Abstract
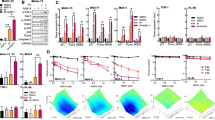
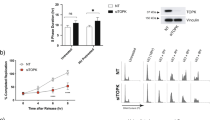
The stress-inducible transcription factor, nuclear factor (NF)-κB induces genes involved in proliferation and apoptosis. Aberrant NF-κB activity is common in cancer and contributes to therapeutic-resistance. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is activated during DNA strand break repair and is a known transcriptional co-regulator. Here, we investigated the role of PARP-1 function during NF-κB activation using p65 small interfering RNA (siRNA), PARP siRNA or the potent PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699. Survival and apoptosis assays showed that NF-κB p65−/− cells were more sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR) than p65+/+ cells. Co-incubation with p65 siRNA, PARP siRNA or AG-014699 radio-sensitized p65+/+, but not p65−/− cells, demonstrating that PARP-1 mediates its effects on survival via NF-κB. Single-strand break (SSB) repair kinetics, and the effect SSB repair inhibition by AG-014699 were similar in p65+/+ and p65−/− cells. As preventing SSB repair did not radio-sensitize p65−/− cells, we conclude that radio-sensitization by AG-014699 is due to downstream inhibition of NF-κB activation, and independent of SSB repair inhibition. PARP-1 catalytic activity was essential for IR-induced p65 DNA binding and NF-κB-dependent gene transcription, whereas for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-treated cells, PARP-1 protein alone was sufficient. We hypothesize that this stimulus-dependent differential is mediated via stimulation of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymer, which was induced following IR, not TNF-α. Targeting DNA damage-activated NF-κB using AG-014699 may therefore overcome toxicity observed with classical NF-κB inhibitors without compromising other vital inflammatory functions. These data highlight the potential of PARP-1 inhibitors to overcome NF-κB-mediated therapeutic resistance and widens the spectrum of cancers in which these agents may be utilized.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02524-2
References
Althaus FR, Hofferer L, Kleczkowska HE, Malanga M, Naegeli H, Panzeter PL et al. (1994). Histone shuttling by poly ADP-ribosylation. Mol Cell Biochem 138: 53–59.
Barkett M, Gilmore T . (1999). Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18: 6910–6924.
Basseres DS, Baldwin AS . (2006). Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25: 6817–6830.
Biswas DK, Shi Q, Baily S, Strickland I, Ghosh S, Pardee AB et al. (2004). NF-kappa B activation in human breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 10137–10142.
Bonicalzi ME, Haince JF, Droit A, Poirier GG . (2005). Regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism by poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase: where and when? Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 739–750.
Brach MA, Hass R, Sherman ML, Gunji H, Weichselbaum R, Kufe D . (1991). Ionizing radiation induces expression and binding activity of the nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest 88: 691–695.
Brady ME, Ozanne DM, Gaughan L, Waite I, Cook S, Neal DE et al. (1999). Tip60 is a nuclear hormone receptor coactivator. J Biol Chem 274: 17599–17604.
Burger PC, Vogel FS, Green SB, Strike TA . (1985). Glioblsstoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma pathologic criteria and prognostic implications. Cancer 56: 1106–1111.
Chang WJ, Alvarez-Gonzalez R . (2001). The sequence-specific DNA binding of NF-kappa B is reversibly regulated by the automodification reaction of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1. J Biol Chem 276: 47664–47670.
Chariot A . (2009). The NF-kappaB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 19: 404–413.
Clevers H . (2004). At the crossroads of inflammation and cancer. Cell 118: 671–674.
Criollo A, Senovilla L, Authier H, Chiara Maiuri M, Morselli E, Vitale I et al. (2010). The IKK complex contributes to the induction of autophagy. EMBO J 29: 619–631.
Criswell T, Leskov K, Miyamoto S, Luo G, Boothman DA . (2003). Transcription factors activated in mammalian cells after clinically relevant doses of ionizing radiation. Oncogene 22: 5813–5827.
Daniel RA, Rozanska AL, Thomas HD, Mulligan EA, Drew Y, Castelbuono DJ et al. (2009). Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 enhances temozolomide and topotecan activity against childhood neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 15: 1241–1249.
