Abstract
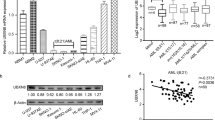
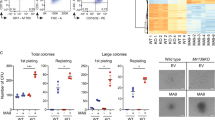
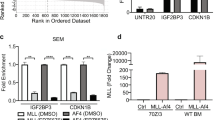
Fusion proteins containing the amino terminus of mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) are common in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) due to translocations. The MLL–AF4 fusion protein is generated by the translocation t(4;11)(q21;q23), and t(4;11)-positive ALL patients (MLL–AF4 ALL), have a notoriously poorer prognosis compared with patients with other MLL-associated leukemias. The detailed role of this fusion protein in leukemogenesis is not well understood. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) targeting the AF4 3′ untranslated regions may modulate MLL–AF4 fusion protein levels, raising the question of whether regulation of these miRNAs are involved in the progression of MLL–AF4 ALL. In this study, we show that miR-143 was identified as a regulator of MLL–AF4 expression in MLL–AF4 ALL samples. Restoration of miR-143 in MLL–AF4-positive RS4;11 and MV4-11 cells induced apoptosis, negatively contributing to leukemia cell growth by reducing MLL–AF4 fusion protein levels. Furthermore, miR-143 was epigenetically repressed by promoter hypermethylation in MLL–AF4-positive primary blasts and cell lines, but not in normal bone marrow cells and MLL–AF4-negative primary blasts, which was directly associated with expression of the MLL–AF4 oncogene. This is the first study to show that miR-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in MLL–AF4 B-cell ALL. These data reveal the therapeutic promise of upregulating miR-143 expression for MLL–AF4 B-cell ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Hirata I, Iio A, Itoh T, Kojima K et al. (2010). Role of anti-oncomirs miR-143 and -145 in human colorectal tumors. Cancer Gene Ther 17: 398–408.
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Iio A, Naoe T . (2009). Role of microRNA-143 in Fas-mediated apoptosis in human T-cell leukemia Jurkat cells. Leuk Res 33: 1530–1538.
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Kitade Y, Kinoshita T, Naoe T . (2007). Downregulation of microRNAs-143 and -145 in B-cell malignancies. Cancer Sci 98: 1914–1920.
Bittner S, Bobak N, Herrmann AM, Göbel K, Meuth P, Höhn KG et al. (2010). Upregulation of K2P5. 1 potassium channels in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 68: 58–69.
Chen X, Guo X, Zhang H, Xiang Y, Chen J, Yin Y et al. (2009). Role of miR-143 targeting KRAS in colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 28: 1385–1392.
Clape C, Fritz V, Henriquet C, Apparailly F, Fernandez PL, Iborra F et al. (2009). miR-143 interferes with ERK5 signaling, and abrogates prostate cancer progression in mice. PLoS One 4: e7542.
Cordes KR, Sheehy NT, White MP, Berry EC, Morton SU, Muth AN et al. (2009). miR-145 and miR-143 regulate smooth muscle cell fate and plasticity. Nature 460: 705–710.
Erfurth FE, Popovic R, Grembecka J, Cierpicki T, Theisler C, Xia ZB et al. (2008). MLL protects CpG clusters from methylation within the Hoxa9 gene, maintaining transcript expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 7517–7522.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . (2006). Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269.
Fazi F, Racanicchi S, Zardo G, Starnes LM, Mancini M, Travaglini L et al. (2007). Epigenetic silencing of the myelopoiesis regulator microRNA-223 by the AML1/ETO oncoprotein. Cancer Cell 12: 457–466.
Gao W, Yu Y, Cao H, Shen H, Li X, Pan S et al. (2010). Deregulated expression of miR-21, miR-143 and miR-181a in non small cell lung cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Biomed Pharmacother 64: 399–408.
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA, Croce CM . (2006). MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol Med 12: 580–587.
Glas M, Rath BH, Simon M, Reinartz R, Schramme A, Trageser D et al. (2010). Residual tumor cells are unique cellular targets in glioblastoma. Ann Neurol 68: 264–269.
Langevin SM, Stone RA, Bunker CH, Lyons-Weiler MA, Laframboise WA, Kelly L et al. (2011). MicroRNA-137 promoter methylation is associated with poorer overall survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 117: 1454–1462.
