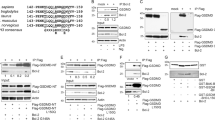
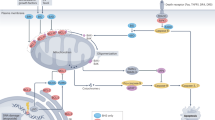
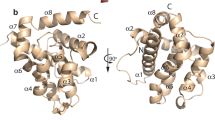
Abstract
The control of apoptosis in mammals has been historically associated with the activity of the BCL-2 family of proteins at the mitochondria. In the past years, a novel group of cell death regulators have emerged, known as the Transmembrane BAX Inhibitor-1 Motif-containing (TMBIM) protein family. This group of proteins is composed of at least six highly conserved members expressed in mammals, with homologs in insects, fish, plants, viruses and yeast. Different studies indicate that all TMBIM family members have inhibitory activities in different setting of apoptosis. Here, we overview and integrate possible mechanisms underlying the impact of the TMBIM protein family in the regulation of cell death, which include activities at diverse subcellular compartments, including death receptor regulation, modulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium homeostasis, ER stress signaling, autophagy, reactive oxygen species production, among other effects. The possible intersection between the BCL-2 and TMBIM family in the control of cell death is also discussed, in addition to their implication in the progression of cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . Cell death: critical control points. Cell 2004; 116: 205–219.
Youle RJ, Strasser A . The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 47–59.
Ow YP, Green DR, Hao Z, Mak TW . Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 532–542.
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Zanin C, Vayssiere JL, Petit PX et al. Reduction in mitochondrial potential constitutes an early irreversible step of programmed lymphocyte death in vivo. J Exp Med 1995; 181: 1661–1672.
Dussmann H, Rehm M, Kogel D, Prehn JH . Outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during apoptosis triggers caspase-independent mitochondrial and caspase-dependent plasma membrane potential depolarization: a single-cell analysis. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 525–536.
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X . Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 1996; 86: 147–157.
Antignani A, Youle RJ . How do Bax and Bak lead to permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane? Curr Opin Cell Biol 2006; 18: 685–689.
Green DR, Kroemer G . The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 2004; 305: 626–629.
Kelekar A, Thompson CB . Bcl-2-family proteins: the role of the BH3 domain in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 1998; 8: 324–330.
Martinou JC, Youle RJ . Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 2011; 21: 92–101.
Tait SW, Green DR . Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 621–632.
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC, Jeffers JR, Zambetti GP, Hsieh JJ et al. Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 1348–1358.
Ren D, Tu HC, Kim H, Wang GX, Bean GR, Takeuchi O et al. BID, BIM, and PUMA are essential for activation of the BAX- and BAK-dependent cell death program. Science 2010; 330: 1390–1393.
Happo L, Strasser A, Cory S . BH3-only proteins in apoptosis at a glance. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 1081–1087.
Buttner S, Eisenberg T, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Ruli D, Knauer H, Ruckenstuhl C et al. Endonuclease G regulates budding yeast life and death. Mol Cell 2007; 25: 233–246.
Carmona-Gutierrez D, Eisenberg T, Buttner S, Meisinger C, Kroemer G, Madeo F . Apoptosis in yeast: triggers, pathways, subroutines. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 763–773.
Eisenberg T, Buttner S, Kroemer G, Madeo F . The mitochondrial pathway in yeast apoptosis. Apoptosis 2007; 12: 1011–1023.
Ludovico P, Rodrigues F, Almeida A, Silva MT, Barrientos A, Corte-Real M . Cytochrome c release and mitochondria involvement in programmed cell death induced by acetic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 2002; 13: 2598–2606.
Madeo F, Frohlich E, Frohlich KU . A yeast mutant showing diagnostic markers of early and late apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1997; 139: 729–734.
Madeo F, Herker E, Maldener C, Wissing S, Lachelt S, Herlan M et al. A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Mol Cell 2002; 9: 911–917.
