Abstract
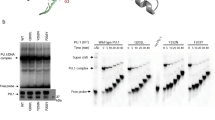
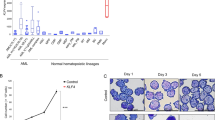
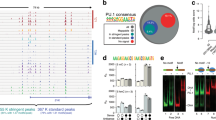
Generation of myeloid and lymphoid cells from progenitors involves dynamic changes in transcription factor expression and use, and disruption of hematopoietic transcription factor function and expression can contribute to leukemic transformation. PU.1 and Ikaros are pivotal factors whose expression and utilization are dynamically altered during hematopoietic development. Here, we demonstrate that expression of PU.1, encoded by the Sfpi1 gene, is divergently regulated by Ikaros in distinct cell type-specific contexts. Chromatin immune precipitation analysis and functional perturbations revealed that Ikaros can directly repress or activate Sfpi1 transcription via different PU.1 cis-elements, with PU.1 and Ikaros collaborating at myeloid-specific elements but not at other elements. Our results thus shed light on how PU.1 and Ikaros can act as lineage competency factors to facilitate both myeloid and lymphoid developmental programs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreau-Gachelin F, Tavitian A, Tambourin P . Spi-1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine erythroleukaemias. Nature 1988; 331: 277–280.
Iwasaki H, Akashi K . Hematopoietic developmental pathways: on cellular basis. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6687–6696.
Laiosa CV, Stadtfeld M, Graf T . Determinants of lymphoid-myeloid lineage diversification. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 705–738.
Swiers G, Patient R, Loose M . Genetic regulatory networks programming hematopoietic stem cells and erythroid lineage specification. Dev Biol 2006; 294: 525–540.
Nutt SL, Metcalf D, D′Amico A, Polli M, Wu L . Dynamic regulation of PU.1 expression in multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 221–231.
Back J, Allman D, Chan S, Kastner P . Visualizing PU.1 activity during hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol 2005; 33: 395–402.
DeKoter RP, Singh H . Regulation of B lymphocyte and macrophage development by graded expression of PU.1. Science 2000; 288: 1439–1441.
Rosenbauer F, Wagner K, Kutok JL, Iwasaki H, Le Beau MM, Okuno Y et al. Acute myeloid leukemia induced by graded reduction of a lineage-specific transcription factor, PU.1. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 624–630.
Houston I, Kamath M, Schweitzer B, Chlon T, DeKoter R . Reduction in PU.1 activity results in a block to B-cell development, abnormal myeloid proliferation, and neonatal lethality. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1056–1068.
Li Y, Okuno Y, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Chen H-M, Iwasaki H et al. Regulation of the PU.1 gene by distal elements. Blood 2001; 98: 2958–2965.
Chen H, Ray-Gallet D, Zhang P, Hetherington CJ, Gonzalez DA, Zhang DE et al. PU.1 (Spi-1) autoregulates its expression in myeloid cells. Oncogene 1995; 11: 1549–1560.
Okuno Y, Huang G, Rosenbauer F, Evans EK, Radomska HS, Iwasaki H et al. Potential autoregulation of transcription factor PU.1 by an upstream regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 2832–2845.
Spooner C, Cheng J, Pujadas E, Laslo P, Singh H . A recurrent network involving the transcription factors PU.1 and Gfi1 orchestrates innate and adaptive immune cell fates. Immunity 2009; 31: 576–586.
Zarnegar MA, Chen J, Rothenberg EV . Cell-type-specific activation and repression of PU.1 by a complex of discrete, functionally specialized cis-regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 4922–4939.
Leddin M, Perrod C, Hoogenkamp M, Ghani S, Assi S, Heinz S et al. Two distinct auto-regulatory loops operate at the PU.1 locus in B cells and myeloid cells. Blood 2011; 117: 2827–2838.
Georgopoulos K . Transcription factors required for lymphoid lineage commitment. Curr Opin Immunol 1997; 9: 222–227.
