Abstract
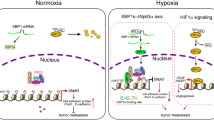
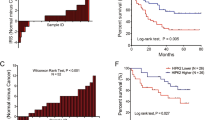
Hypoxic microenvironment is a powerful driving force for the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), as a crucial regulator of transcriptional responses to hypoxia, induces the expression of multiple target genes involved in different steps of HCC metastatic process. It is critical to find target genes associated with metastasis under hypoxia for shedding new light on molecular mechanism of HCC metastasis. In this study, we uncovered that hypoxia could induce the upregulation of Rab11-family interacting protein 4 (Rab11-FIP4) and activation of Rab11-FIP4 promoter by HIF-1α. The overexpression of Rab11-FIP4 significantly enhanced the mobility and invasiveness of HCC cells in vitro, also contributed to distant lung metastasis in vivo, whereas silencing of Rab11-FIP4 decreased the ability of migration and invasion in HCC cells in vitro and suppressed lung metastasis in vivo. Rab11-FIP4 facilitated HCC metastasis through the phosphorylation of PRAS40, which was regulated by mTOR. Furthermore, the expression level of Rab11-FIP4 was significantly increased in HCC tissues and high expression of Rab11-FIP4 was closely correlated with vascular invasion and poor prognosis in HCC patients. A markedly positive correlation between the expression of Rab11-FIP4 and HIF-1α was observed in HCC tissues and combination of Rab11-FIP4 and HIF-1α was a more valuable predictor of poor prognosis for HCC patients. In conclusion, Rab11-FIP4 is a target gene of HIF-1α and has a pro-metastatic role in HCC, suggesting that Rab11-FIP4 may be a promising candidate target for HCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HIF-1α:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
- PHDs:
-
prolyl hydroxylases
- HREs:
-
hypoxia-responsive elements
- CoCl2:
-
cobalt chloride
- Rab11-FIP4:
-
Rab11-family interacting protein 4
- OS:
-
overall survival
- DFS:
-
disease-free survival
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM . Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2893–2917.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J . Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012; 379: 1245–1255.
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA et al. Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg 2006; 243: 229–235.
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN . Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008; 48: 2047–2063.
Hernandez-Gea V, Toffanin S, Friedman SL, Llovet JM . Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013; 144: 512–527.
Semenza GL . Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2012; 33: 207–214.
Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC . The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 967–975.
Sullivan R, Graham CH . Hypoxia-driven selection of the metastatic phenotype. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2007; 26: 319–331.
Semenza GL . Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 2010; 29: 625–634.
Wu XZ, Xie GR, Chen D . Hypoxia and hepatocellular carcinoma: the therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 22: 1178–1182.
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC . Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 294–309.
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M et al. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001; 292: 464–468.
Semenza GL . HIF-1 and mechanisms of hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 167–171.
Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ . Activation of the HIF pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2001; 11: 293–299.
Nagase T, Kikuno R, Ohara O . Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XXII. The complete sequences of 50 new cDNA clones which code for large proteins. DNA Res 2001; 8: 319–327.
Wallace DM, Lindsay AJ, Hendrick AG, McCaffrey MW . The novel Rab11-FIP/Rip/RCP family of proteins displays extensive homo- and hetero-interacting abilities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 292: 909–915.
Ullrich O, Reinsch S, Urbe S, Zerial M, Parton RG . Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J Cell Biol 1996; 135: 913–924.
Chen W, Feng Y, Chen D, Wandinger-Ness A . Rab11 is required for trans-golgi network-to-plasma membrane transport and a preferential target for GDP dissociation inhibitor. Mol Biol Cell 1998; 9: 3241–3257.
Wilcke M, Johannes L, Galli T, Mayau V, Goud B, Salamero J . Rab11 regulates the compartmentalization of early endosomes required for efficient transport from early endosomes to the trans-golgi network. J Cell Biol 2000; 151: 1207–1220.