Wissing S, Ludovico P, Herker E, Buttner S, Engelhardt SM, Decker T et al. An AIF orthologue regulates apoptosis in yeast. J Cell Biol 2004; 166: 969–974.
Ligr M, Madeo F, Frohlich E, Hilt W, Frohlich KU, Wolf DH . Mammalian Bax triggers apoptotic changes in yeast. FEBS Lett 1998; 438: 61–65.
Priault M, Camougrand N, Chaudhuri B, Schaeffer J, Manon S . Comparison of the effects of bax-expression in yeast under fermentative and respiratory conditions: investigation of the role of adenine nucleotides carrier and cytochrome c. FEBS Lett 1999; 456: 232–238.
Xu Q, Reed JC . Bax inhibitor-1, a mammalian apoptosis suppressor identified by functional screening in yeast. Mol Cell 1998; 1: 337–346.
Huckelhoven R . BAX Inhibitor-1, an ancient cell death suppressor in animals and plants with prokaryotic relatives. Apoptosis 2004; 9: 299–307.
Ishikawa T, Watanabe N, Nagano M, Kawai-Yamada M, Lam E . Bax inhibitor-1: a highly conserved endoplasmic reticulum-resident cell death suppressor. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1271–1278.
Carrara G, Saraiva N, Gubser C, Johnson BF, Smith GL . Six-transmembrane topology for Golgi anti-apoptotic protein (GAAP) and Bax inhibitor 1 (BI-1) provides model for the transmembrane Bax inhibitor-containing motif (TMBIM) family. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 15896–15905.
Chae HJ, Kim HR, Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Krajewska M, Krajewski S et al. BI-1 regulates an apoptosis pathway linked to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell 2004; 15: 355–366.
Kawai M, Pan L, Reed JC, Uchimiya H . Evolutionally conserved plant homologue of the Bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) gene capable of suppressing Bax-induced cell death in yeast(1). FEBS Lett 1999; 464: 143–147.
Henke N, Lisak DA, Schneider L, Habicht J, Pergande M, Methner A . The ancient cell death suppressor BAX inhibitor-1. Cell Calcium 2011; 50: 251–260.
Reimers K, Choi CY, Bucan V, Vogt PM . The Bax Inhibitor-1 (BI-1) family in apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Curr Mol Med 2008; 8: 148–156.
Zhou J, Zhu T, Hu C, Li H, Chen G, Xu G et al. Comparative genomics and function analysis on BI1 family. Comput Biol Chem 2008; 32: 159–162.
Hu L, Smith TF, Goldberger G . LFG: a candidate apoptosis regulatory gene family. Apoptosis 2009; 14: 1255–1265.
Rojas-Rivera D, Armisen R, Colombo A, Martinez G, Eguiguren AL, Diaz A et al. TMBIM3/GRINA is a novel unfolded protein response (UPR) target gene that controls apoptosis through the modulation of ER calcium homeostasis. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: 1013–1026.
Yamaji T, Nishikawa K, Hanada K, Transmembrane BAX . inhibitor motif containing (TMBIM) family proteins perturbs a trans-Golgi network enzyme, Gb3 synthase, and reduces Gb3 biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 35505–35518.
Robinson KS, Clements A, Williams AC, Berger CN, Frankel G . Bax inhibitor 1 in apoptosis and disease. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2391–2400.
Buttner S, Ruli D, Vogtle FN, Galluzzi L, Moitzi B, Eisenberg T et al. A yeast BH3-only protein mediates the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. EMBO J 2011; 30: 2779–2792.
Aouacheria A, Rech de Laval V, Combet C, Hardwick JM . Evolution of Bcl-2 homology motifs: homology versus homoplasy. Trends Cell Biol 2013; 23: 103–111.
Yoshisue H, Suzuki K, Kawabata A, Ohya T, Zhao H, Sakurada K et al. Large scale isolation of non-uniform shear stress-responsive genes from cultured human endothelial cells through the preparation of a subtracted cDNA library. Atherosclerosis 2002; 162: 323–334.