Drew Y, Mulligan EA, Vong WT, Thomas HD, Kahn S, Kyle S et al. (2010). Therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor AG014699 in human cancers with mutated or methylated BRCA1 or BRCA2. J Natl Cancer Inst 103: 334–346.
Drew Y, Plummer R . (2009). PARP inhibitors in cancer therapy: two modes of attack on the cancer cell widening the clinical applications. Drug Resist Updat 12: 153–156.
Durkacz BW, Omidiji O, Gray DA, Shall S . (1980). (ADP-ribose) participates in DNA excision repair. Nature 283: 593–596.
Ghosh G, Huang DB, Huxford T . (1999). Structural insights into NF-κB/IκB signaling. Gene Ther Mol Biol 4: 75–82.
Ghosh S, Karin M . (2002). Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109 (Suppl): S81–S96.
Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M . (2006). Inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 25: 6887–6899.
Grossman M, Metcalf D, Merryfull J, Beg A, Baltimore D, Gerondakis S . (1999). The combined absence of the transcription factors Rel and RelA leads to multiple hemopoietic cell defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 11848–11853.
Hassa PO, Covic M, Hasan S, Imhof R, Hottiger MO . (2001). The enzymatic and DNA binding activity of PARP-1 are not required for NF-kappa B coactivator function. J Biol Chem 276: 45588–45597.
Hassa PO, Haenni SS, Buerki C, Meier NI, Lane WS, Owen H et al. (2005). Acetylation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 by p300/CREB-binding protein regulates coactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 280: 40450–40464.
Hassa PO, Hottiger MO . (1999). A role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in NF-kappaB transcriptional activation. Biol Chem 380: 953–959.
Hewamana S, Alghazal S, Lin TT, Clement M, Jenkins C, Guzman ML et al. (2008a). The NF-kappaB subunit Rel A is associated with in vitro survival and clinical disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and represents a promising therapeutic target. Blood 111: 4681–4689.
Hewamana S, Lin TT, Jenkins C, Burnett AK, Jordan CT, Fegan C et al. (2008b). The novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor LC-1 is equipotent in poor prognostic subsets of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and shows strong synergy with fludarabine. Clin Cancer Res 14: 8102–8111.
Hewamana S, Lin TT, Rowntree C, Karunanithi K, Pratt G, Hills R et al. (2009). Rel a is an independent biomarker of clinical outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 27: 763–769.
Jackson A, Linsley P . (2004). Noise amidst the silence: off target effects of siRNAs? Trends Genet 20: 521–524.
Jung M, Dritschilo A . (2001). NF-kappa B signaling pathway as a target for human tumor radiosensitization. Semin Radiat Oncol 11: 346–351.
Kanzawa T, Ito H, Kondo Y, Kondo S . (2003). Current and future gene therapy for malignant gliomas. J Biomed Biotechnol 2003: 25–34.
Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA . (2005). Poly(ADP-ribose); polymerase-1 promotes microgial activation, proliferation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediated neuron death. J Immunol 174: 2288–2296.
Kraus WL, Lis JT . (2003). PARP goes transcription. Cell 113: 677–683.
Martin-Oliva D, Aguliar-Quesada R, O'valle F, Munoz-Gamez JA, Martinez-Romero R, Garcia Del-Moral R et al. (2006). Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase modulates tumor-related gene expression, including hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activation, during skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 66: 5744–5756.
Mulligan EA, Hunter JE, Baird AEG, Elliott SL, Summerfield GP, Hamlen K et al. (2010). Relationships between aberrant activity of the NF-κB subunits and outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: the dual role of DNA damage sensor kinases. Blood 116: 1477.
Ogorek B, Bryant PE . (1985). Repair of DNA single-strand breaks in X-irradiated yeast. II. Kinetics of repair as measured by the DNA-unwinding method. Mutat Res 146: 63–70.
Oliver FJ, Menissier de Murcia J, Nacci C, Decker P, Andriantsitohaina R, Muller S et al. (1999). Resistance to endotoxic shock as a consequence of defective NF-kappaB activation in poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 deficient mice. EMBO J 18: 4446–4454.
Prasad S, Ravindran J, Aggarwal B . (2009). NF-κB and cancer: how intimate is this relationship. Mol Cell Biochem 336: 25–37.
