Abstract
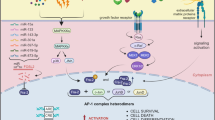
Fos-related antigen 1 (Fra-1) is a Fos family member overexpressed in several types of human cancers. Here, we report that Fra-1 is highly expressed in the muscle-invasive form of the carcinoma of the bladder (80%) and to a lesser extent in superficial bladder cancer (42%). We demonstrate that in this type of cancer Fra-1 is regulated via a C-terminal instability signal and C-terminal phosphorylation. We show that manipulation of Fra-1 expression levels in bladder cancer cell lines affects cell morphology, motility and proliferation. The gene coding for AXL tyrosine kinase is directly upregulated by Fra-1 in bladder cancer and in other cell lines. Importantly, our data demonstrate that AXL mediates the effect of Fra-1 on tumour cell motility but not on cell proliferation. We suggest that AXL may represent an attractive therapeutic target in cancers expressing high Fra-1 levels.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen H, Mahmood S, Tkach V, Cohn M, Kustikova O, Grigorian M et al. (2002). The ability of Fos family members to produce phenotypic changes in epithelioid cells is not directly linked to their transactivation potentials. Oncogene 21: 4843–4848.
Andersen H, Mejlvang J, Mahmood S, Gromova I, Gromov P, Lukanidin E et al. (2005). Immediate and delayed effects of E-cadherin inhibition on gene regulation and cell motility in epidermoid carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 20: 9138–9150.
Basbous J, Chalbos D, Hipskind R, Jariel-Encontre I, Piechaczyk M . (2007). Ubiquitin-independent degradation of Fra-1 is antagonized by Erk1/2 pathway-mediated phosphorylation of a unique C-terminal destabilize. Mol Cell Biol 27: 3936–3950.
Belguise K, Kersual N, Galtier F, Chalbos D . (2005). Fra-1 expression level regulates proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 1434–1444.
Bellosta P, Costa M, Lin DA, Basilico C . (1995). The receptor tyrosine kinase ARK mediates cell aggregation by homophilic binding. Mol Cell Biol 15: 614–625.
Bergers G, Graninger P, Braselmann S, Wrighton C, Busslinger M . (1995). Transcriptional activation of the fra-1 gene by AP-1 is mediated by regulatory sequences in the first intron. Mol Cell Biol 15: 3748–3758.
Burch PM, Yuan Z, Loonen A, Heintz NH . (2004). An extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1- and 2-dependent program of chromatin trafficking of c-Fos and Fra-1 is required for cyclin D1 expression during cell cycle entry. Mol Cell Biol 24: 4696–4709.
Casalino L, Bakiri L, Talotta F, Weitzman JB, Fusco A, Yaniv M et al. (2007). Fra-1 promotes growth and survival in RAS-transformed thyroid cells by controlling cyclin A transcription. EMBO J 26: 1878–1890.
Casalino L, De Cesare D, Verde P . (2003). Accumulation of Fra-1 in ras-transformed cells depends on both transcriptional autoregulation and MEK-dependent posttranslational stabilization. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4401–4415.
Chiappetta G, Ferraro A, Botti G, Monaco M, Pasquinelli R, Vuttariello E et al. (2007). FRA-1 protein overexpression is a feature of hyperplastic and neoplastic breast disorders. BMC Cancer 7: 17.
Chiappetta G, Tallini G, De Biaso MC, Pentimalli F, de Nigris F, Losito S et al. (2000). FRA-1 expression in hyperplastic and neoplastic thyroid diseases. Clin Cancer 6: 4300–4306.
Debinski W, Gibo DM . (2005). Fos-related antigen 1 modulates malignant features of glioma cells. Mol Cancer Res 3: 237–249.
Dixon JM, Lubomirski M, Amaratunga D, Morrison TB, Brenan CJH, Ilyin SE . (2009). Nanoliter high-throughput RT-qPCR: statistical analysis and assessment. Biotechniques 46: ii–vii.
Doehn U, Hauge C, Frank SR, Jensen CJ, Duda K, Nielsen JV et al. (2009). RSK is a principal effector of the RAS-ERK pathway for eliciting a coordinate promotile/invasive gene prgram and phenotype in epithelial cells. Mol Cell 35: 511–522.
Eferl R, Wagner EF . (2003). AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 859–868.
Hafizi S, Dahlbaeck B . (2006). Signalling and functional diversity within the Axl subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 295–304.
Heiring C, Dahlbaeck B, Muller YA . (2004). Ligand recognition and homophilic interactions in Tyro3: structural insights into the Axl/Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase family. J Biol Chem 279: 6952–6958.
Holland SJ, Pan A, Franci C, Hu Y, Chang B, Li W et al. (2010). R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 70: 1544–1554.
Hu CY, King YL, Law S, Wong J, Srivastava G . (2001). Identification of differently expressed genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) by cDNA expression array. Clin Cancer Res 7: 2213–2221.
Hutterer M, Knyazev P, Abate A, Reschke M, Maier H, Stefanova N et al. (2008). Axl and growth arrest-specific gene 6 are frequently overexpressed in human gliomas and predict poor prognosis in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 14: 130–138.
Kakumoto K, Sasai K, Sukezane T, Oneyama C, Ishimaru S, Shibutani K et al. (2006). FRA1 is a determinant for the difference in RAS-induced transformation between human and rat fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5490–5495.