Deneka M, van der Sluijs P . 'Rab'ing up endosomal membrane transport. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: E33–E35.
Wallace DM, Lindsay AJ, Hendrick AG, McCaffrey MW . Rab11-FIP4 interacts with Rab11 in a GTP-dependent manner and its overexpression condenses the Rab11 positive compartment in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 299: 770–779.
Prekeris R, Davies JM, Scheller RH . Identification of a novel Rab11/25 binding domain present in Eferin and Rip proteins. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 38966–38970.
Horgan CP, McCaffrey MW . The dynamic Rab11-FIPs. Biochem Soc Trans 2009; 37: 1032–1036.
Meyers JM, Prekeris R . Formation of mutually exclusive Rab11 complexes with members of the family of Rab11-interacting proteins regulates Rab11 endocytic targeting and function. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 49003–49010.
Fielding AB, Schonteich E, Matheson J, Wilson G, Yu X, Hickson GR et al. Rab11-FIP3 and FIP4 interact with Arf6 and the exocyst to control membrane traffic in cytokinesis. EMBO J 2005; 24: 3389–3399.
Krzyzaniak MA, Mach M, Britt WJ . HCMV-encoded glycoprotein M (UL100) interacts with Rab11 effector protein FIP4. Traffic 2009; 10: 1439–1457.
Muto A, Aoki Y, Watanabe S . Mouse Rab11-FIP4 regulates proliferation and differentiation of retinal progenitors in a Rab11-independent manner. Dev Dyn 2007; 236: 214–225.
Muto A, Arai K, Watanabe S . Rab11-FIP4 is predominantly expressed in neural tissues and involved in proliferation as well as in differentiation during zebrafish retinal development. Dev Biol 2006; 292: 90–102.
Wiza C, Nascimento EB, Ouwens DM . Role of PRAS40 in Akt and mTOR signaling in health and disease. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012; 302: E1453–E1460.
Xiong X, Xie R, Zhang H, Gu L, Xie W, Cheng M et al. PRAS40 plays a pivotal role in protecting against stroke by linking the Akt and mTOR pathways. Neurobiol Dis 2014; 66: 43–52.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW . Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 2004; 36: 1–12.
Wu MZ, Tsai YP, Yang MH, Huang CH, Chang SY, Chang CC et al. Interplay between HDAC3 and WDR5 is essential for hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell 2011; 43: 811–822.
Oshiro N, Takahashi R, Yoshino K, Tanimura K, Nakashima A, Eguchi S et al. The proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa (PRAS40) is a physiological substrate of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 20329–20339.
Vander Haar E, Lee SI, Bandhakavi S, Griffin TJ, Kim DH . Insulin signalling to mTOR mediated by the Akt/PKB substrate PRAS40. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 316–323.
Nascimento EB, Ouwens DM . PRAS40: target or modulator of mTORC1 signalling and insulin action? Arch Physiol Biochem 2009; 115: 163–175.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China (2012ZX10002011-004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201627 and 81371883), Shanghai Municipal Program of International Cooperation in Science and Technology (12410709800), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20120073110091), Key Basic Research Program of Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (11JC1412201), Grant from the State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes (91-1201, 91-1305), Doctoral Innovation Fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (BXJ201243) and Key Discipline and Specialty Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, F., Deng, X., Yang, X. et al. Hypoxia upregulates Rab11-family interacting protein 4 through HIF-1α to promote the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 34, 6007–6017 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.49
This article is cited by
-
Rab11-FIP4 interacts with ARF5 to promote cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2023)
-
PGK1 represses autophagy-mediated cell death to promote the proliferation of liver cancer cells by phosphorylating PRAS40
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
USP14 maintains HIF1-α stabilization via its deubiquitination activity in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Sema4D expression and secretion are increased by HIF-1α and inhibit osteogenesis in bone metastases of lung cancer
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2019)
-
Identification of important invasion and proliferation related genes in adrenocortical carcinoma
Medical Oncology (2019)