Lin TC, Hou HA, Chou WC, Ou DL, Yu SL, Tien HF et al. (2011). CEBPA methylation as a prognostic biomarker in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 25: 32–40.
Liu H, Cheng EH, Hsieh JJ . (2009). MLL fusions: pathways to leukemia. Cancer Biol Ther 8: 1204–1211.
Liu Q, Fu H, Sun F, Zhang H, Tie Y, Zhu J et al. (2008). miR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 5391–5404.
Lowenberg B . (2008). Diagnosis and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia--the art of distinction. N Engl J Med 358: 1960–1962.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435: 834–838.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D et al. (2008). A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 13556–13561.
Luty AA, Kwok JBJ, Dobson-Stone C, Loy CT, Coupland KG, Karlström H et al. (2010). Sigma nonopioid intracellular receptor 1 mutations cause frontotemporal lobar degeneration-Cmotor neuron disease. Ann Neurol 68: 639–649.
Metzler M, Forster A, Pannell R, Arends MJ, Daser A, Lobato MN et al. (2006). A conditional model of MLL-AF4 B-cell tumourigenesis using invertor technology. Oncogene 25: 3093–3103.
Meyer B, Wurm JP, Kotter P, Leisegang MS, Schilling V, Buchhaupt M et al. (2011). The Bowen-Conradi syndrome protein Nep1 (Emg1) has a dual role in eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis, as an essential assembly factor and in the methylation of {Psi}1191 in yeast 18S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 39: 1526–1537.
Ronchi AE, Bottardi S, Mazzucchelli C, Ottolenghi S, Santoro C . (1995). Differential binding of the NFE3 and CP1/NFY transcription factors to the human gamma- and epsilon-globin CCAAT boxes. J Biol Chem 270: 21934–21941.
Santoro R, Li J, Grummt I . (2002). The nucleolar remodeling complex NoRC mediates heterochromatin formation and silencing of ribosomal gene transcription. Nat Genet 32: 393–396.
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T, Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M et al. (2007). Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology 72: 397–402.
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T, Tanigawa N, Akao Y . (2009). Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and -145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology 77: 12–21.
Thomas M, Gessner A, Vornlocher HP, Hadwiger P, Greil J, Heidenreich O . (2005). Targeting MLL-AF4 with short interfering RNAs inhibits clonogenicity and engraftment of t(4;11)-positive human leukemic cells. Blood 106: 3559–3566.
Walker BA, Wardell CP, Chiecchio L, Smith EM, Boyd KD, Neri A et al. (2011). Aberrant global methylation patterns affect the molecular pathogenesis and prognosis of multiple myeloma. Blood 117: 553–562.
Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Wang L, Yang L, Zhou B, Gu J et al. (2009). Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-31, -143 and -145 expression in colorectal cancer. Dis Markers 26: 27–34.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M et al. (2006). Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9: 189–198.
Yu L, Liu C, Vandeusen J, Becknell B, Dai Z, Wu YZ et al. (2005). Global assessment of promoter methylation in a mouse model of cancer identifies ID4 as a putative tumor-suppressor gene in human leukemia. Nat Genet 37: 265–274.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Xiaofei Zheng for miRNA-expressing plasmids. We thank Wei Wang, Yi Ding, Yuanyuan Xu, Nan Wang, Chengwang Xu, Meng Li, Xufeng Luo, Huiyuan Kang, Xinrong Wang and Xiaoning Gao for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30800482, 30971297 and 90919044), Medical Capital Development Fund (2007-2040), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 7102147) and the National 973 Project of China (No. 2005CB522400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dou, L., Zheng, D., Li, J. et al. Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA-143 enhances MLL–AF4 oncogene expression. Oncogene 31, 507–517 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.248
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Methylation-associated silencing of BASP1 contributes to leukemogenesis in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
MicroRNA-143 targets ERK5 in granulopoiesis and predicts outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Clinical utility of miR-143/miR-182 levels in prognosis and risk stratification specificity of BFM-treated childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Annals of Hematology (2018)
-
Molecular processes involved in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
miR-139-5p controls translation in myeloid leukemia through EIF4G2
Oncogene (2016)