Shukla S, Fujita K, Xiao Q, Liao Z, Garfield S, Srinivasula SM . A shear stress responsive gene product PP1201 protects against Fas-mediated apoptosis by reducing Fas expression on the cell surface. Apoptosis 2011; 16: 162–173.
Zhao H, Ito A, Kimura SH, Yabuta N, Sakai N, Ikawa M et al. RECS1 deficiency in mice induces susceptibility to cystic medial degeneration. Genes Genet Syst 2006; 81: 41–50.
Somia NV, Schmitt MJ, Vetter DE, Van Antwerp D, Heinemann SF, Verma IM . LFG: an anti-apoptotic gene that provides protection from Fas-mediated cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 12667–12672.
Schweitzer B, Suter U, Taylor V . Neural membrane protein 35/Lifeguard is localized at postsynaptic sites and in dendrites. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2002; 107: 47–56.
Hurtado de Mendoza T, Perez-Garcia CG, Kroll TT, Hoong NH, O'Leary DD, Verma IM . Antiapoptotic protein Lifeguard is required for survival and maintenance of Purkinje and granular cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 17189–17194.
Fernandez M, Segura MF, Sole C, Colino A, Comella JX, Cena V . Lifeguard/neuronal membrane protein 35 regulates Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis in neurons via microdomain recruitment. J Neurochem 2007; 103: 190–203.
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong WX, Rathmell JC, Shiels HA et al. The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members bak and bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues. Mol Cell 2000; 6: 1389–1399.
Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Thielen P, Zamorano S, Todd D, Martinon F et al. BAX inhibitor-1 is a negative regulator of the ER stress sensor IRE1alpha. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 679–691.
Krajewska M, Xu L, Xu W, Krajewski S, Kress CL, Cui J et al. Endoplasmic reticulum protein BI-1 modulates unfolded protein response signaling and protects against stroke and traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 2011; 1370: 227–237.
Bailly-Maitre B, Fondevila C, Kaldas F, Droin N, Luciano F, Ricci JE et al. Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2809–2814.
Bailly-Maitre B, Belgardt BF, Jordan SD, Coornaert B, von Freyend MJ, Kleinridders A et al. Hepatic Bax inhibitor-1 inhibits IRE1alpha and protects from obesity-associated insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 6198–6207.
Kotsafti A, Farinati F, Cardin R, Burra P, Bortolami M . Bax inhibitor-1 down-regulation in the progression of chronic liver diseases. BMC Gastroenterol 2010; 10: 35.
Gubser C, Bergamaschi D, Hollinshead M, Lu X, van Kuppeveld FJ, Smith GL . A new inhibitor of apoptosis from vaccinia virus and eukaryotes. PLoS Pathogen 2007; 3: e17.
Alcami A, Smith GL . Vaccinia, cowpox, and camelpox viruses encode soluble gamma interferon receptors with novel broad species specificity. J Virol 1995; 69: 4633–4639.
Moore JB, Smith GL . Steroid hormone synthesis by a vaccinia enzyme: a new type of virus virulence factor. EMBO J 1992; 11: 1973–1980.
Oka T, Sayano T, Tamai S, Yokota S, Kato H, Fujii G et al. Identification of a novel protein MICS1 that is involved in maintenance of mitochondrial morphology and apoptotic release of cytochrome c. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 2597–2608.
Chen YB, Aon MA, Hsu YT, Soane L, Teng X, McCaffery JM et al. Bcl-xL regulates mitochondrial energetics by stabilizing the inner membrane potential. J Cell Biol 2011; 195: 263–276.
Li Y, Kelder B, Kopchick JJ . Identification, isolation, and cloning of growth hormone (GH)-inducible interscapular brown adipose complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from GH antagonist mice. Endocrinology 2001; 142: 2937–2945.
