Abstract
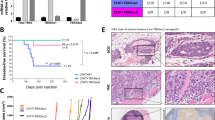
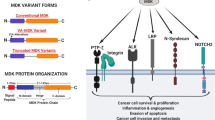
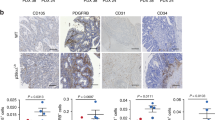
Although the hyper-glycosylated transmembrane protein Mucin 1 (MUC1) is aberrantly overexpressed in human breast carcinoma, the biological significance of MUC1 overexpression is unclear. This study showed that MUC1 expression promoted the synthesis and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) through the AKT signaling pathway. Increase VEGF production through MUC1 expression had a number of effect. First, MUC1 transfection increased expression of VEGF in breast cancer cells. Second, MUC1-mediated VEGF induction was attenuated by a chemical inhibitor of AKT or MUC1 knock-down by MUC1 siRNA. Third, MUC1 expression led to the activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, which correlated with VEGF expression. In addition, when MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells were directly injected into NOD/SCID mice, MUC1 expression accelerated xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Finally, MUC1 expression enhanced tumor growth and angiogenesis in a PyMT-MMTV/hMUC1 transgenic mouse model. Concurrent with these results, analysis of a human tissue microarray identified a high correlation between MUC1 and VEGF expression in human breast carcinoma. The current report is the first to demonstrate that MUC1 expression promotes angiogenesis in human breast cancer in vivo and in vitro.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Av P, Crofford LJ, Wilder RL, Hla T . (1995). Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in synovial fibroblasts by prostaglandin E and interleukin-1: a potential mechanism for inflammatory angiogenesis. FEBS Lett 372: 83–87.
Borgstrom P, Hillan KJ, Sriramarao P, Ferrara N . (1996). Complete inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of microtumors by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor neutralizing antibody: novel concepts of angiostatic therapy from intravital videomicroscopy. Cancer Res 56: 4032–4039.
Brayman M, Thathiah A, Carson DD . (2004). MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2: 4.
Cho JA, Yeo DJ, Son HY, Kim HW, Jung DS, Ko JK et al. (2005). Exosomes: a new delivery system for tumor antigens in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Cancer 114: 613–622.
Cohen T, Nahari D, Cerem LW, Neufeld G, Levi BZ . (1996). Interleukin 6 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem 271: 736–741.
Duffy MJ, Shering S, Sherry F, McDermott E, O'Higgins N . (2000). CA 15-3: a prognostic marker in breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers 15: 330–333.
Duraisamy S, Kufe T, Ramasamy S, Kufe D . (2007). Evolution of the human MUC1 oncoprotein. Int J Oncol 31: 671–677.
Dvorak HF, Nagy JA, Feng D, Brown LF, Dvorak AM . (1999). Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and the significance of microvascular hyperpermeability in angiogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 237: 97–132.
Feldkamp MM, Lau N, Rak J, Kerbel RS, Guha A . (1999). Normoxic and hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by astrocytoma cells is mediated by Ras. Int J Cancer 81: 118–124.
Ferrara N . (2002). Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 29: 10–14.
Fessler SP, Wotkowicz MT, Mahanta SK, Bamdad C . (2009). MUC1* is a determinant of trastuzumab (Herceptin) resistance in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118: 113–124.
Fontana J, Fulton D, Chen Y, Fairchild TA, McCabe TJ, Fujita N et al. (2002). Domain mapping studies reveal that the M domain of hsp90 serves as a molecular scaffold to regulate Akt-dependent phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and NO release. Circ Res 90: 866–873.
Frank S, Hubner G, Breier G, Longaker MT, Greenhalgh DG, Werner S . (1995). Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem 270: 12607–12613.
Geddis AE, Fox NE, Kaushansky K . (2006). The Mpl receptor expressed on endothelial cells does not contribute significantly to the regulation of circulating thrombopoietin levels. Exp Hematol 34: 82–86.
Gendler SJ . (2001). MUC1, the renaissance molecule. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6: 339–353.
