Abstract
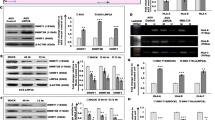
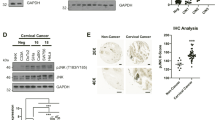
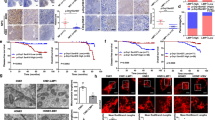
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is an oncogenic γ-herpes virus associated with malignancies that develop in both lymphoid and epithelial cells including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The EBV protein, latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A), is expressed in NPC and can modulate epithelial proliferation, transformation and differentiation, and as such may promote malignancy. A key regulator of epithelial-cell differentiation is the transcription factor p63, a member of the p53 family. This study examines the potential contribution of p63 to LMP2A-mediated inhibition of epithelial-cell differentiation. Stable expression of LMP2A increased the protein level and stability of the ΔNp63α isoform and in two epithelial cell lines, LMP2A interacted with ΔNp63α under stable- and transient-expression systems. LMP2A and ΔNp63α were localized to the cytoplasm and nuclear membrane and co-immunoprecipitated in the same fractions. Following induction of epithelial-cell differentiation by calcium, expression of differentiation markers was impaired in both ΔNp63α- and LMP2A-expressing cells. Induction of p63α, association of p63α with LMP2A and impairment of differentiation required the PY and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) signaling motif of LMP2A. By associating with and being regulated by LMP2A, ΔNp63α may function as a unique regulator of LMP2A effects on epithelial differentiation and contribute to EBV-associated epithelial cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamberger C, Pollet D, Schmale H . (2002). Retinoic acid inhibits downregulation of DeltaNp63alpha expression during terminal differentiation of human primary keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 118: 133–138.
Brooks L, Yao QY, Rickinson AB, Young LS . (1992). Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol 66: 2689–2697.
Bultema R, Longnecker R, Swanson-Mungerson M . (2009). Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A accelerates MYC-induced lymphomagenesis. Oncogene 28: 1471–1476.
Busson P, McCoy R, Sadler R, Gilligan K, Tursz T, Raab-Traub N . (1992). Consistent transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP2 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol 66: 3257–3262.
Candi E, Cipollone R, Rivetti di Val Cervo P, Gonfloni S, Melino G, Knight R . (2008). p63 in epithelial development. Cell Mol Life Sci 65: 3126–3133.
Candi E, Dinsdale D, Rufini A, Salomoni P, Knight RA, Mueller M et al. (2007). TAp63 and DeltaNp63 in cancer and epidermal development. Cell Cycle 6: 274–285.
Deyrieux AF, Wilson VG . (2007). in vitro culture conditions to study keratinocyte differentiation using the HaCaT cell line. Cytotechnology 54: 77–83.
Fukuda M, Longnecker R . (2007). Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediates transformation through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3-K/Akt pathway. J Virol 81: 9299–9306.
Guo C, Pan ZG, Li DJ, Yun JP, Zheng MZ, Hu ZY et al. (2006). The expression of p63 is associated with the differential stage in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and EBV infection. J Transl Med 4: 23.
Ikeda A, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R, Ikeda M . (2003). Itchy, a Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase, downregulates latent membrane protein 2A activity in B-cell signaling. J Virol 77: 5529–5534.
Ikeda M, Ikeda A, Longan LC, Longnecker R . (2000). The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A PY motif recruits WW domain-containing ubiquitin-protein ligases. Virology 268: 178–191.
Ikeda M, Ikeda A, Longnecker R . (2001). PY motifs of Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A regulate protein stability and phosphorylation of LMP2A-associated proteins. J Virol 75: 5711–5718.
Koster MI, Kim S, Mills AA, DeMayo FJ, Roop DR . (2004). p63 is the molecular switch for initiation of an epithelial stratification program. Genes Dev 18: 126–131.
Li Y, Peart MJ, Prives C . (2009). Stxbp4 regulates DeltaNp63 stability by suppression of RACK1-dependent degradation. Mol Cell Biol 29: 3953–3963.
Longnecker R, Merchant M, Brown ME, Fruehling S, Bickford JO, Ikeda M et al. (2000). WW- and SH3-domain interactions with Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A. Exp Cell Res 257: 332–340.