Yoshida T, Nagata S, Kataoka H . Ghitm is an ortholog of the Bombyx mori prothoracic gland-derived receptor (Pgdr) that is ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells and requires an N-terminal signal sequence for expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 13–18.
Reimers K, Choi CY, Bucan V, Vogt PM . The growth-hormone inducible transmembrane protein (Ghitm) belongs to the Bax inhibitory protein-like family. Int J Biol Sci 2007; 3: 471–476.
Kumar KN, Tilakaratne N, Johnson PS, Allen AE, Michaelis EK . Cloning of cDNA for the glutamate-binding subunit of an NMDA receptor complex. Nature 1991; 354: 70–73.
Hollmann M, Heinemann S . Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 1994; 17: 31–108.
Szuchet S, Plachetzki DC, Eaton KS . Oligodendrocyte transmembrane protein: a novel member of the glutamate-binding protein subfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 283: 900–907.
Nielsen JA, Chambers MA, Romm E, Lee LY, Berndt JA, Hudson LD . Mouse transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif 3 (Tmbim3) encodes a 38 kDa transmembrane protein expressed in the central nervous system. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 357: 73–81.
Galindo KA, Lu WJ, Park JH, Abrams JM . The Bax/Bak ortholog in Drosophila, Debcl, exerts limited control over programmed cell death. Development 2009; 136: 275–283.
Sevrioukov EA, Burr J, Huang EW, Assi HH, Monserrate JP, Purves DC et al. Drosophila Bcl-2 proteins participate in stress-induced apoptosis, but are not required for normal development. Genesis 2007; 45: 184–193.
Jette CA, Flanagan AM, Ryan J, Pyati UJ, Carbonneau S, Stewart RA et al. BIM and other BCL-2 family proteins exhibit cross-species conservation of function between zebrafish and mammals. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 1063–1072.
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S . Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition in cell death. Apoptosis 2007; 12: 835–840.
Zhivotovsky B, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G . Adenine nucleotide translocase: a component of the phylogenetically conserved cell death machinery. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 1419–1425.
de Mattia F, Gubser C, van Dommelen MM, Visch HJ, Distelmaier F, Postigo A et al. Human Golgi antiapoptotic protein modulates intracellular calcium fluxes. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20: 3638–3645.
Kiviluoto S, Vervliet T, Ivanova H, Decuypere JP, De Smedt H, Missiaen L et al. Regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1833: 1612–1624.
Kim HR, Lee GH, Ha KC, Ahn T, Moon JY, Lee BJ et al. Bax inhibitor-1 Is a pH-dependent regulator of Ca2+ channel activity in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 15946–15955.
Westphalen BC, Wessig J, Leypoldt F, Arnold S, Methner A . BI-1 protects cells from oxygen glucose deprivation by reducing the calcium content of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 304–306.
Bultynck G, Kiviluoto S, Henke N, Ivanova H, Schneider L, Rybalchenko V et al. The C terminus of Bax inhibitor-1 forms a Ca2+-permeable channel pore. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 2544–2557.
Lee GH, Hwang JD, Choi JY, Park HJ, Cho JY, Kim KW et al. An acidic pH environment increases cell death and pro-inflammatory cytokine release in osteoblasts: the involvement of BAX inhibitor-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011; 43: 1305–1317.
Kiviluoto S, Schneider L, Luyten T, Vervliet T, Missiaen L, De Smedt H et al. Bax inhibitor-1 is a novel IP(3) receptor-interacting and -sensitizing protein. Cell Death Disease 2012; 3: e367.
Kiviluoto S, Luyten T, Schneider L, Lisak D, Rojas-Rivera D, Welkenhuyzen K et al. Bax inhibitor-1-mediated Ca(2+) leak is decreased by cytosolic acidosis. Cell Calcium 2013; 54: 186–192.
Xu C, Xu W, Palmer AE, Reed JC . BI-1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis downstream of Bcl-2 family proteins. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 11477–11484.
