat 2011; 14: 177–190.
Lassus H, Sihto H, Leminen A, Joensuu H, Isola J, Nupponen NN et al. Gene amplification, mutation, and protein expression of EGFR and mutations of ERBB2 in serous ovarian carcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl) 2006; 84: 671–681.
Brustmann H . Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in serous ovarian carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study with galectin-3 and cyclin D1 and outcome. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2008; 27: 380–389.
Lindzen M, Lavi S, Leitner O, Yarden Y . Tailored cancer immunotherapy using combinations of chemotherapy and a mixture of antibodies against EGF-receptor ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 12559–12563.
Van Zoelen EJ, Stortelers C, Lenferink AE, Van de Poll ML . The EGF domain: requirements for binding to receptors of the ErbB family. Vitam Horm 2000; 59: 99–131.
Sato S, Drake AW, Tsuji I, Fan J . A potent anti-HB-EGF monoclonal antibody inhibits cancer cell proliferation and multiple angiogenic activities of HB-EGF. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e51964.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Sporn MB, Todaro GJ . Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med 1980; 303: 878–880.
Normanno N, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, Maiello MR, De Luca A et al. The ErbB receptors and their ligands in cancer: an overview. Curr Drug Targets 2005; 6: 243–257.
Esposito CL, Passaro D, Longobardo I, Condorelli G, Marotta P, Affuso A et al. A neutralizing RNA aptamer against EGFR causes selective apoptotic cell death. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e24071.
Pedersen MW, Jacobsen HJ, Koefoed K, Hey A, Pyke C, Haurum JS et al. Sym004: a novel synergistic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody mixture with superior anticancer efficacy. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 588–597.
Friedman LM, Rinon A, Schechter B, Lyass L, Lavi S, Bacus SS et al. Synergistic down-regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by combinations of mAbs: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 1915–1920.
Lindzen M, Carvalho S, Starr A, Ben-Chetrit N, Pradeep CR, Kostler WJ et al. A recombinant decoy comprising EGFR and ErbB-4 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3505–3515.
Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, Basik M, Harbison CT, Wu S et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3230–3237.
Yonesaka K, Zejnullahu K, Lindeman N, Homes AJ, Jackman DM, Zhao F et al. Autocrine production of amphiregulin predicts sensitivity to both gefitinib and cetuximab in EGFR wild-type cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 6963–6973.
Ciarloni L, Mallepell S, Brisken C . Amphiregulin is an essential mediator of estrogen receptor alpha function in mammary gland development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5455–5460.
Hsu D, Fukata M, Hernandez YG, Sotolongo JP, Goo T, Maki J et al. Toll-like receptor 4 differentially regulates epidermal growth factor-related growth factors in response to intestinal mucosal injury. Lab Invest 2010; 90: 1295–1305.
Panupinthu N, Yu S, Zhang D, Zhang F, Gagea M, Lu Y et al. Self-reinforcing loop of amphiregulin and Y-box binding protein-1 contributes to poor outcomes in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2013; 33: 2846–2856.
Sauer L, Gitenay D, Vo C, Baron VT . Mutant p53 initiates a feedback loop that involves Egr-1/EGF receptor/ERK in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2628–2637.
Bast RC Jr., Hennessy B, Mills GB . The biology of ovarian cancer: new opportunities for translation. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 415–428.
Blivet-Van Eggelpoel M-J, Chettouh H, Fartoux L, Aoudjehane L, Barbu V, Rey C et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER-3 restrict cell response to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Hepatol 2012; 57: 108–115.
Acknowledgements
We thank Julian Downward for lung cell lines. This work was performed at the Marvin Tanner Laboratory for Cancer Research and it was supported, in part, by Merck KGaA. The research in our laboratory is supported by the Israel Cancer Research Fund and the Dr Miriam and Sheldon G Adelson Medical Research Foundation and by the MD Moross Institute for Cancer Research. YY is the incumbent of the Harold and Zelda Goldenberg Professorial Chair. The Sheba Institutional Tissue Banks have received financial support from the Flight Attendants Medical Research Institute (FAMRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, S., Lindzen, M., Lauriola, M. et al. An antibody to amphiregulin, an abundant growth factor in patients’ fluids, inhibits ovarian tumors. Oncogene 35, 438–447 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.93
This article is cited by
-
The role of amphiregulin in ovarian function and disease
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
A toolkit for recombinant production of seven human EGF family growth factors in active conformation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Targeting autocrine amphiregulin robustly and reproducibly inhibits ovarian cancer in a syngeneic model: roles for wildtype p53
Oncogene (2021)
-
Amphiregulin can predict treatment resistance to palliative first-line cetuximab plus FOLFIRI chemotherapy in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Transient commensal clonal interactions can drive tumor metastasis
Nature Communications (2020)