Medawar A, Virolle T, Rostagno P, de la Forest-Divonne S, Gambaro K, Rouleau M et al. (2008). DeltaNp63 is essential for epidermal commitment of embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 3: e3441.
Melino G, Knight RA, Cesareni G . (2006). Degradation of p63 by Itch. Cell Cycle 5: 1735–1739.
Merchant M, Swart R, Katzman RB, Ikeda M, Ikeda A, Longnecker R et al. (2001). The effects of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A on B cell function. Int Rev Immunol 20: 805–835.
Morrison JA, Raab-Traub N . (2005). Roles of the ITAM and PY motifs of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A in. J Virol 79: 2375–2382.
Murray-Zmijewski F, Lane DP, Bourdon JC . (2006). p53/p63/p73 isoforms: an orchestra of isoforms to harmonise cell differentiation and response to stress. Cell Death Differ 13: 962–972.
Ogawa E, Okuyama R, Egawa T, Nagoshi H, Obinata M, Tagami H et al. (2008). p63/p51-induced onset of keratinocyte differentiation via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway is counteracted by keratinocyte growth factor. J Biol Chem 283: 34241–34249.
Okuyama R, Ogawa E, Nagoshi H, Yabuki M, Kurihara A, Terui T et al. (2007). p53 homologue, p51/p63, maintains the immaturity of keratinocyte stem cells by inhibiting Notch1 activity. Oncogene 26: 4478–4488.
Raab-Traub N . (1992a). Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 3: 297–307.
Raab-Traub N . (1992b). Epstein-Barr virus infection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Infect Agents Dis 1: 173–184.
Raab-Traub N . (2002). Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of NPC. Semin Cancer Biol 12: 431–441.
Rossi M, Aqeilan RI, Neale M, Candi E, Salomoni P, Knight RA et al. (2006a). The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch controls the protein stability of p63. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 12753–12758.
Rossi M, De Simone M, Pollice A, Santoro R, La Mantia G, Guerrini L et al. (2006b). Itch/AIP4 associates with and promotes p63 protein degradation. Cell Cycle 5: 1816–1822.
Scholle F, Bendt KM, Raab-Traub N . (2000). Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A transforms epithelial cells, inhibits cell differentiation, and activates Akt. J Virol 74: 10681–10689.
Testoni B, Mantovani R . (2006). Mechanisms of transcriptional repression of cell-cycle G2/M promoters by p63. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 928–938.
Truong AB, Khavari PA . (2007). Control of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation by p63. Cell Cycle 6: 295–299.
Westfall MD, Mays DJ, Sniezek JC, Pietenpol JA . (2003). The Delta Np63 alpha phosphoprotein binds the p21 and 14–3–3 sigma promoters in vivo and has transcriptional repressor activity that is reduced by Hay-Wells syndrome-derived mutations. Mol Cell Biol 23: 2264–2276.
Winberg G, Matskova L, Chen F, Plant P, Rotin D, Gish G et al. (2000). Latent membrane protein 2A of Epstein-Barr virus binds WW domain E3 protein-ubiquitin ligases that ubiquitinate B-cell tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol 20: 8526–8535.
Wu G, Nomoto S, Hoque MO, Dracheva T, Osada M, Lee CC et al. (2003). DeltaNp63alpha and TAp63alpha regulate transcription of genes with distinct biological functions in cancer and development. Cancer Res 63: 2351–2357.
Yip YL, Tsao SW . (2008). Regulation of p63 expression in primary and immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Int J Oncol 33: 713–724.
Young LS, Rowe M . (1992). Epstein-Barr virus, lymphomas and Hodgkin′s disease. Semin Cancer Biol 3: 273–284.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr M Oren for providing the ΔNp63α plasmid and Dr R Longnecker for providing the LMP2A PY mutant. Funding for this study was provided by the National Institutes of Health grants CA19014, CA32979 and CA103634.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fotheringham, J., Mazzucca, S. & Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-2A-induced ΔNp63α expression is associated with impaired epithelial-cell differentiation. Oncogene 29, 4287–4296 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.175
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.175
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epstein–Barr virus latent genes
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2015)
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Virologica Sinica (2015)
-
Expression profiling of 21 biomolecules in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinomas of Caucasian patients
BMC Clinical Pathology (2013)