Ahn T, Yun CH, Kim HR, Chae HJ . Cardiolipin phosphatidylserine, and BH4 domain of Bcl-2 family regulate Ca2+/H+ antiporter activity of human Bax inhibitor-1. Cell Calcium 2010; 47: 387–396.
Bailly-Maitre B, Bard-Chapeau E, Luciano F, Droin N, Bruey JM, Faustin B et al. Mice lacking bi-1 gene show accelerated liver regeneration. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 1442–1450.
Lee GH, Ahn T, Kim DS, Park SJ, Lee YC, Yoo WH et al. Bax inhibitor 1 increases cell adhesion through actin polymerization: involvement of calcium and actin binding. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 1800–1813.
Lee GH, Kim HK, Chae SW, Kim DS, Ha KC, Cuddy M et al. Bax inhibitor-1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated reactive oxygen species and heme oxygenase-1 expression. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 21618–21628.
Lee GH, Kim HR, Chae HJ . Bax inhibitor-1 regulates the expression of P450 2E1 through enhanced lysosome activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2012; 44: 600–611.
Kim JH, Lee ER, Jeon K, Choi HY, Lim H, Kim SJ et al. Role of BI-1 (TEGT)-mediated ERK1/2 activation in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and splenomegaly in BI-1 transgenic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1823: 876–888.
Saraiva N, Prole DL, Carrara G, Maluquer de Motes C, Johnson BF, Byrne B et al. Human and viral Golgi anti-apoptotic proteins (GAAPs) oligomerize via different mechanisms and monomeric GAAP inhibits apoptosis and modulates calcium. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 13057–13067.
Saraiva N, Prole DL, Carrara G, Johnson BF, Taylor CW, Parsons M et al. hGAAP promotes cell adhesion and migration via the stimulation of store-operated Ca2+ entry and calpain 2. J Cell Biol 2013; 202: 699–713.
Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH . The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1alpha. Physiol Rev 2011; 91: 1219–1243.
Walter P, Ron D . The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011; 334: 1081–1086.
Hetz C, Glimcher LH . Fine-tuning of the unfolded protein response: assembling the IRE1alpha interactome. Mol Cell 2009; 35: 551–561.
Hetz C . The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 89–102.
Tabas I, Ron D . Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 184–190.
Urra H, Dufey E, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Hetz C . When ER stress reaches a dead end. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1833: 3507–3517.
Hetz C, Bernasconi P, Fisher J, Lee AH, Bassik MC, Antonsson B et al. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK modulate the unfolded protein response by a direct interaction with IRE1alpha. Science 2006; 312: 572–576.
Rodriguez DA, Zamorano S, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Urra H, Cubillos-Ruiz JR et al. BH3-only proteins are part of a regulatory network that control the sustained signalling of the unfolded protein response sensor IRE1alpha. EMBO J 2012; 31: 2322–2335.
Rong J, Chen L, Toth JI, Tcherpakov M, Petroski MD, Reed JC . Bifunctional apoptosis regulator (BAR), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated E3 ubiquitin ligase, modulates BI-1 protein stability and function in ER Stress. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 1453–1463.
Lee GH, Kim DS, Kim HT, Lee JW, Chung CH, Ahn T et al. Enhanced lysosomal activity is involved in Bax inhibitor-1-induced regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response and cell death against ER stress: involvement of vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase). J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 24743–24753.
Castillo K, Rojas-Rivera D, Lisbona F, Caballero B, Nassif M, Court FA et al. BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1alpha branch of the unfolded protein response. EMBO J 2011; 30: 4465–4478.
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005; 122: 927–939.
Sano R, Hou YC, Hedvat M, Correa RG, Shu CW, Krajewska M et al. Endoplasmic reticulum protein BI-1 regulates Ca(2)(+)-mediated bioenergetics to promote autophagy. Genes Devel 2012; 26: 1041–1054.
