Abstract
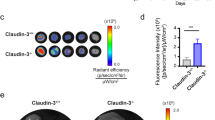
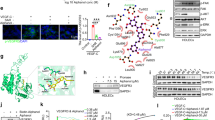
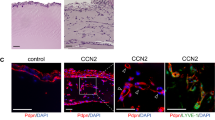
Transforming growth factor-β-induced protein (TGFBIp) is an extracellular matrix protein that has a role in a wide range of pathological conditions. However, the role of TGFBIp signaling in lymphangiogenesis is poorly understood. The purpose of this study was therefore to analyze the effects of TGFBIp on lymphangiogenesis and determine whether TGFBIp-related lymphangiogenesis is important for the metastasis of tumor cells. TGFBIp increased adhesion, migration, and morphologic differentiation of human lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), consistent with an increase in lymphatic vessel sprouting in a three-dimensional lymphatic ring assay. TGFBIp also induced phosphorylation of intracellular signaling molecules SRC, FAK, AKT, JNK and ERK. TGFBIp-induced lymphatic vessel sprouting was inhibited by addition of anti-integrin β3 antibody and pharmacologic inhibitors of FAK, AKT, JNK or ERK. TGFBIp increased both CCL21 expression in LECs, a chemokine that actively recruits tumor cells expressing the cognate chemokine receptors to lymphatic vessels and LEC permeability by inducing the dissociation of VE-cadherin junctions between LECs via the activation of SRC signaling. In vivo, inhibition of TGFBIp expression in SW620 cancer cells dramatically reduced tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that TGFBIp is a lymphangiogenic factor contributing to tumor dissemination and represents a potential target to inhibit metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fidler IJ, Balch CM . The biology of cancer metastasis and implications for therapy. Curr Probl Surg 1987; 24: 129–209.
Sporn MB . The war on cancer. Lancet 1996; 347: 1377–1381.
Stacker SA, Baldwin ME, Achen MG . The role of tumor lymphangiogenesis in metastatic spread. FASEB J 2002; 16: 922–934.
Sleeman JP, Thiele W . Tumor metastasis and the lymphatic vasculature. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 2747–2756.
Conway EM, Collen D, Carmeliet P . Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel growth. Cardiovasc Res 2001; 49: 507–521.
Thapa N, Lee BH, Kim IS . TGFBIp/betaig-h3 protein: a versatile matrix molecule induced by TGF-beta. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 39: 2183–2194.
Park SW, Bae JS, Kim KS, Park SH, Lee BH, Choi JY et al. Beta ig-h3 promotes renal proximal tubular epithelial cell adhesion, migration and proliferation through the interaction with alpha3beta1 integrin. Exp Mol Med 2004; 36: 211–219.
Kim YH, Kwon HJ, Kim DS . Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9)-dependent processing of betaig-h3 protein regulates cell migration, invasion, and adhesion. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 38957–38969.
Skonier J, Bennett K, Rothwell V, Kosowski S, Plowman G, Wallace P et al. beta ig-h3: a transforming growth factor-beta-responsive gene encoding a secreted protein that inhibits cell attachment in vitro and suppresses the growth of CHO cells in nude mice. DNA Cell Biol 1994; 13: 571–584.
Kim JE, Kim EH, Han EH, Park RW, Park IH, Jun SH et al. A TGF-beta-inducible cell adhesion molecule, betaig-h3, is downregulated in melorheostosis and involved in osteogenesis. J Cell Biochem 2000; 77: 169–178.
Bae JS, Lee SH, Kim JE, Choi JY, Park RW, Yong Park J et al. Betaig-h3 supports keratinocyte adhesion, migration, and proliferation through alpha3beta1 integrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 294: 940–948.
Kim JE, Kim SJ, Jeong HW, Lee BH, Choi JY, Park RW et al. RGD peptides released from beta ig-h3, a TGF-beta-induced cell-adhesive molecule, mediate apoptosis. Oncogene 2003; 22: 2045–2053.
Zhang Y, Wen G, Shao G, Wang C, Lin C, Fang H et al. TGFBI deficiency predisposes mice to spontaneous tumor development. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 37–44.
Becker J, Erdlenbruch B, Noskova I, Schramm A, Aumailley M, Schorderet DF et al. Keratoepithelin suppresses the progression of experimental human neuroblastomas. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 5314–5321.
Ween MP, Oehler MK, Ricciardelli C . Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein (TGFBI)/(betaig-H3): a matrix protein with dual functions in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2012; 13: 10461–10477.
Nam JO, Kim JE, Jeong HW, Lee SJ, Lee BH, Choi JY et al. Identification of the alphavbeta3 integrin-interacting motif of betaig-h3 and its anti-angiogenic effect. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 25902–25909.