Gendler SJ, Lancaster CA, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Duhig T, Peat N, Burchell J et al. (1990). Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor-associated polymorphic epithelial mucin. J Biol Chem 265: 15286–15293.
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E, O'Byrne K, Cox G, Thorpe PE et al. (2000). Coexpression of MUC1 glycoprotein with multiple angiogenic factors in non-small cell lung cancer suggests coactivation of angiogenic and migration pathways. Clin Cancer Res 6: 1917–1921.
Guy CT, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ . (1992). Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: a transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol Cell Biol 12: 954–961.
Hattrup CL, Gendler SJ . (2006). MUC1 alters oncogenic events and transcription in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 8: R37.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E . (2010). Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60: 277–300.
Kim B, Leventhal PS, Saltiel AR, Feldman EL . (1997). Insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated neurite outgrowth in vitro requires mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 272: 21268–21273.
Kimura T, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Sumii K, Kajiyama G, Shimamoto F et al. (2000). Clinical significance of MUC1 and E-cadherin expression, cellular proliferation, and angiogenesis at the deepest invasive portion of colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 16: 55–64.
Kohno N, Hamada H, Fujioka S, Hiwada K, Yamakido M, Akiyama M . (1992). Circulating antigen KL-6 and lactate dehydrogenase for monitoring irradiated patients with lung cancer. Chest 102: 117–122.
Kucab JE, Dunn SE . (2003). Role of IGF-1R in mediating breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Breast Dis 17: 41–47.
Kurmasheva RT, Dudkin L, Billups C, Debelenko LV, Morton CL, Houghton PJ . (2009). The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-targeting antibody, CP-751,871, suppresses tumor-derived VEGF and synergizes with rapamycin in models of childhood sarcoma. Cancer Res 69: 7662–7671.
Lee HY, Oh SH, Woo JK, Kim WY, Van Pelt CS, Price RE et al. (2005). Chemopreventive effects of deguelin, a novel Akt inhibitor, on tobacco-induced lung tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 97: 1695–1699.
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N . (1989). Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246: 1306–1309.
Li J, Perrella MA, Tsai JC, Yet SF, Hsieh CM, Yoshizumi M et al. (1995). Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression by interleukin-1 beta in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 270: 308–312.
Mikami Y, Hisatsune A, Tashiro T, Isohama Y, Katsuki H . (2009). Hypoxia enhances MUC1 expression in a lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379: 1060–1065.
Milanini-Mongiat J, Pouyssegur J, Pages G . (2002). Identification of two Sp1 phosphorylation sites for p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases: their implication in vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription. J Biol Chem 277: 20631–20639.
Morgillo F, Woo JK, Kim ES, Hong WK, Lee HY . (2006). Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinib. Cancer Res 66: 10100–10111.
Okajima E, Thorgeirsson UP . (2000). Different regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by the ERK and p38 kinase pathways in v-ras, v-raf, and v-myc transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270: 108–111.
Papadopoulos I, Sivridis E, Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI . (2001). Tumor angiogenesis is associated with MUC1 overexpression and loss of prostate-specific antigen expression in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7: 1533–1538.
Parrizas M, Saltiel AR, LeRoith D . (1997). Insulin-like growth factor 1 inhibits apoptosis using the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 272: 154–161.
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G et al. (1999). Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7203–7215.
Pochampalli MR, Bitler BG, Schroeder JA . (2007a). Transforming growth factor alpha dependent cancer progression is modulated by Muc1. Cancer Res 67: 6591–6598.
Pochampalli MR, el Bejjani RM, Schroeder JA . (2007b). MUC1 is a novel regulator of ErbB1 receptor trafficking. Oncogene 26: 1693–1701.
Pollak MN . (2004). Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Novartis Found Symp 262: 84–98; discussion 98–107, 265–108.
Pore N, Liu S, Shu HK, Li B, Haas-Kogan D, Stokoe D et al. (2004). Sp1 is involved in Akt-mediated induction of VEGF expression through an HIF-1-independent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell 15: 4841–4853.