Cebulski J, Malouin J, Pinches N, Cascio V, Austriaco N . Yeast Bax inhibitor, Bxi1p, is an ER-localized protein that links the unfolded protein response and programmed cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One 2011; 6: e20882.
Chae HJ, Ke N, Kim HR, Chen S, Godzik A, Dickman M et al. Evolutionarily conserved cytoprotection provided by Bax inhibitor-1 homologs from animals, plants, and yeast. Gene 2003; 323: 101–113.
Cakir B . Bax induces activation of the unfolded protein response by inducing HAC1 mRNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2012; 29: 395–406.
Dejeans N, Hetz C, Bard F, Hupp T, Agostinis P, Samali A et al. Addicted to secrete—novel concepts and targets in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 2014.
Hetz C, Chevet E, Harding HP . Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2013; 12: 703–719.
Tanaka R, Ishiyama T, Uchihara T, Inadome Y, Iijima T, Morishita Y et al. Expression of the Bax inhibitor-1 gene in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2006; 106: 648–653.
Grzmil M, Kaulfuss S, Thelen P, Hemmerlein B, Schweyer S, Obenauer S et al. Expression and functional analysis of Bax inhibitor-1 in human breast cancer cells. J Pathol 2006; 208: 340–349.
Grzmil M, Thelen P, Hemmerlein B, Schweyer S, Voigt S, Mury D et al. Bax inhibitor-1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer and its specific down-regulation by RNA interference leads to cell death in human prostate carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 2003; 163: 543–552.
Schmits R, Cochlovius B, Treitz G, Regitz E, Ketter R, Preuss KD et al. Analysis of the antibody repertoire of astrocytoma patients against antigens expressed by gliomas. Int J Cancer 2002; 98: 73–77.
Villalva C, Trempat P, Greenland C, Thomas C, Girard JP, Moebius F et al. Isolation of differentially expressed genes in NPM-ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 791–798.
Zhang M, Li X, Zhang Y, Zhou K . Bax inhibitor-1 mediates apoptosis-resistance in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2010; 333: 1–7.
Schmidt SM, Konig T, Bringmann A, Held S, von Schwarzenberg K, Heine A et al. Characterization of BAX inhibitor-1 as a novel leukemia-associated antigen. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1818–1824.
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia 2007; 9: 166–180.
Wu X, Wang L, Ye Y, Aakre JA, Pu X, Chang GC et al. Genome-wide association study of genetic predictors of overall survival for non-small cell lung cancer in never smokers. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 4028–4038.
Li XY, Lai YK, Zhang JF, Luo HQ, Zhang MH, Zhou KY et al. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting Bax inhibitor-1 suppresses ex vivo cell proliferation and in vivo tumor growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther 2011; 22: 1201–1208.
Lee GH, Yan C, Shin SJ, Hong SC, Ahn T, Moon A et al. BAX inhibitor-1 enhances cancer metastasis by altering glucose metabolism and activating the sodium-hydrogen exchanger: the alteration of mitochondrial function. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2130–2141.
Lee GH, Chae HJ, Kim HR . Monoamine carboxylate transporters are involved in BI-1-associated cancer metastasis in HT1080 colon fibrosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol 2011; 39: 209–216.
Hsu CF, Sui CL, Wu WC, Wang JJ, Yang DH, Chen YC et al. Klf10 induces cell apoptosis through modulation of BI-1 expression and Ca2+ homeostasis in estrogen-responding adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011; 43: 666–673.
Xiang-yong L, Yang-chao C, Ke-yuan Z, Mei-hong Z, Hai-qing L, Hsiang-fu K et al. Overexpression of Bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) induces cell transformation in NIH3T3 cells. Cell Biol Int 2010; 34: 1099–1104.
Yun CH, Chae HJ, Kim HR, Ahn T . Doxorubicin- and daunorubicin-induced regulation of Ca2+ and H+ fluxes through human bax inhibitor-1 reconstituted into membranes. J Pharm Sci 2012; 101: 1314–1326.