Irigoyen M, Anso E, Salvo E, Dotor de las Herrerias J, Martinez-Irujo JJ, Rouzaut A . TGFbeta-induced protein mediates lymphatic endothelial cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix under low oxygen conditions. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008; 65: 2244–2255.
Lee AS, Kim DH, Lee JE, Jung YJ, Kang KP, Lee S et al. Erythropoietin induces lymph node lymphangiogenesis and lymph node tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4506–4517.
Christiansen A, Detmar M . Lymphangiogenesis and cancer. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 1146–1158.
Albrecht I, Christofori G . Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in development and cancer. Int J Dev Biol 2011; 55: 483–494.
Miyagaki T, Sugaya M, Okochi H, Asano Y, Tada Y, Kadono T et al. Blocking MAPK signaling downregulates CCL21 in lymphatic endothelial cells and impairs contact hypersensitivity responses. J Invest Dermatol 2011; 131: 1927–1935.
Baluk P, Fuxe J, Hashizume H, Romano T, Lashnits E, Butz S et al. Functionally specialized junctions between endothelial cells of lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 2349–2362.
Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Lampugnani MG . The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. J Cell Sci 2008; 121: 2115–2122.
Hewitt RE, McMarlin A, Kleiner D, Wersto R, Martin P, Tsokos M et al. Validation of a model of colon cancer progression. J Pathol 2000; 192: 446–454.
Mohammed RA, Green A, El-Shikh S, Paish EC, Ellis IO, Martin SG . Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors -A, -C and -D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio- and lymphangiogenesis. Br J Cancer 2007; 96: 1092–1100.
Schoppmann SF, Fenzl A, Nagy K, Unger S, Bayer G, Geleff S et al. VEGF-C expressing tumor-associated macrophages in lymph node positive breast cancer: impact on lymphangiogenesis and survival. Surgery 2006; 139: 839–846.
Wartiovaara U, Salven P, Mikkola H, Lassila R, Kaukonen J, Joukov V et al. Peripheral blood platelets express VEGF-C and VEGF which are released during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 1998; 80: 171–175.
Cao R, Eriksson A, Kubo H, Alitalo K, Cao Y, Thyberg J . Comparative evaluation of FGF-2-, VEGF-A-, and VEGF-C-induced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, vascular fenestrations, and permeability. Circ Res 2004; 94: 664–670.
Weis S, Cui J, Barnes L, Cheresh D . Endothelial barrier disruption by VEGF-mediated Src activity potentiates tumor cell extravasation and metastasis. J Cell Biol 2004; 167: 223–229.
Aguilar B, Choi I, Choi D, Chung HK, Lee S, Yoo J et al. Lymphatic reprogramming by Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus promotes the oncogenic activity of the virus-encoded G-protein-coupled receptor. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 5833–5842.
Min JK, Cho YL, Choi JH, Kim Y, Kim JH, Yu YS et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB ligand (RANKL) increases vascular permeability: impaired permeability and angiogenesis in eNOS-deficient mice. Blood 2007; 109: 1495–1502.
Maeng YS, Choi HJ, Kwon JY, Park YW, Choi KS, Min JK et al. Endothelial progenitor cell homing: prominent role of the IGF2-IGF2R-PLCbeta2 axis. Blood 2009; 113: 233–243.
Bruyere F, Melen-Lamalle L, Blacher S, Roland G, Thiry M, Moons L et al. Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system. Nat Methods 2008; 5: 431–437.
Paterson AD, Parton RG, Ferguson C, Stow JL, Yap AS . Characterization of E-cadherin endocytosis in isolated MCF-7 and chinese hamster ovary cells: the initial fate of unbound E-cadherin. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 21050–21057.
Boensch C, Huang SS, Connolly DT, Huang JS . Cell surface retention sequence binding protein-1 interacts with the v-sis gene product and platelet-derived growth factor beta-type receptor in simian sarcoma virus-transformed cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 10582–10589.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2011-0028699).
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: YSM, BA, SIC. Performed the experiments: YSM, SIC. Analyzed the data: YSM, SIC, EKK. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: YSM, SIC, EKK. Wrote the manuscript: YSM, BA, EKK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeng, YS., Aguilar, B., Choi, SI. et al. Inhibition of TGFBIp expression reduces lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Oncogene 35, 196–205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.73
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.73
This article is cited by
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling in tumor progression and immune escape: from mechanisms to treatments
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma-secreted exosomal miR-221-3p promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis by targeting VASH1
Oncogene (2019)
-
Lithium inhibits tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis through the inhibition of TGFBIp expression in cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2016)