Plummer ER, Middleton MR, Jones C, Olsen A, Hickson I, McHugh P et al. (2005a). Temozolomide pharmacodynamics in patients with metastatic melanoma: DNA damage and activity of repair enzymes O6-alkylguanine alkyltransferase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Clin Cancer Res 11: 3402–3409.
Plummer ER, Jones C, Middleton MR, Wilson R, Evans J, Olsen A et al. (2008). Phase I study of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, AG014699, in combination with temozolomide in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14: 7917–7923.
Plummer R, Lorigan P, Evans J, Steven N, Middleton M, Wilson R et al. (2006). First and final report of a phase II study of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, AG014699, in combination with temozolomide (TMZ) in patients with metastatic malignantmelanoma (MM). J Clin Oncol 24 No. 18S, Part I: 8013.
Plummer R, Middleton M, Wilson R, Jones C, Evans J, Robson L et al. (2005b). First in human phase I trial of the PARP inhibitor AG-014699 with temozolomide (TMZ) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 23 No.16S, Part I: 3065.
Russo SM, Tepper JE, Baldwin Jr AS, Lui R, Adams J, Elliott P et al. (2001). Enhancement of radiosensitivity by proteasome inhibition: implications for a role of NF-kappaB. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50: 183–193.
Sahijdak WM, Yang CR, Zuckerman JS, Meyers M, Boothman DA . (1994). Alterations in transcription factor binding in radioresistant human melanoma cells after ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 138: S47–S51.
Slama JT, Aboul-Ela N, Goli DM, Cheesman BV, Simmons AM, Jacobson MK . (1995). Specific inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase by adenosine diphosphate (hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidinediol. J Med Chem 38: 389–393.
Smith S . (2001). The world according to PARP. Trends Biochem Sci 26: 174–179.
Stilmann M, Hinz M, Arslan SC, Zimmer A, Schreiber V, Schreiderit C . (2009). A nuclear poly(ADP-ribose)-dependent signalosome confers DNA damage-induced IkappaB kinase activation. Mol Cell 36: 365–378.
Trucco C, Javier Oliver F, de Murcia G, Menissier de Murcia J . (1998). DNA repair defect in poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-deficient cell lines. Nucleic Acid Res 26: 2644–2649.
Tschaharganeh D, Ehemann V, Nussbaum T, Schrimacher P, Breuhahn K . (2007). Non-specific effects of siRNAs on tumor cells with implications on therapeutic applicability using RNA interference. Pathol Oncol Res 13: 84–90.
Turco MC, Romano MF, Petrella A, Bisgoni R, Tassone P, Ventuna S . (2004). NF-kappaB/Rel-mediated regulation of apoptosis in hematologic malignancies and normal hematopoietic progenitors. Leukemia 18: 11–17.
Ueda K, Hayaishi O . (1985). ADP-RIBOSYLATION Ann. Rev Biochem 54: 73–100.
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Richardson CJ, Smith GC, Durkacz BW . (2003). Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res 63: 6008–6015.
Veuger SJ, Hunter JE, Durkacz BW . (2009). Ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation requires PARP-1 function to confer radioresistance. Oncogene 28: 832–842.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin Jr AS . (1996). TNF and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science 274: 784–787.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin Jr AS . (1998). NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281: 1680–1683.
Wang H, Wang H, Zhang W, Huang HJ, Liao WS, Fuller GN . (2004). Analysis of the activation status of Akt, NFkappaB and Stat3 in human diffuse gliomas. Lab Invest 84: 941–951.
Wu JT, Kral JG . (2005). The NF-kappaB/IkappaB signaling system: a molecular target in breast cancer therapy. J Surg Res 123: 158–169.
Zaremba T, Ketzer P, Cole M, Coulthard S, Plummer ER, Curtin NJ . (2009). Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 polymorphisms, expression and activity in selected human tumour cell lines. Br J Cancer I 101: 256–262.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Pfizer for the supply of AG-014699. This work was supported by Cancer Research UK, grant number C7369/A8048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hunter, J., Willmore, E., Irving, J. et al. NF-κB mediates radio-sensitization by the PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699. Oncogene 31, 251–264 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.229
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.229
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Rucaparib: First Global Approval
Drugs (2017)
-
MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-κB axis
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2016)
-
Opportunities and challenges of radiotherapy for treating cancer
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2015)