Georgopoulos K, Bigby M, Wang JH, Molnar A, Wu P, Winandy S et al. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 1994; 79: 143–156.
Ng SY-M, Yoshida T, Zhang J, Georgopoulos K . Genome-wide lineage-specific transcriptional networks underscore Ikaros-dependent lymphoid priming in hematopoietic stem cells. Immunity 2009; 30: 493–507.
Yagi T, Hibi S, Takanashi M, Kano G, Tabata Y, Imamura T et al. High frequency of Ikaros isoform 6 expression in acute myelomonocytic and monocytic leukemias: implications for up-regulation of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-XL in leukemogenesis. Blood 2002; 99: 1350–1355.
Yoshida T, Ng S, Zuniga-Pflucker J, Georgopoulos K . Early hematopoietic lineage restrictions directed by Ikaros. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 382–391.
Carotta S, Dakic A, D’Amico A, Pang SHM, Greig KT, Nutt SL et al. The transcription factor PU.1 controls dendritic cell development and Flt3 cytokine receptor expression in a dose-dependent manner. Immunity 2010; 32: 628–641.
Reynaud D, A Demarco I, L Reddy K, Schjerven H, Bertolino E, Chen Z et al. Regulation of B cell fate commitment and immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene rearrangements by Ikaros. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 927–936.
Dijon M, Bardin F, Murati A, Batoz M, Chabannon C, Tonnelle C . The role of Ikaros in human erythroid differentiation. Blood 2008; 111: 1138–1146.
Trinh LA, Ferrini R, Cobb BS, Weinmann AS, Hahm K, Ernst P et al. Down-regulation of TDT transcription in CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by Ikaros proteins in direct competition with an Ets activator. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 1817–1832.
DeKoter RP, Lee H-J, Singh H . PU.1 regulates expression of the interleukin-7 receptor in lymphoid progenitors. Immunity 2002; 16: 297–309.
Stehling-Sun S, Dade J, Nutt SL, DeKoter RP, Camargo FD . Regulation of lymphoid versus myeloid fate ‘choice’ by the transcription factor Mef2c. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 289–296.
Anderson MK, Hernandez-Hoyos G, Diamond RA, Rothenberg EV . Precise developmental regulation of Ets family transcription factors during specification and commitment to the T cell lineage. Development 1999; 126: 3131–3148.
Hoogenkamp M, Krysinska H, Ingram R, Huang G, Barlow R, Clarke D et al. The Pu.1 locus is differentially regulated at the level of chromatin structure and noncoding transcription by alternate mechanisms at distinct developmental stages of hematopoiesis. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7425–7438.
Ebralidze AK, Guibal FC, Steidl U, Zhang P, Lee S, Bartholdy B et al. PU.1 expression is modulated by the balance of functional sense and antisense RNAs regulated by a shared cis-regulatory element. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2085–2092.
Chou ST, Khandros E, Bailey LC, Nichols KE, Vakoc CR, Yao Y et al. Graded repression of PU.1/Sfpi1 gene transcription by GATA factors regulates hematopoietic cell fate. Blood 2009; 114: 983–994.
Koipally J, Georgopoulos K . Ikaros interactions with CtBP reveal a repression mechanism that is independent of histone deacetylase activity. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 19594–19602.
Papathanasiou P, Perkins AC, Cobb BS, Ferrini R, Sridharan R, Hoyne GF et al. Widespread failure of hematolymphoid differentiation caused by a recessive niche-filling allele of the Ikaros transcription factor. Immunity 2003; 19: 131–144.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH Grant R01 CA90233, the LA Garfinkle Memorial Laboratory Fund, the Al Sherman Foundation and the AB Ruddock Professorship to EVR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarnegar, M., Rothenberg, E. Ikaros represses and activates PU.1 cell-type-specifically through the multifunctional Sfpi1 URE and a myeloid specific enhancer. Oncogene 31, 4647–4654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.597
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.597