Knowles MA . (2008). Molecular pathogenesis of bladder cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 13: 287–297.
Kustikova O, Kramerov D, Grigorian M, Berezin V, Bock E, Lukanidin E et al. (1998). Fra-1 induces morphological transformation and increases in vitro invasiveness and motility of epithelioid adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 18: 7095–7105.
Linger RM, Keating AK, Earp HS, Graham DK . (2008). TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: biological functions, signalling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res 100: 35–83.
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML, Gratchev A, Ilyas M et al. (1999). Target genes of beta-catenin-T-cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signalling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1603–1608.
McHugh LA, Sayan AE, Mejlvang J, Griffiths TR, Sun Y, Manson MM et al. (2009). Lapatinib, a dual inhibitor of ErbB-1/-2 receptors, enhances effects of combination chemotherapy in bladder cancer cells. Int J Oncol 34: 1155–1163.
Milde-Langosh K . (2005). The Fos family of transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. Eur J Cancer 16: 2449–2461.
Mitra AP, Cote RJ . (2009). Molecular pathogenesis and diagnostics in bladder cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 4: 251–285.
Murphy LO, MacKeigan JP, Blenis J . (2004). A network of immediate early gene products propagates subtle differences in mitogen-activated protein kinase signal amplitude and duration. Mol Cell Biol 24: 144–153.
Ozanne BW, Spence HJ, McGarry LC, Hennigan RF . (2006). Invasion is a genetic program regulated by transcription factors. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16: 65–70.
Pollock CB, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, Kolch W, Dhillon AS . (2005). Oncogenic K-RAS is required to maintain changes in cytoskeletal organization, adhesion, and motility in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 1244–1250.
Ramos-Nino ME, Scapoli L, Martinelli M, Land S, Mossman BT . (2003). Microarray analysis and RNA silencing link fra-1 to cd44 and c-met expression in mesothelioma. Cancer Res 63: 3539–3545.
Rankin EB, Fuh KC, Taylor TE, Krieg AJ, Musser M, Yuan J et al. (2010). AXL is an essential factor and therapeutic target for metastatic ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 70: 7570–7579.
Sainaghi PP, Castello L, Bergamasco L, Galletti M, Bellosta P, Avanzi GC . (2005). Gas6 induces proliferation in prostate carcinoma cell lines expressing the Axl receptor. J Cell Physiol 204: 36–44.
Shaulian E, Karin M . (2002). AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4: E131–E136.
Shieh YS, Lai CY, Kao YR, Shiah SG, Chu YW, Lee HS et al. (2005). Expression of axl in lung adenocarcinoma and correlation with tumor progression. Neoplasia 7: 1058–1064.
Shin S, Dimitri CA, Yoon SO, Dowdle W, Blenis J . (2010). ERK2 but not ERK1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation via DEF motif-dependent signalling events. Mol Cell 38: 114–127.
Verde P, Casalino L, Talotta F, Yaniv M, Weitzman JB . (2007). Deciphering AP-1 function in tumorigenesis: fra-ternizing on target promoters. Cell Cycle 6: 2633–2639.
Vial E, Marshall CJ . (2003). Elevated ERK-MAP kinase activity protects the FOS family member FRA-1 against proteasomal degradation in colon carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 116: 4957–4963.
Vial E, Sahai E, Marshall CJ . (2003). ERK-MAPK signalling co-ordinately regulates activity of Rac1 and RhoA for tumor cell motility. Cancer Cell 4: 67–79.
Vikhanskaya F, Toh WH, Dulloo I, Wu Q, Boominathan L, Ng HH et al. (2007). p73 supports cellular growth through c-Jun-dependent AP-1 transactivation. Nat Cell Biol 6: 698–705.
Yeh CY, Shin SM, Yeh HH, Wu TJ, Shin JW, Chang TY et al. (2011). Transcriptional activation of the Axl and PDGFR-a by c-Met throudg a ras- and Src-independent mechanism in human bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 11: 139.
Young MR, Colburn NH . (2006). Fra-1 a target for cancer prevention or intervention. Gene 379: 1–11.
Zhang Y-X, Knyazev PG, Cheburkin YV, Sharma K, Knyazev YP, Orfi L et al. (2008). AXL is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 68: 1905–1915.
Zhang W, Hart J, McLeod HL, Wang HL . (2005). Differential expression of the AP-1 transcription factor family members in human colorectal epithelial and neuroendocrine neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol 124: 11–19.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Association for International Cancer Research grant 07–0083 (to ET) and by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (to AD). MP is supported by an ‘Equipe Labelisée’ grant from the French Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayan, A., Stanford, R., Vickery, R. et al. Fra-1 controls motility of bladder cancer cells via transcriptional upregulation of the receptor tyrosine kinase AXL. Oncogene 31, 1493–1503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.336
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.336
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification and validation of prognostic signature genes of bladder cancer by integrating methylation and transcriptomic analysis
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
ERCC1 abundance is an indicator of DNA repair-apoptosis decision upon DNA damage
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
Multiple Fra-1-bound enhancers showing different molecular and functional features can cooperate to repress gene transcription
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
FLI1 and FRA1 transcription factors drive the transcriptional regulatory networks characterizing muscle invasive bladder cancer
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Silencing AHNAK promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by upregulating the ANXA2 protein
Cellular Oncology (2023)