Bucan V, Adili MY, Choi CY, Eddy MT, Vogt PM, Reimers K . Transactivation of lifeguard (LFG) by Akt-/LEF-1 pathway in MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 human breast cancer cells. Apoptosis 2010; 15: 814–821.
Bucan V, Reimers K, Choi CY, Eddy MT, Vogt PM . The anti-apoptotic protein lifeguard is expressed in breast cancer cells and tissues. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2010; 15: 296–310.
Bucan V, Choi CY, Lazaridis A, Vogt PM, Reimers K . Silencing of anti-apoptotic transmembrane protein lifeguard sensitizes solid tumor cell lines MCF-7 and SW872 to perifosine-induced cell death activation. Oncol Lett 2011; 2: 419–422.
Hunsberger JG, Machado-Vieira R, Austin DR, Zarate C, Chuang DM, Chen G et al. Bax inhibitor 1, a modulator of calcium homeostasis, confers affective resilience. Brain Res 2011; 1403: 19–27.
Lewis TB, Wood S, Michaelis EK, DuPont BR, Leach RJ . Localization of a gene for a glutamate binding subunit of a NMDA receptor (GRINA) to 8q24. Genomics 1996; 32: 131–133.
Goswami DB, Jernigan CS, Chandran A, Iyo AH, May WL, Austin MC et al. Gene expression analysis of novel genes in the prefrontal cortex of major depressive disorder subjects. Progr Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2012; 43C: 126–133.
Reich A, Spering C, Gertz K, Harms C, Gerhardt E, Kronenberg G et al. Fas/CD95 regulatory protein Faim2 is neuroprotective after transient brain ischemia. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 225–233.
Markkula E, Hulkkonen J, Penttila T, Puolakkainen M . Host cell Golgi anti-apoptotic protein (GAAP) and growth of Chlamydia pneumoniae. Microb Pathogen 2013; 54: 46–53.
Hemrajani C, Berger CN, Robinson KS, Marches O, Mousnier A, Frankel G . NleH effectors interact with Bax inhibitor-1 to block apoptosis during enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 3129–3134.
Robinson KS, Mousnier A, Hemrajani C, Fairweather N, Berger CN, Frankel G . The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli effector NleH inhibits apoptosis induced by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Microbiology 2010; 156: 1815–1823.
Ameisen JC . The origin of programmed cell death. Science 1996; 272: 1278–1279.
Kroemer G . Mitochondrial implication in apoptosis. Towards an endosymbiont hypothesis of apoptosis evolution. Cell Death Differ 1997; 4: 443–456.
Schmits R, Cochlovius B, Treitz G, Regitz E, Ketter R, Preuss KD et al. Analysis of the antibody repertoire of astrocytoma patients against antigens expressed by gliomas. Int J Cancer 2002; 98: 73–77.
Lima RT, Martins LM, Guimaraes JE, Sambade C, Vasconcelos MH . Specific downregulation of bcl-2 and xIAP by RNAi enhances the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 2004; 11: 309–316.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by FONDEF D11I1007, Ring Initiative ACT1109, Millennium Institute No. P09-015-F, the Alzheimeŕs Association, FONDECYT No. 1100176, FONDECYT No. 1140549, ECOS CONICYT C13S02 CONICYT Grant USA2013-0003, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, ALS Therapy Alliance (CH) and FONDECYT No. 3130365 Post-doctoral grant (DRR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-Rivera, D., Hetz, C. TMBIM protein family: ancestral regulators of cell death. Oncogene 34, 269–280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
miR-125a-3p regulates apoptosis by suppressing TMBIM4 in lens epithelial cells
International Ophthalmology (2022)
-
Up-regulation of apoptotic- and cell survival-related gene pathways following exposures of western corn rootworm to B. thuringiensis crystalline pesticidal proteins in transgenic maize roots
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1
Cell & Bioscience (2021)
-
Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2020)
-
Transmembrane protein GRINA modulates aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor progression in gastric cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)