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, McMullan C, Sykoutri D, Fanourakis G, Kotoula V et al. (2003). Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by insulin-like growth factor I in thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88: 5392–5398.
Raina D, Kharbanda S, Kufe D . (2004). The MUC1 oncoprotein activates the anti-apoptotic phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and Bcl-xL pathways in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 279: 20607–20612.
Ren J, Raina D, Chen W, Li G, Huang L, Kufe D . (2006). MUC1 oncoprotein functions in activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling. Mol Cancer Res 4: 873–883.
Risau W . (1997). Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386: 671–674.
Sachdeva M, Mo YY . (2010). MicroRNA-145 suppresses cell invasion and metastasis by directly targeting mucin 1. Cancer Res 70: 378–387.
Sakamoto H, Yonezawa S, Utsunomiya T, Tanaka S, Kim YS, Sato E . (1997). Mucin antigen expression in gastric carcinomas of young and old adults. Hum Pathol 28: 1056–1065.
Sorokin LM, Pausch F, Frieser M, Kroger S, Ohage E, Deutzmann R . (1997). Developmental regulation of the laminin alpha5 chain suggests a role in epithelial and endothelial cell maturation. Dev Biol 189: 285–300.
Tang Y, Zhang D, Fallavollita L, Brodt P . (2003). Vascular endothelial growth factor C expression and lymph node metastasis are regulated by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 63: 1166–1171.
Wang BF, Cheng YA, Dang SS . (2009). [Angiogenesis inhibitory effect of saikosaponin-d on chicken embryo]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 29: 425–429.
Wei X, Xu H, Kufe D . (2006). MUC1 oncoprotein stabilizes and activates estrogen receptor alpha. Mol Cell 21: 295–305.
Werner H, Le Roith D . (2000). New concepts in regulation and function of the insulin-like growth factors: implications for understanding normal growth and neoplasia. Cell Mol Life Sci 57: 932–942.
Yin L, Kharbanda S, Kufe D . (2007). Mucin 1 oncoprotein blocks hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha activation in a survival response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 282: 257–266.
Yoshiji H, Harris SR, Thorgeirsson UP . (1997). Vascular endothelial growth factor is essential for initial but not continued in vivo growth of human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 57: 3924–3928.
Yu H, Wu J, Li H, Wang Z, Chen X, Tian Y et al. (2007). Inhibition of corneal neovascularization by recombinant adenovirus-mediated sFlk-1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361: 946–952.
Yuen JS, Cockman ME, Sullivan M, Protheroe A, Turner GD, Roberts IS et al. (2007). The VHL tumor suppressor inhibits expression of the IGF1R and its loss induces IGF1R upregulation in human clear cell renal carcinoma. Oncogene 26: 6499–6508.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs Dong-Young Noh and Hyeong-Gon Moon for providing the human breast cancer tissues microarray. This work was supported in part by grants from the R&D Project, the Ministry of Knowledge Economy (MOST, 10035353) and the Korean Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) through the Tumor Immunity Medical Research Center at Seoul National University college of Medicine, Republic of Korea
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, J., Choi, Y., Oh, SH. et al. Mucin 1 enhances the tumor angiogenic response by activation of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncogene 31, 2187–2198 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.410
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.410
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting KK-LC-1 inhibits malignant biological behaviors of triple-negative breast cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Antiproliferative Activity of Whey and Casein Bioactive Peptides on Breast Cancer: An In Vitro and In Silico Study
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2022)
-
The multifaceted role of MUC1 in tumor therapy resistance
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2022)
-
Crosstalk between MUC1 and VEGF in angiogenesis and metastasis: a review highlighting roles of the MUC1 with an emphasis on metastatic and angiogenic signaling
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Essential role of Ahnak in adipocyte differentiation leading to the transcriptional regulation of Bmpr1α expression
Cell Death & Disease (2018)